El método Pilates es considerado uno de los programas de ejercicios más populares usados en la práctica clínica. Este trabajo tiene como objetivo evaluar la repercusión del método Pilates en pacientes con espondilitis anquilosante (EA).
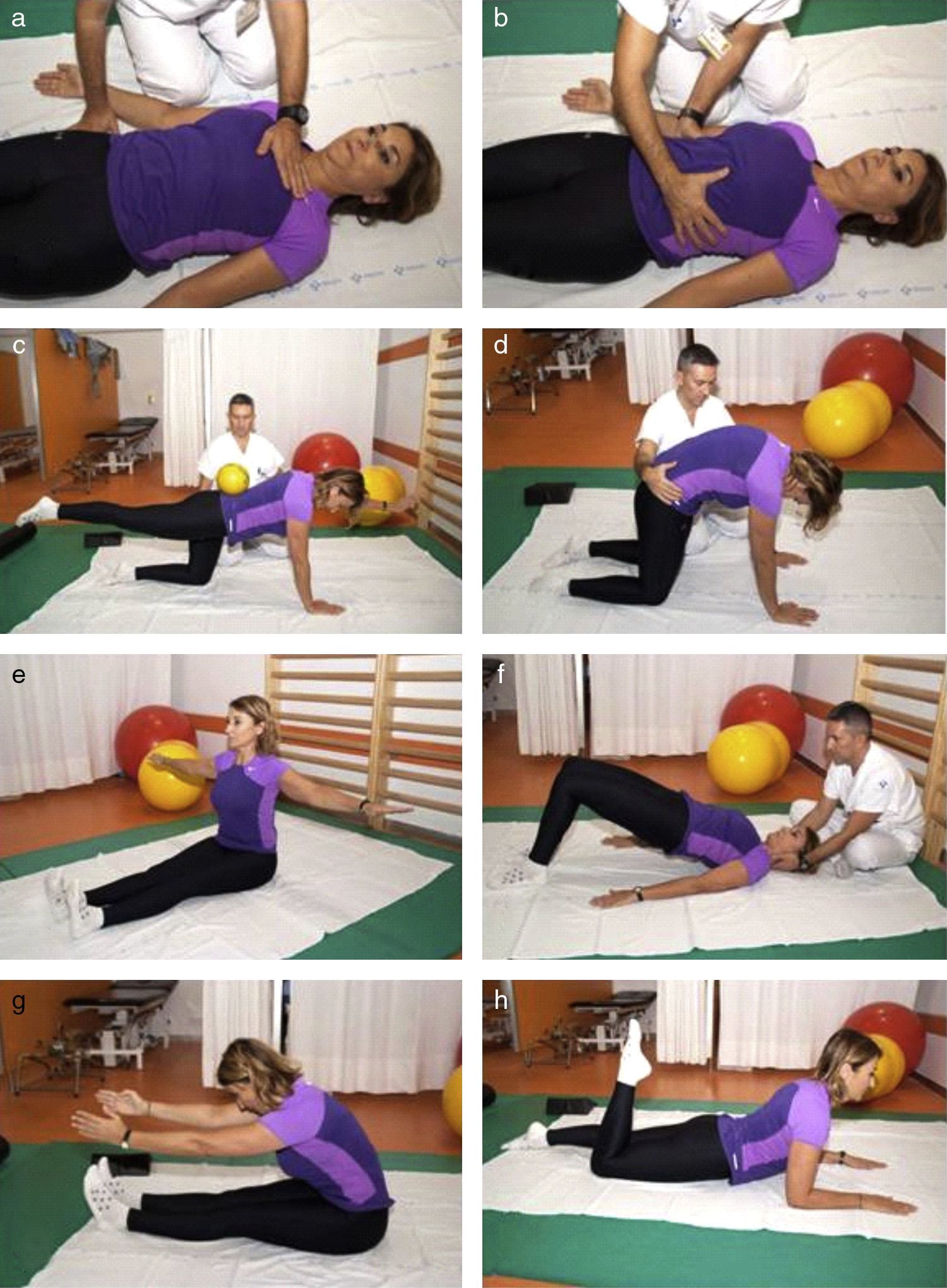
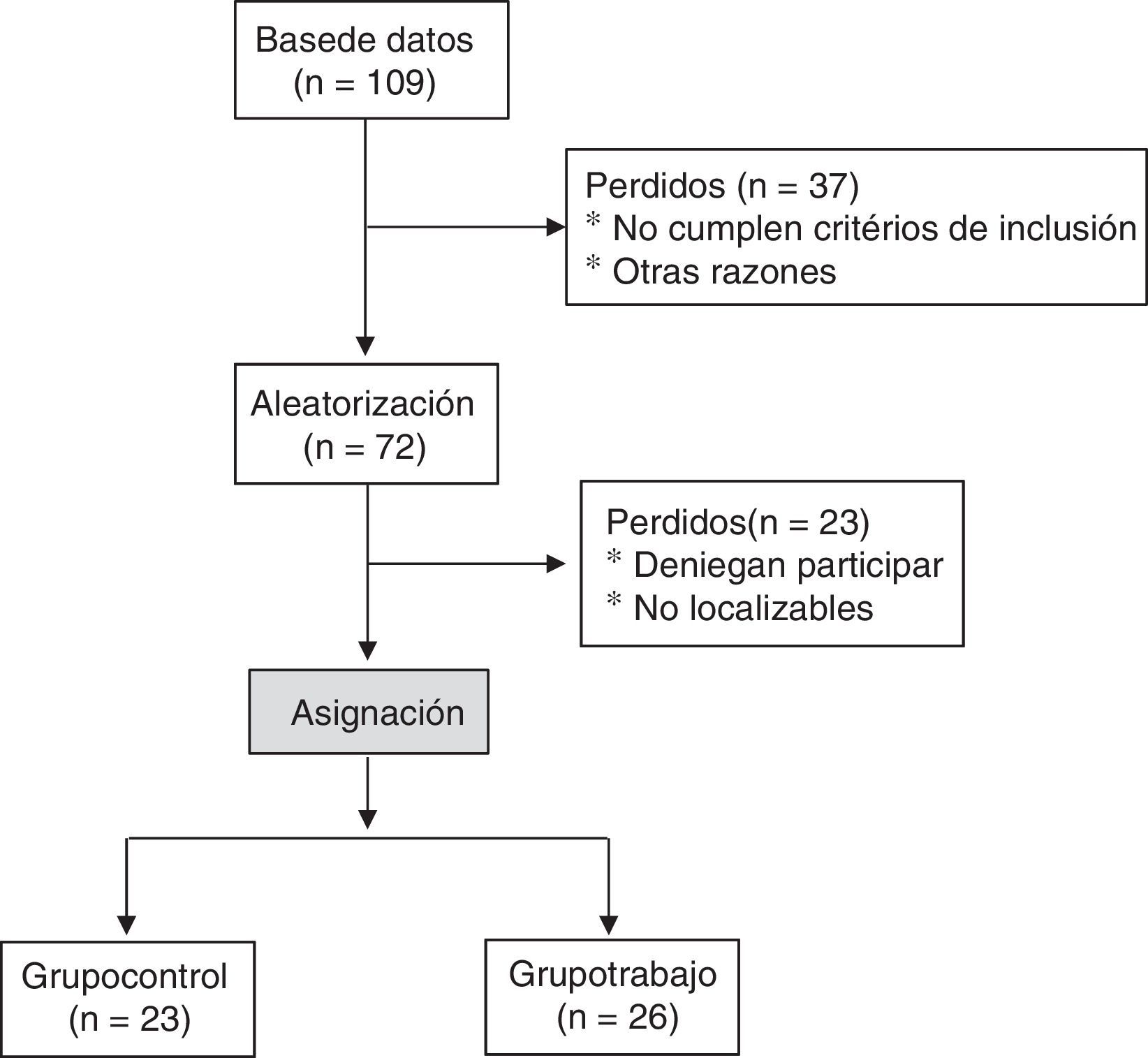
Pacientes y métodosEnsayo clínico realizado en el Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias (HUCA), a 49 pacientes con EA, seleccionados y distribuidos al azar en 2 grupos. El grupo de intervención (GI, n=26) realizó bajo la supervisión de un fisioterapeuta un protocolo de Pilates 5 semanas, a días alternos, durante 90min, continuando en el domicilio 3 meses más. Un grupo control (GC, n=23) realizó ejercicios convencionales en el domicilio durante el mismo periodo. Se analizaron las variables: índice de Bath Metrológico (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index [BASMI]), índice de Bath Funcional (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index [BASFI]) e índice de Bath de Actividad de la Enfermedad (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index [BASDAI]).
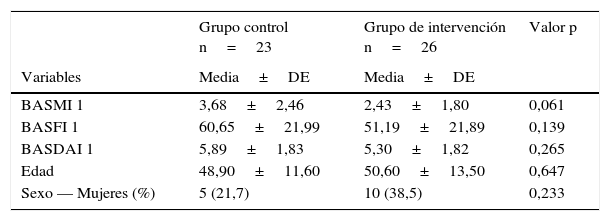
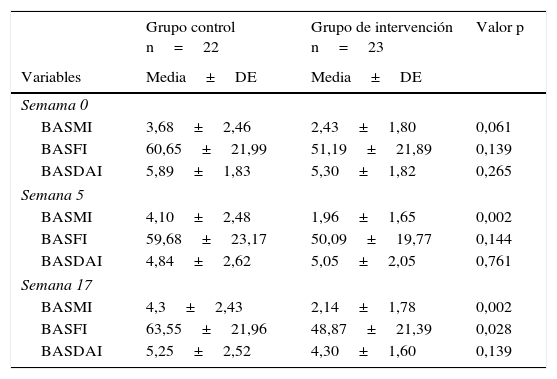
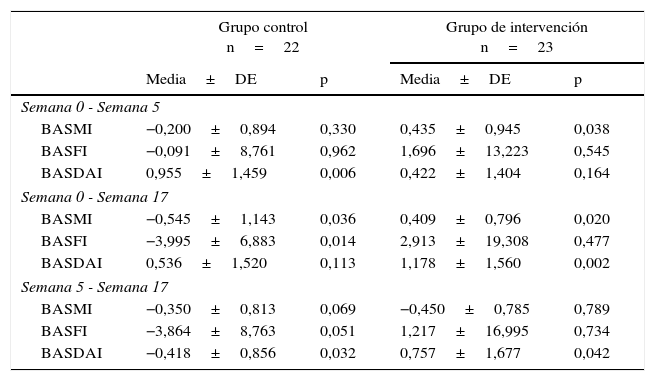
ResultadosEl BASMI en el GC aumenta de forma significativa (p<0,05). En el GI el BASMI disminuye a corto y a medio plazo (p=0,038, p=0,020). Hay diferencias significativas (p=0,028) entre el GC y el GI en el índice BASFI al finalizar el estudio. El BASDAI no presenta diferencias entre GC y GI (p>0,05), pero en el GI hay diferencias significativas intragrupo antes y después de la intervención con el método Pilates (p=0,002), mientras que el GC permanece sin variaciones (p=0,113).
ConclusionesLos pacientes sometidos a un programa de fisioterapia supervisada basada en el método Pilates mejoran la movilidad espinal y su capacidad funcional comparados con los pacientes que practican ejercicio convencional en el domicilio.
The Pilates method is considered one of the most popular exercise programmes in clinical practice. This study aimed to assess the impact of the Pilates method in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Patients and methodsA clinical trial was conducted at the Central University Hospital of Asturias (HUCA) in 49 patients with AS, randomly selected and divided into two groups. The intervention group (IG, n=26) participated in a Pilates method protocol of 90-min sessions on alternate days for 5 weeks under the supervision of a physiotherapist. At the end of the 5-week period, the IG continued to perform the exercises at home for 3 months. A control group (CG, n=23) performed conventional exercises at home during the same period. The following variables were analysed: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis index (BASMI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI).
ResultsBASMI scores significantly increased in the CG (P<.05) and decreased in the short- and medium-term in the IG (P=.038, P=.020). At the end of the study, significant differences were found in the BASFI index between the CG and the IG (P=.028). The BASDAI showed no differences between the CG and the IG (P>.05), but significant intragroup differences were found in the IG before and after the Pilates intervention (P=.002), while no intragroup differences were found in the CG (P=.113).
ConclusionsPatients undergoing a supervised Pilates-based physiotherapy programme showed improved spinal mobility and functional capacity compared with patients who carried out conventional exercise at home.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora