Determinar valores de referencia de recorrido articular (RA) y fuerza isométrica cervical en población sana y valorar la influencia de variables como sexo, edad, medidas antropométricas y actividad física.
Material y métodosMuestra: 80 individuos sanos. Protocolo: el equipo Multi Cervical Unit (MCU) registra RA y fuerza isométrica cervical ángulo-específico y coeficiente de variación. Estos datos se comparan con valores de la American Medical Association y de fuerza de base de datos del equipo. Se registra también perímetro cervical, índice de masa corporal y actividad física.
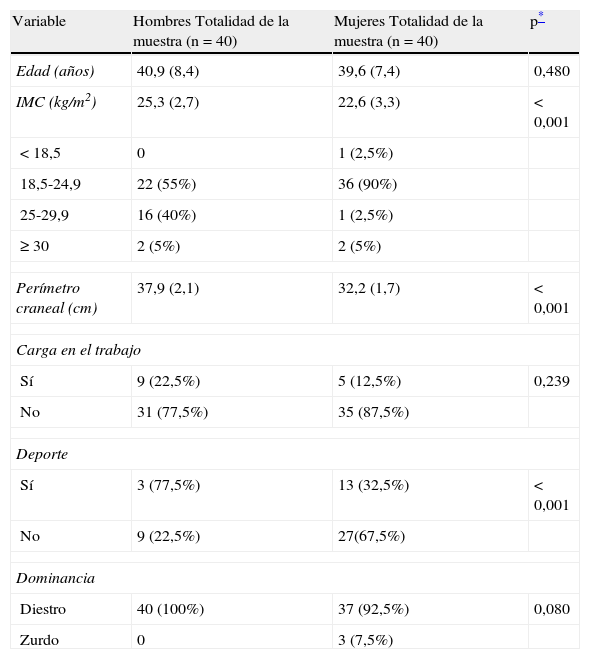
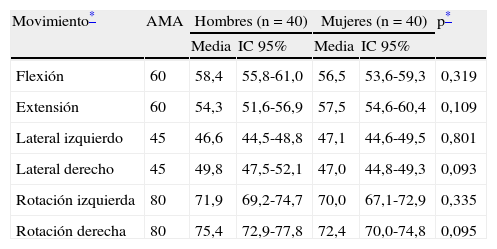
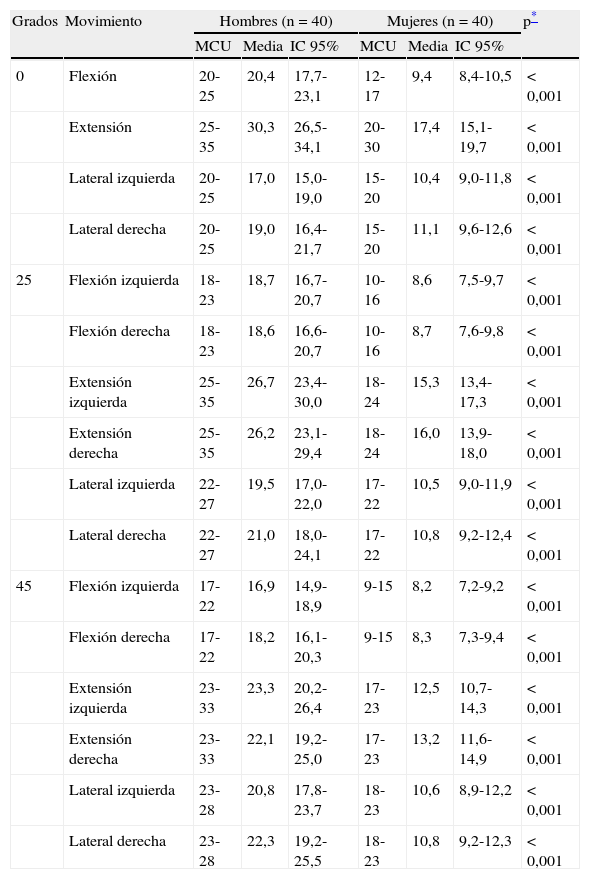
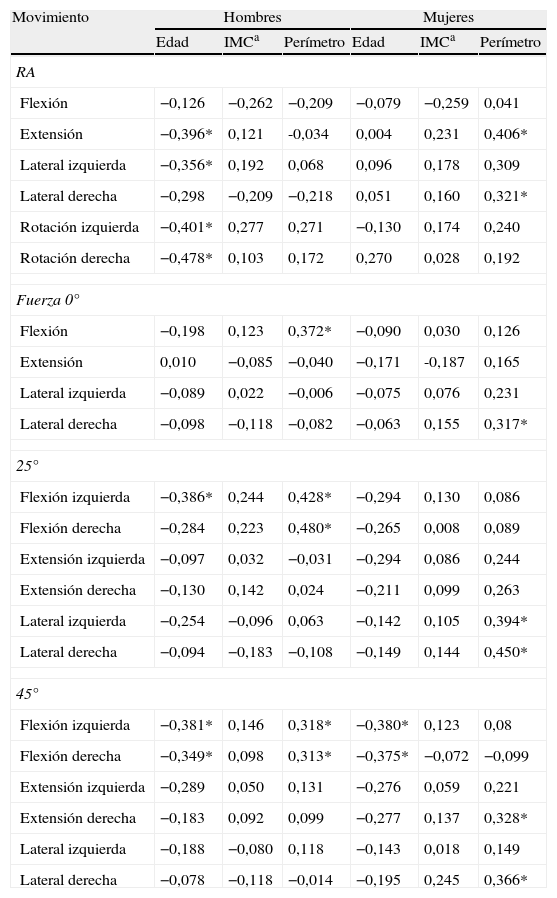
ResultadosLos valores RA obtenidos son cercanos a los valores de la American Medical Association. En esta serie los valores de fuerza son menores que los del MCU. En el análisis de la influencia del sexo en el RA no existen diferencias significativas y en la fuerza comprobamos una fuerte asociación estadística .La influencia de la edad en el RA solo es significativa en hombres
ConclusionesEn los valores de RA no hallamos diferencias significativas entre ambos sexos por lo que no es necesario hacer una diferenciación género-específica. La asociación entre valores de fuerza isométrica cervical y sexo es fuertemente significativa. Se comprueba la relación entre la actividad deportiva y el incremento de la fuerza a nivel cervical
This study aimed to determine the reference values for range of motion (ROM) and cervical isometric strength in a healthy population control group and to assess the influence on it variables such as gender, age, anthropometrical measures and physical activity.
Methods and backgroundData: Sample: 80 healthy persons. Protocol: The Multi-Cervical Unit (MCU) records ROM and cervical isometric strength specific angle and coefficient of variation. These data were then compared with the American Medical Association values and values obtained by the Multi Cervical Unit (MCU) database. Body mass index, cervical circumference and physical activity were also recorded.
ResultsThe ROM values obtained are close to the American Medical Association values. The force values found in our series are below those of the MCU. No significant difference were found regarding the influence of gender on ROM. A strong statistical association was observed in regards to strength. Influence of age on ROM is only significant in men.
ConclusionsSignificant differences in the ROM values were not found between both genders. Therefore, it is not necessary to use specific gender differentiation. The association between gender and isometric cervical spine strength is highly significant. The relationship between physical activity and an increase of the cervical strength has been verified.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora