Last year, some topics discussed in Revista Brasileira de Cardiologia Invasiva (RBCI) attracted great interest from readers: transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), last generation coronary stents, the use of adjuvant strategies to guide percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI), such as intravascular ultrasound or myocardial fractional flow reserve (FFR), and treatment of congenital heart diseases. The current issue features articles that explore new aspects of these topics.
Ribeiro et al., from Quebec Heart & Lung Institute, Laval University (Quebec, Canada), through a systematic review, present the clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients with coronary obstruction post-TAVI valve-in-valve. It is a rare but potentially fatal complication, and the article identifies factors associated with coronary obstruction that must be observed before the procedure, such as the height of the ostium of the left main coronary artery and the mean aortic root diameter, obtained by computed tomography, in addition to the type of previously implanted surgical bioprosthesis. The authors describe the clinical features (persistent hypotension, associated with ST-segment changes) and the poor results of PCI in this setting. Additionally, Candiello et al., from Cardiovascular Institute of Buenos Aires (Buenos Aires, Argentina), report the experience of 51 TAVI cases treated with CoreValve® prosthesis and its evolution after the procedure. Transvalvar gradients, functional class, and mortality are examined in detail in the pre- and post-procedure phases, and at 30 days, six months, and one year.
Authors from Instituto Dante Pazzanese de Cardiologia (São Paulo, Brazil) offer, in their original articles, aspects related to the performance of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS), the first Brazilian clinical experience with this new device. Borghi, Jr. et al. analyze the acute retraction of the vessel immediately after the procedure, a phenomenon linked to the radial force of the stent and a cause for concern with the use of the first polymeric prototypes. Concomitantly, Veloso e Silva et al. address the changes in the angle of the vessel in order to evaluate the changes that such prostheses bring to the treated coronary segment, when compared to metal platforms of second-generation drug-eluting stents. After stenting, the correction of a curved segment of a vessel may alter the dynamics of coronary flow and modify the distribution of intra-stent intimal hyperplasia during its healing phase.
In the scenario of the adjuvant methods, Quizhpe et al., from Hospital José Carrasco Arteaga (Cuenca, Ecuador), describe their experience in treating lesions of left main coronary artery with the use of intravascular ultrasound and/or FFR to guide most procedures. It is an extremely detailed description of the interventions, in which are present not only evaluations of EuroSCORE and Syntax scores and of the classification of Medina, but also the type of technical procedure used, measures of quantitative coronary angiography, and the clinical long-term results. Conversely, Brito et al., from Clínica Santa Helena (Cabo Frio, Brazil), one of the pioneer groups in Brazil in the use of FFR, describe the predictor variables of postprocedural FFR < 0.90 in patients undergoing PCI. It is known that these patients present a major adverse cardiac event index at six months three times larger than those with postprocedural FFR≥0.90.
Within the theme of congenital heart diseases, Haddad et al., from Hospital das Clínicas, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo (Ribeirão Preto, Brazil), present their initial experience with new double disc prosthesis for percutaneous treatment of ostium secundum-type atrial septal defects. This is one of the first publications with results of this prosthesis in the international literature. The article is complemented by its corresponding editorial, by Chamié Francisco Chamié, from Hospital Federal dos Servidores do Estado (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil), who, with his usual mastery, explores the history of this intervention and discusses its outcomes, and the mechanisms of the procedure’s complications, both immediate and long-term, including the rare but dire cardiac erosion.
This edition is complemented by other unique articles of great interest, with topics such as the influence of pre-expansion of PCI in patients with acute coronary syndrome without ST-segment elevation, the occurrence and prognostic impact of acute renal failure in the in-hospital evolution of patients with myocardial infarction with ST-segment elevation treated percutaneously, predictors of major adverse cardiac events in a large series of treated and untreated diabetic patients with drug-eluting stents, the discomforts of the procedure and the cost of PCIs by radial and femoral access, and the use of models for experimental evaluation and development of different catheter-based coronary devices.
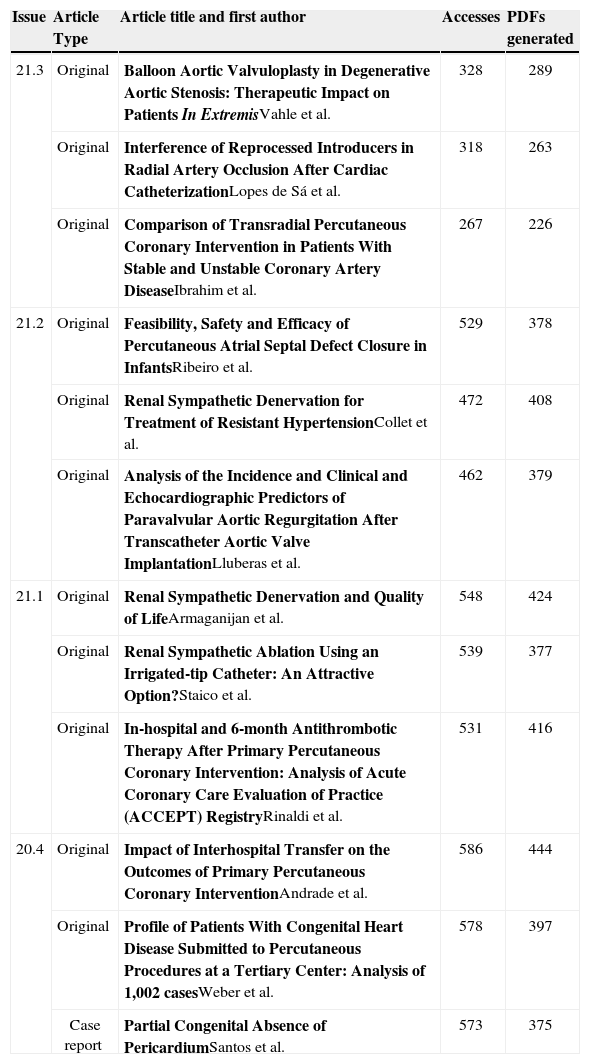
Finally, we conducted a survey to take account of the most popular articles in the last four editions of RBCI until December 1, 2013 on our website (Table). This analysis allows us to evaluate the issues that aroused the greatest interest, thus helping us to redirect the editorial strategy, when necessary. Finally, I would like to thank the SBHCI Board, which is now finishing its current term of its administration, and in particular its President, Dr. Marcelo Queiroga, and RBCI’s Communications Director, José Ary Boechat, for our coexistence and cooperation, and also for their fundamental support for the good management of our journal in the biennium of 2012-13. I also want to acknowledge the continuous and tireless work of the members of the Editorial Council, and of our reviewers and authors – all of them essential for the fulfilment of our main goal: to have an increasingly robust journal, acknowledged in the scientific community. Big thanks to the technical staff related to the production of our jornal for their dedication and professionalism. And last but not least, I want to thank our readers for their interest, which representes the main reason for the existence of this publication.
The most searched RBCI articles published in the last year
| Issue | Article Type | Article title and first author | Accesses | PDFs generated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21.3 | Original | Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty in Degenerative Aortic Stenosis: Therapeutic Impact on Patients In ExtremisVahle et al. | 328 | 289 |
| Original | Interference of Reprocessed Introducers in Radial Artery Occlusion After Cardiac CatheterizationLopes de Sá et al. | 318 | 263 | |
| Original | Comparison of Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery DiseaseIbrahim et al. | 267 | 226 | |
| 21.2 | Original | Feasibility, Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure in InfantsRibeiro et al. | 529 | 378 |
| Original | Renal Sympathetic Denervation for Treatment of Resistant HypertensionCollet et al. | 472 | 408 | |
| Original | Analysis of the Incidence and Clinical and Echocardiographic Predictors of Paravalvular Aortic Regurgitation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve ImplantationLluberas et al. | 462 | 379 | |
| 21.1 | Original | Renal Sympathetic Denervation and Quality of LifeArmaganijan et al. | 548 | 424 |
| Original | Renal Sympathetic Ablation Using an Irrigated-tip Catheter: An Attractive Option?Staico et al. | 539 | 377 | |
| Original | In-hospital and 6-month Antithrombotic Therapy After Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Analysis of Acute Coronary Care Evaluation of Practice (ACCEPT) RegistryRinaldi et al. | 531 | 416 | |
| 20.4 | Original | Impact of Interhospital Transfer on the Outcomes of Primary Percutaneous Coronary InterventionAndrade et al. | 586 | 444 |
| Original | Profile of Patients With Congenital Heart Disease Submitted to Percutaneous Procedures at a Tertiary Center: Analysis of 1,002 casesWeber et al. | 578 | 397 | |
| Case report | Partial Congenital Absence of PericardiumSantos et al. | 573 | 375 |
A great 2014 to all of you!