To recognise the relationship between the needle tip and the median nerve during peripheral nerve block is of interest to avoid neural damage. However, signs of intraneural injection are not clearly established. The aim of this study was to define the changes observed in the peripheral nerve after the intraneural or perineural administration of 1ml of solution.
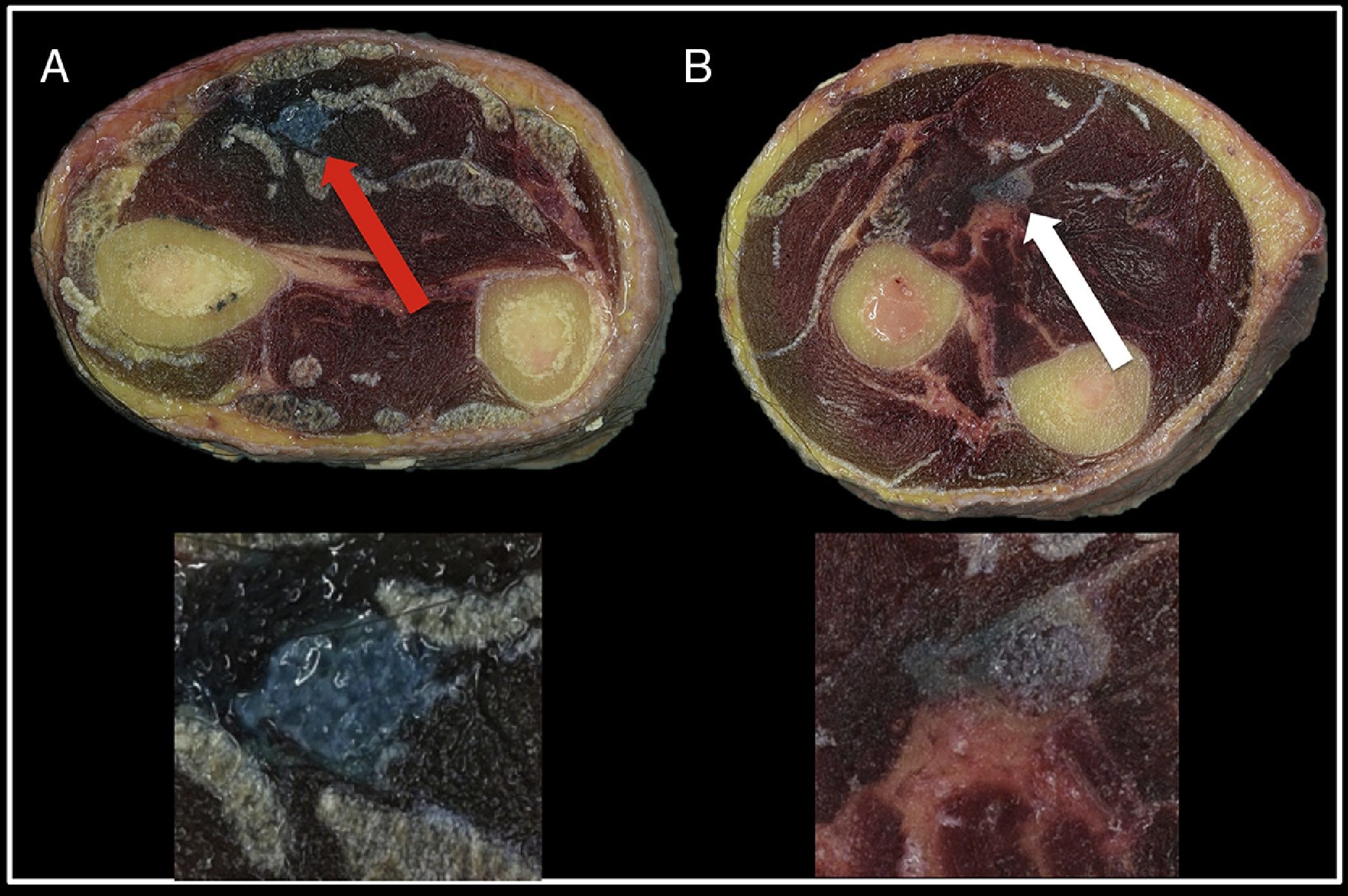
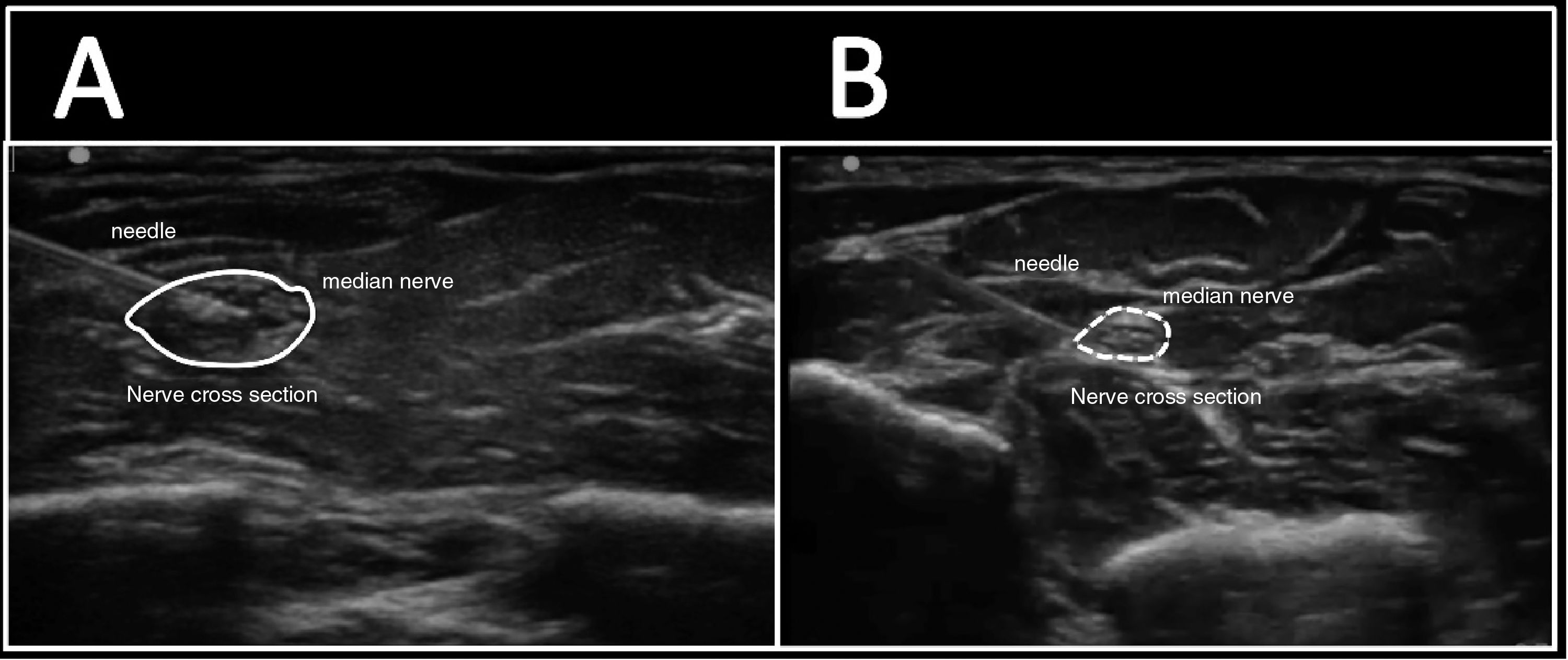
Material and methodsUltrasound guided median nerve blocks were performed in the forearm of 10 fresh cadavers on 60 occasions (3 per forearm). They were randomised into the intraneural (n=30) or perineural (n=30) location of the needle tip, after the consensus of location by 7 specialists. After 1ml of solution was injected an evaluation was made of the changes in the cross-sectional area of the nerve, as well as the displacement along the nerve.
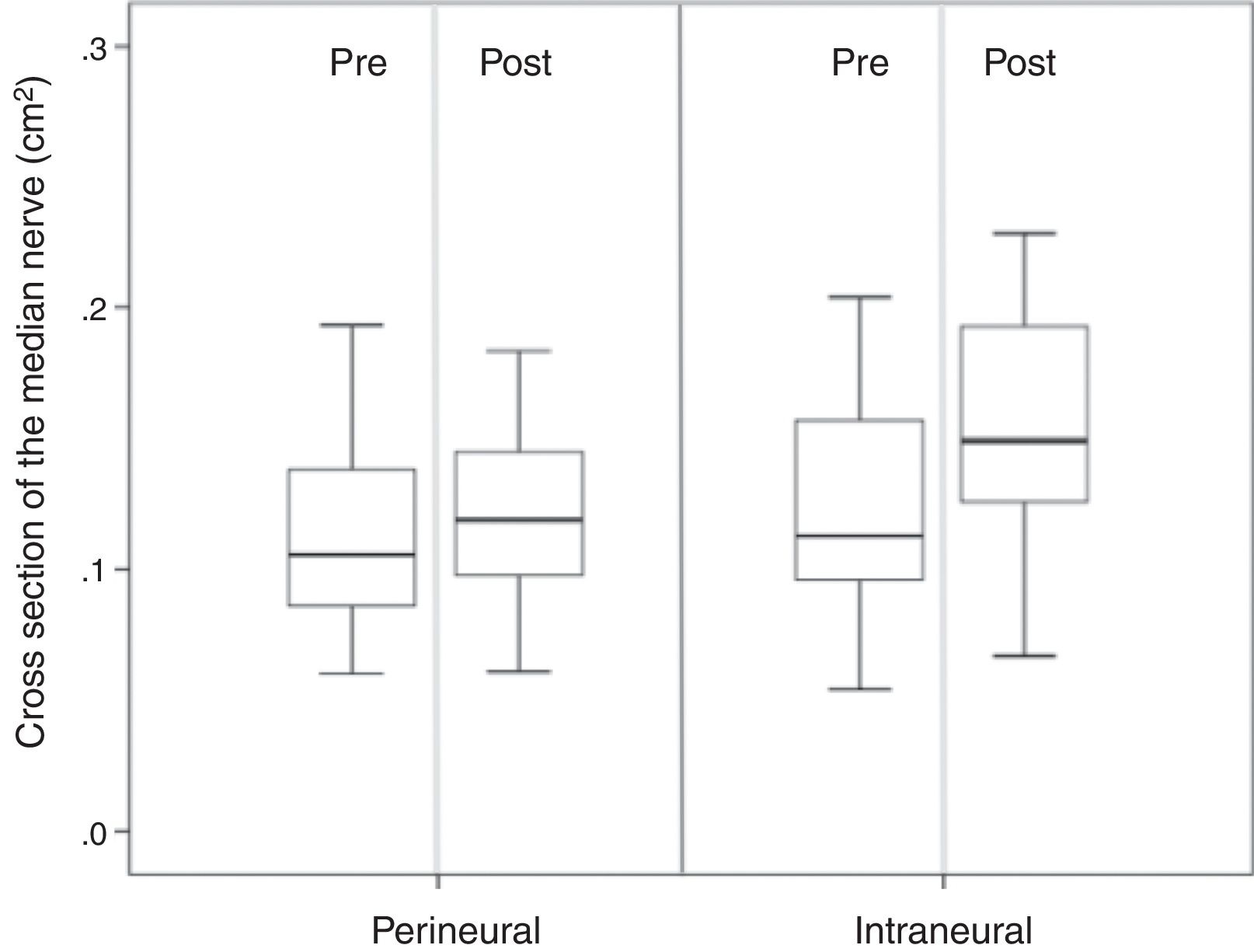
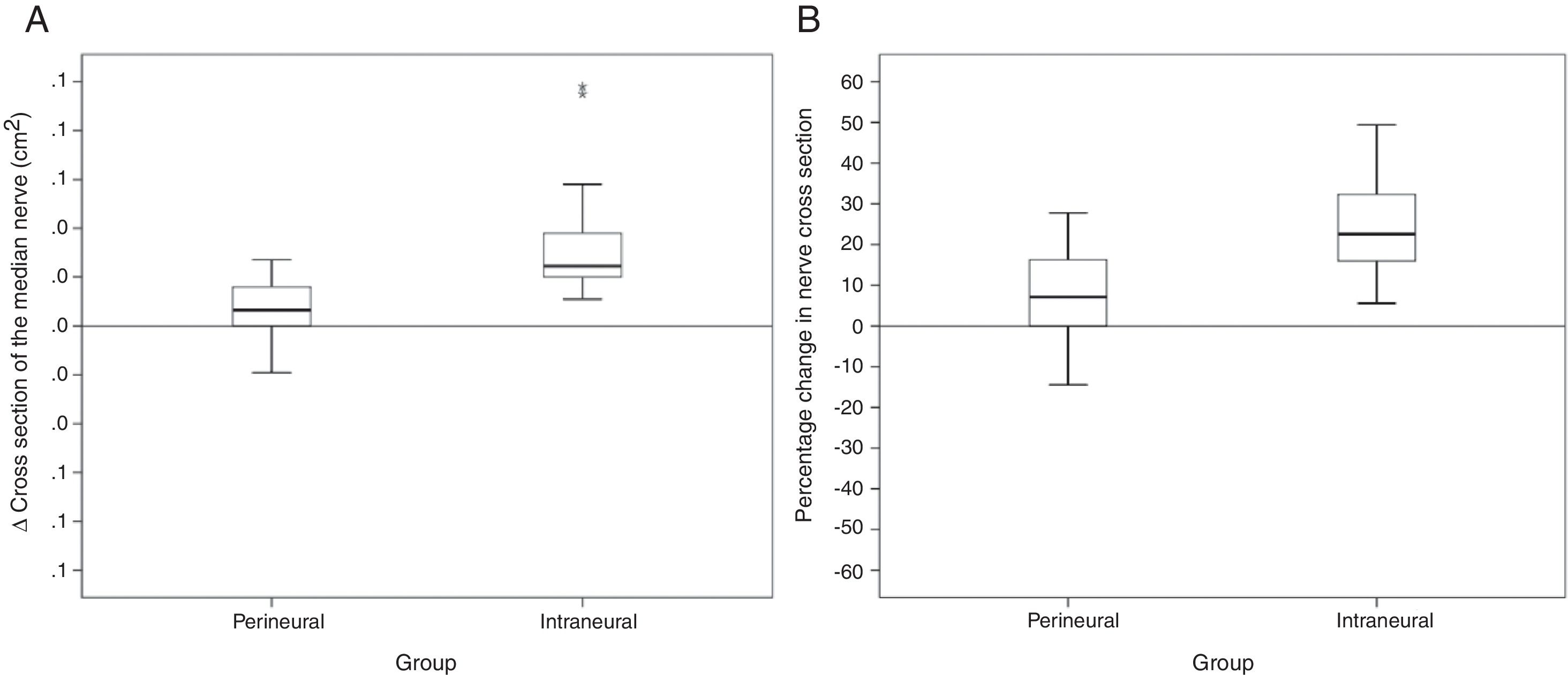
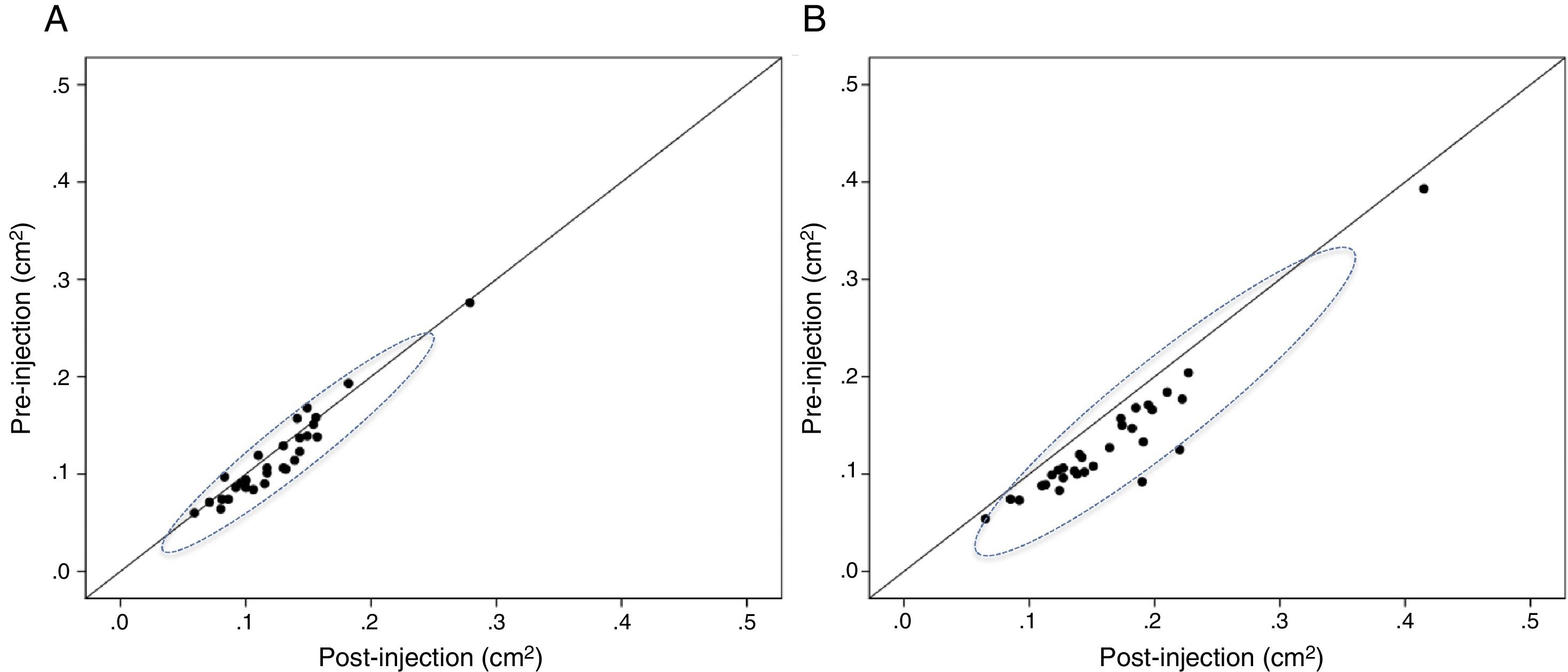
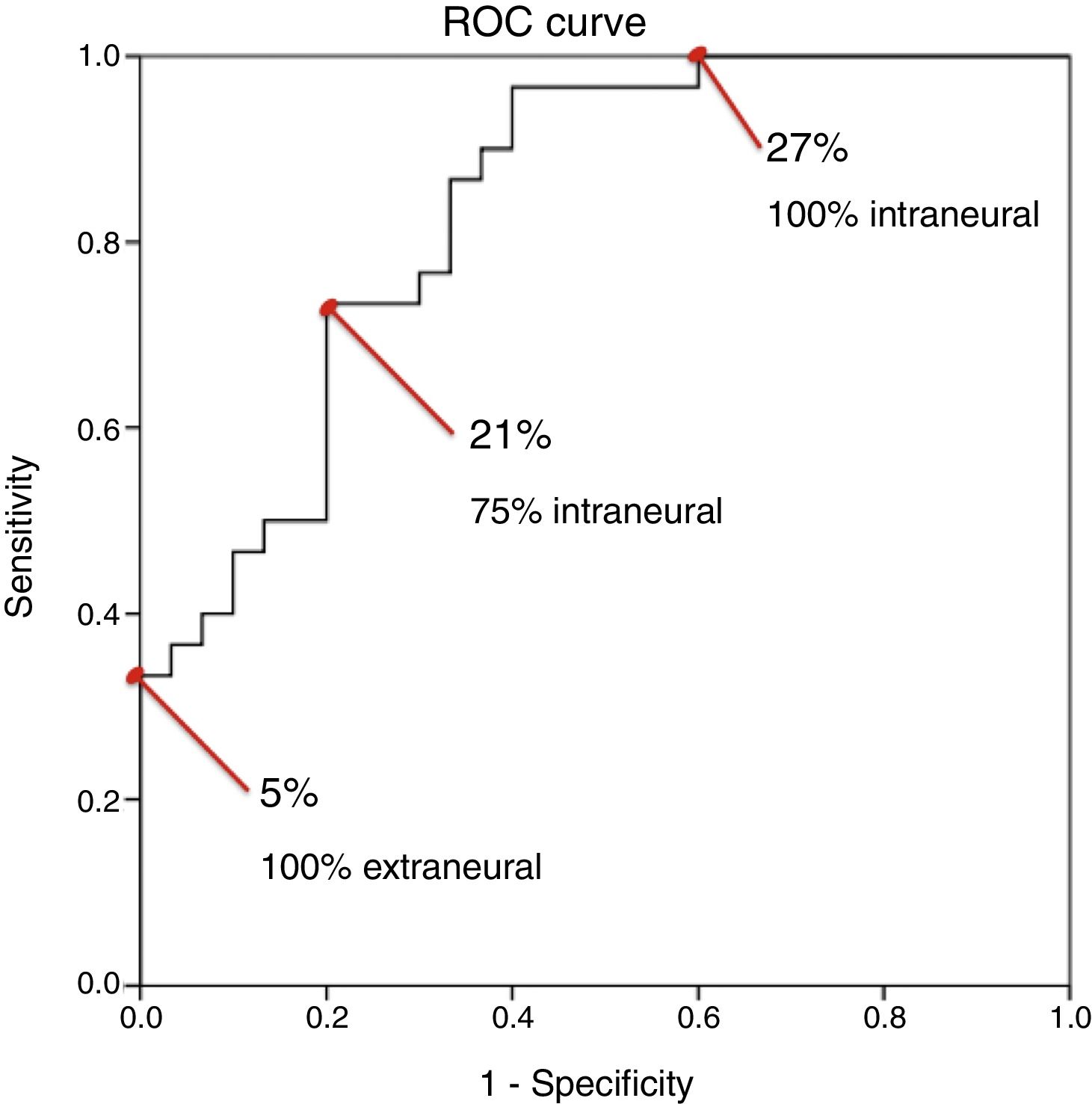
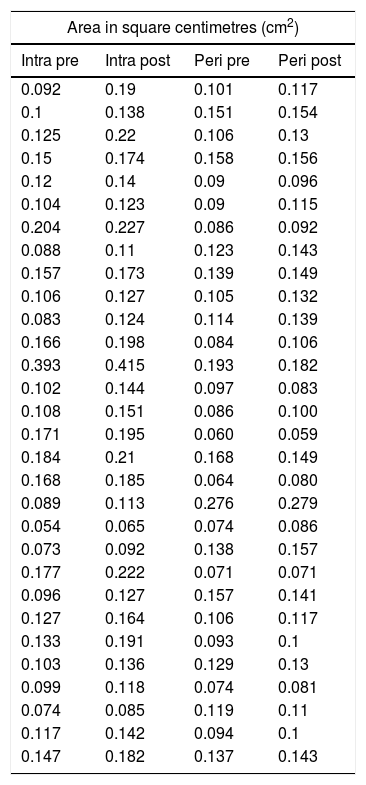
ResultsThe cross-sectional area of the median nerve was increased in both groups, however, the increase was significantly higher in the Intraneural group (perineural 0.007±0.013cm2 vs. intraneural 0.032±0.021cm2, p<0.0001). An increase of more than 27% of the area ensures an intraneural injection in the median nerve according to the ROC curve analysis. Both proximal and distal diffusion were observed more frequently in the Intraneural group (proximal: 86% vs. 14%, p<0.0001, Distal: 43% vs. 4%, p<0.0001).
ConclusionsBased on this experimental study, it is concluded that the injection of a small volume (1ml) allows to discriminate the disposition of the intraneural vs perineural needle in a high percentage of cases. Therefore, it is suggested that this “dose test” should be considered in the safety algorithms if it is required to reduce the incidence of intraneural injection.
Conocer la relación entre la aguja y el nervio durante el bloqueo de nervio periférico es de interés para evitar el daño neural; sin embargo, los signos de inyección intraneural no se hallan claramente establecidos. Nos propusimos determinar los cambios observados en el nervio periférico tras inyectar 1ml de solución en disposición intraneural o perineural de la aguja.
Material y métodosSe utilizaron 10 cadáveres frescos, a los cuales se les realizó bloqueo de nervio mediano ecoguiado en plano en 60 ocasiones (3 por brazo), realizando una punción intraneural (n=30) o perineural (n=30) según aleatorización previa. Tras el consenso de localización por 7 especialistas, se inyectó 1ml de solución y se evaluó el cambio en el área de sección del nervio y el desplazamiento a lo largo del mismo.
ResultadosEl área de sección del nervio mediano se aumentó en ambos grupos, sin embargo, el incremento fue significativamente mayor en el grupo intraneural (perineural 0,007±0,013 vs. intraneural 0,032±0,021cm2, p<0,0001). Un incremento superior al 27% del área de sección asegura una inyección intraneural en el nervio mediano según el análisis de la curva ROC. La difusión proximal y la distal se observó con mayor frecuencia en el grupo intraneural (proximal: 86 vs. 14%; p<0,0001. Distal: 43 vs. 4%; p<0,0001).
ConclusionesEn base a nuestro estudio experimental concluimos que la inyección de un pequeño volumen (1ml) permite discriminar la disposición de la aguja intraneural vs. perineural en un porcentaje elevado de casos. Por ello, sugerimos que esta «dosis test» debe de considerarse en los algoritmos de seguridad si queremos reducir la incidencia de inyección intraneural.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora