The latest Difficult Airway Society (DAS) guidelines recommend that all anaesthesiologists should to be trained in the performing of a surgical cricothyrotomy (CtQ). The aim of this study was to analyse the learning results of a CtQ workshop by assessing the success rate and time to perform CtQ on a porcine tracheal model.
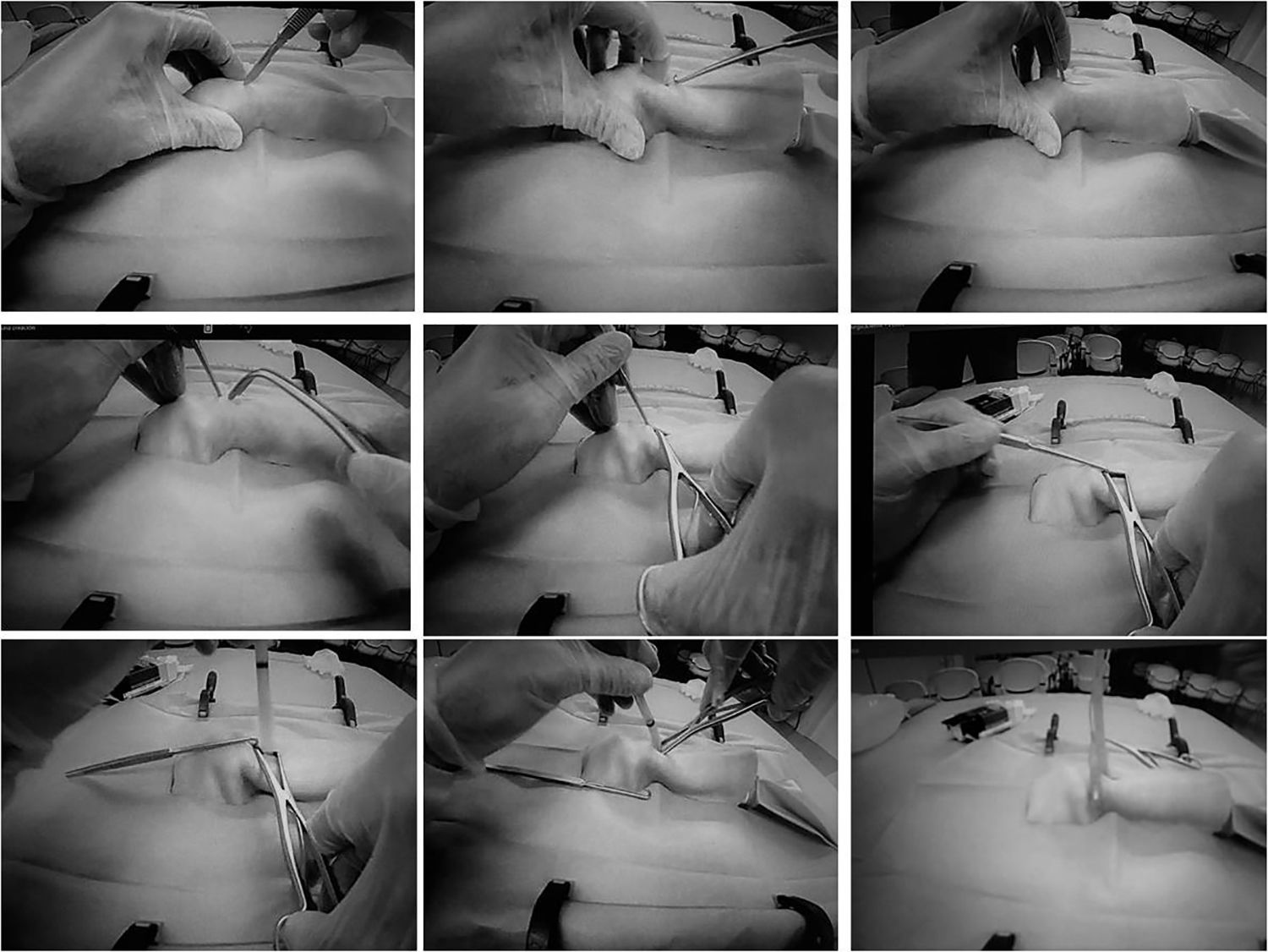
Material and methodsA workshop was designed in which each student completed a questionnaire with demographic data and theoretical knowledge about surgical approaches of airway. During the following hour, a review was presented theoretical aspects of CtQ. The model was shown and a CtQ was performed using a classical technique. Afterwards, in groups of 3–4 students with an instructor, each one of the students performed 6 CtQ. A record was made on whether the ventilation was correct, the time to perform CtQ, and the ease of performing the CtQ by the students and instructors. Finally, students completed a questionnaire on the theoretical aspects. Students and instructors performed a workshop debriefing. A statistical analysis was performed, considering a p-value<0.05 as statistically significant.
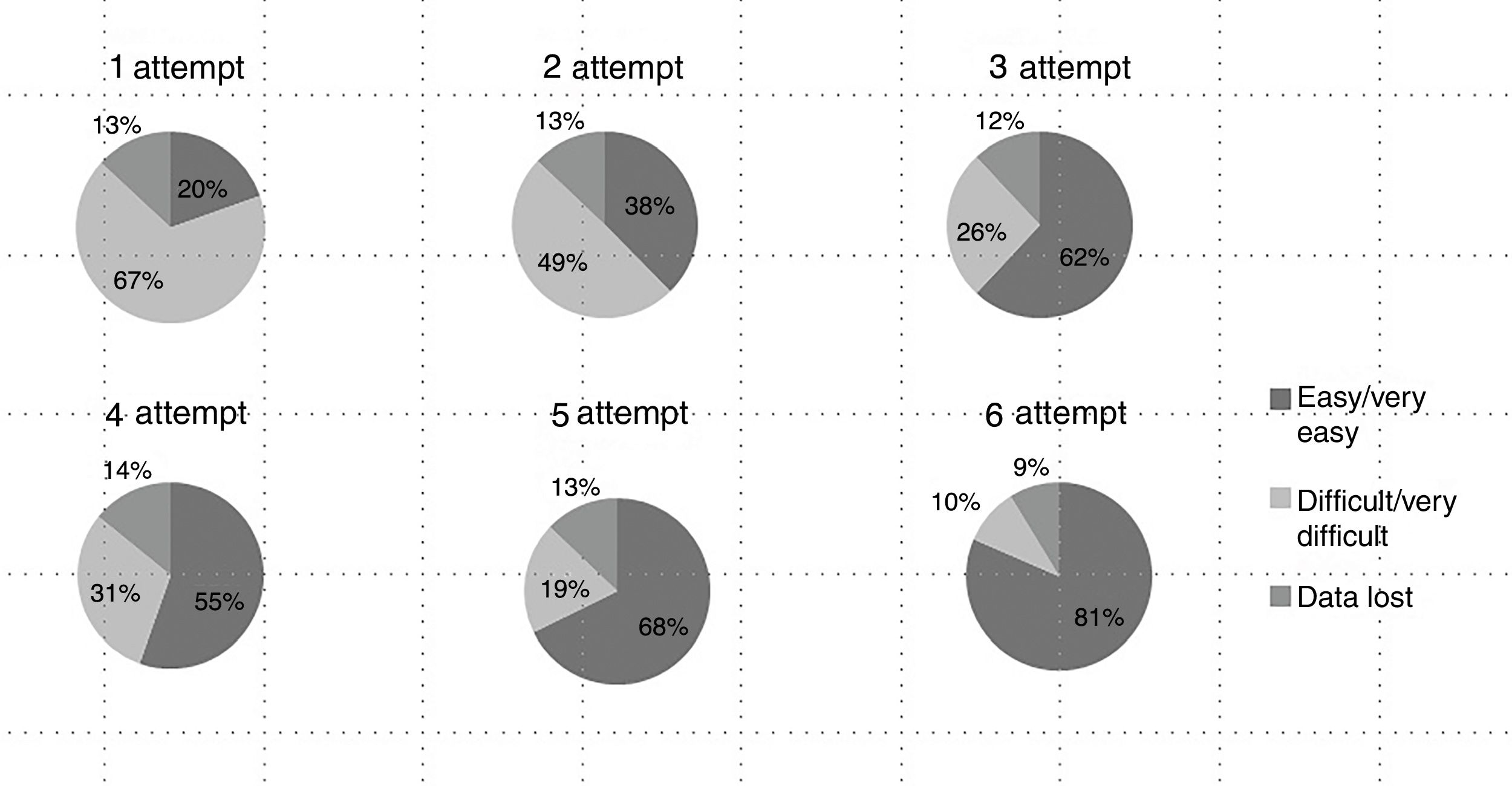
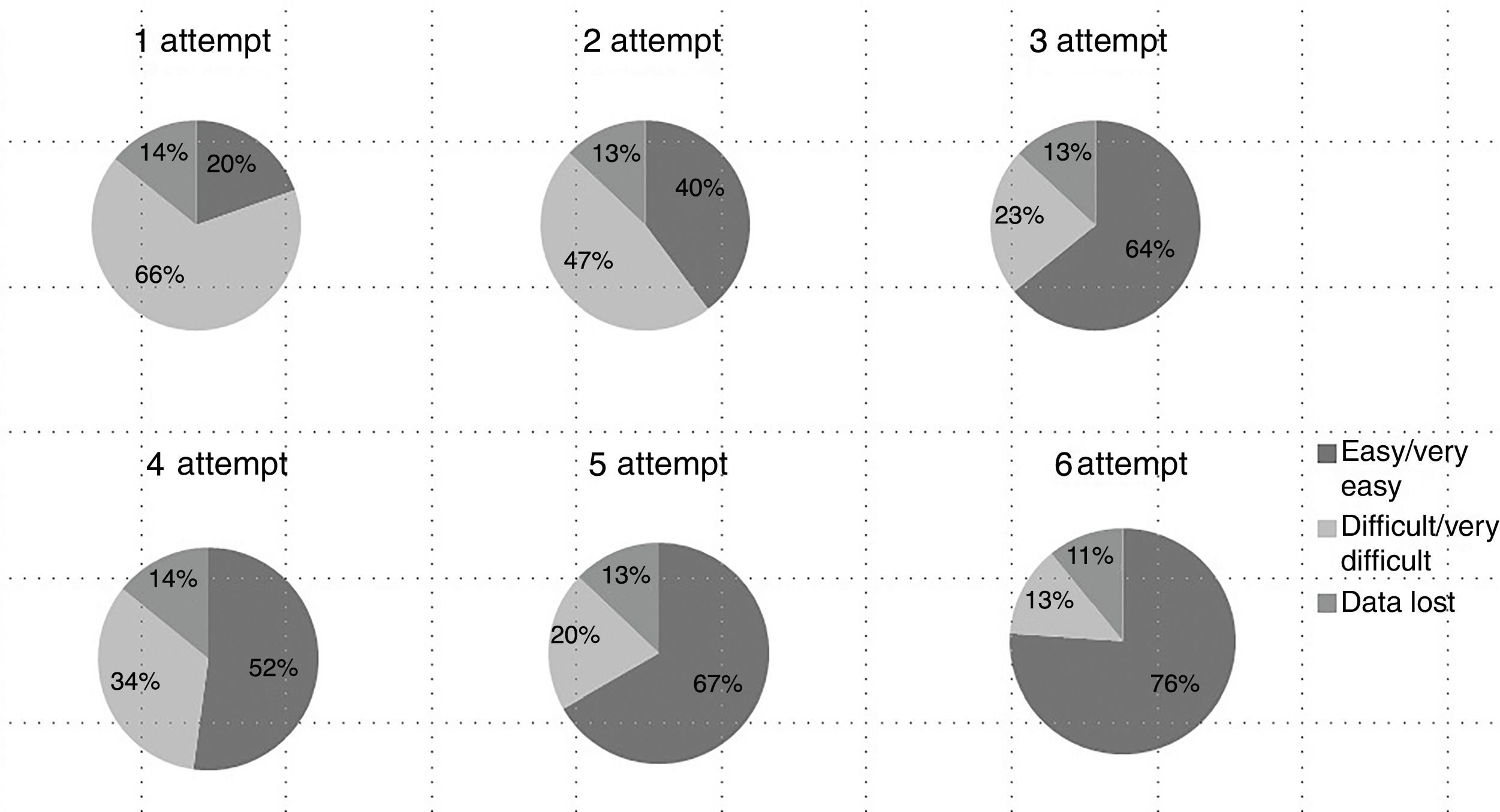
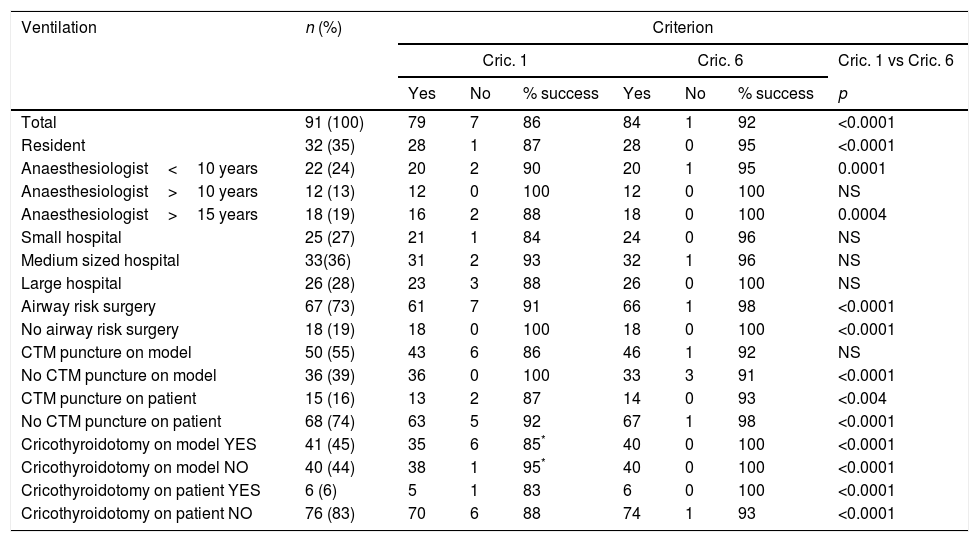
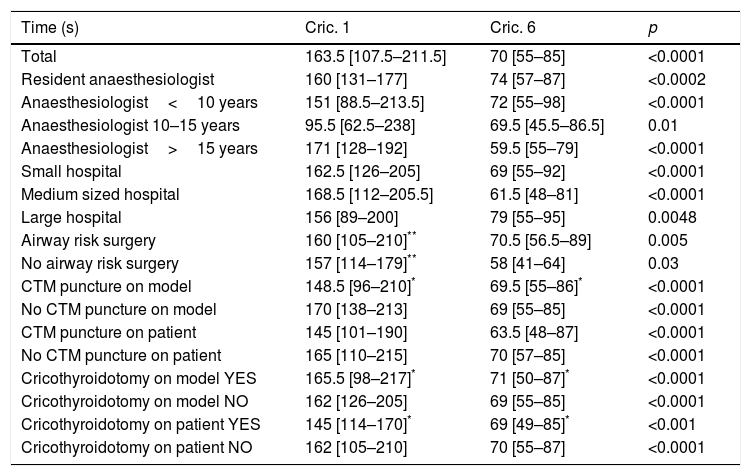
ResultsA total of 8 workshop sessions were held with a total of 91 students. At first attempt, 86% of students performed a CtQ with successful ventilation, and 92% at the sixth attempt (p<0.0001). Time taken was 163 [107–211]s at first attempt, and 70 [55–85]s at the sixth (p<0.0001). At the end of workshop, students had improved their theoretical knowledge (p<0.0001) and perception of the ease of the technique.
ConclusionWorkshop performance improved theoretical knowledge and competence in surgical cricothyrotomy.
Las últimas guías de la Difficult Airway Society recomiendan que todos los anestesiólogos deberían estar entrenados para la realización de una cricotiroidotomía quirúrgica (CtQ). El objetivo de este estudio es analizar los resultados de aprendizaje de un taller de CtQ mediante la evaluación de la tasa de éxito y el tiempo necesario para realizarla en un modelo de tráquea porcina.
Material y métodosDiseñamos un taller en el que cada alumno respondía un cuestionario con datos demográficos y conocimientos teóricos sobre el abordaje quirúrgico de la vía aérea. Durante la hora siguiente se revisaron aspectos teóricos. Se mostró el modelo y realizamos una CtQ siguiendo la técnica clásica. Después, en grupos de 3-4 alumnos con un instructor, los alumnos realizaron 6 CtQ cada uno. Registramos si la ventilación era correcta, el tiempo necesario para realizarla y la facilidad de realización evaluada por alumno e instructor. Finalmente, los alumnos respondieron un cuestionario de aspectos teóricos. Realizamos un análisis estadístico, considerando estadísticamente significativo un valor de p<0,05.
ResultadosLlevamos a cabo 8 ediciones del taller, con 91 alumnos. Consiguieron hacer la CtQ y ventilar correctamente el 86% en el primer intento y el 92% en el sexto (p<0,0001). El tiempo necesario para hacer una CtQ pasó de 163 [107-211] a 70 [55-85] segundos (p<0,0001). Al final del taller los alumnos habían mejorado sus conocimientos teóricos (p<0,0001) y la percepción de facilidad de la técnica.
ConclusiónEl taller realizado mejora los conocimientos teóricos y la competencia en la realización de una CtQ.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora