Identificar los primeros síntomas y signos de los pacientes con sospecha de infección o sepsis y su asociación con la necesidad de ingreso a la unidad de cuidados intensivos o la mortalidad hospitalaria.
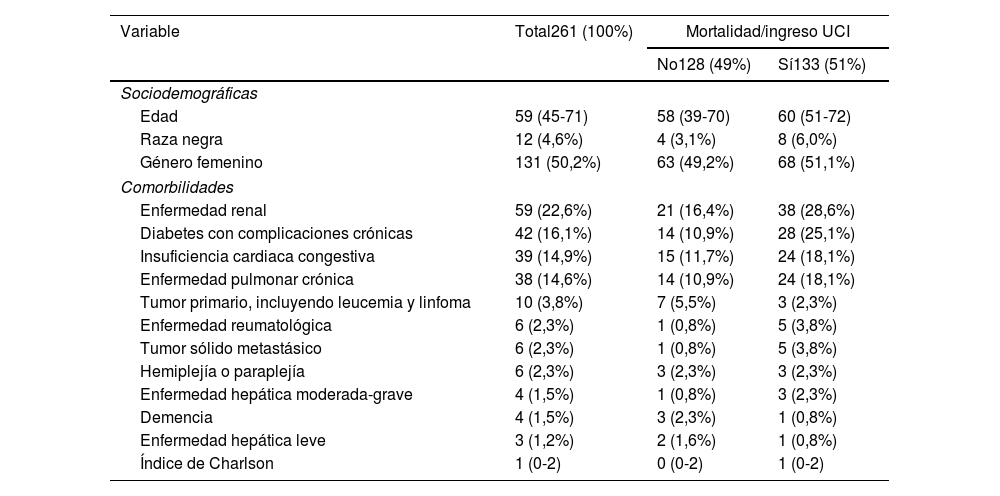
DiseñoEstudio de cohorte prospectivo entre junio de 2019 y marzo de 2020.
ÁmbitoHospital Universitario San Vicente Fundación, Colombia.
PacientesMayores de 18 años con sepsis confirmada o sospechada que requirieron hospitalización.
IntervencionesNinguna.
Variables de interés principalesSíntomas y signos asociados con la infección y su tiempo de evolución.
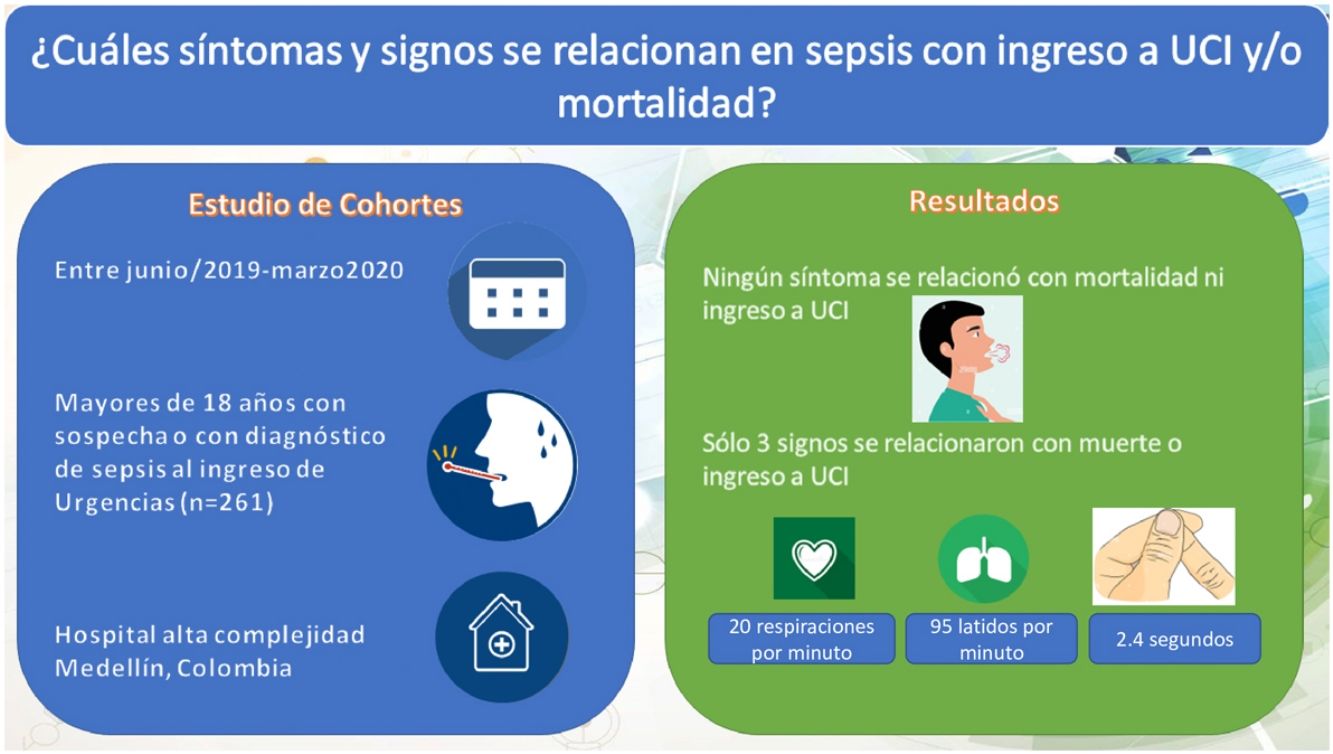
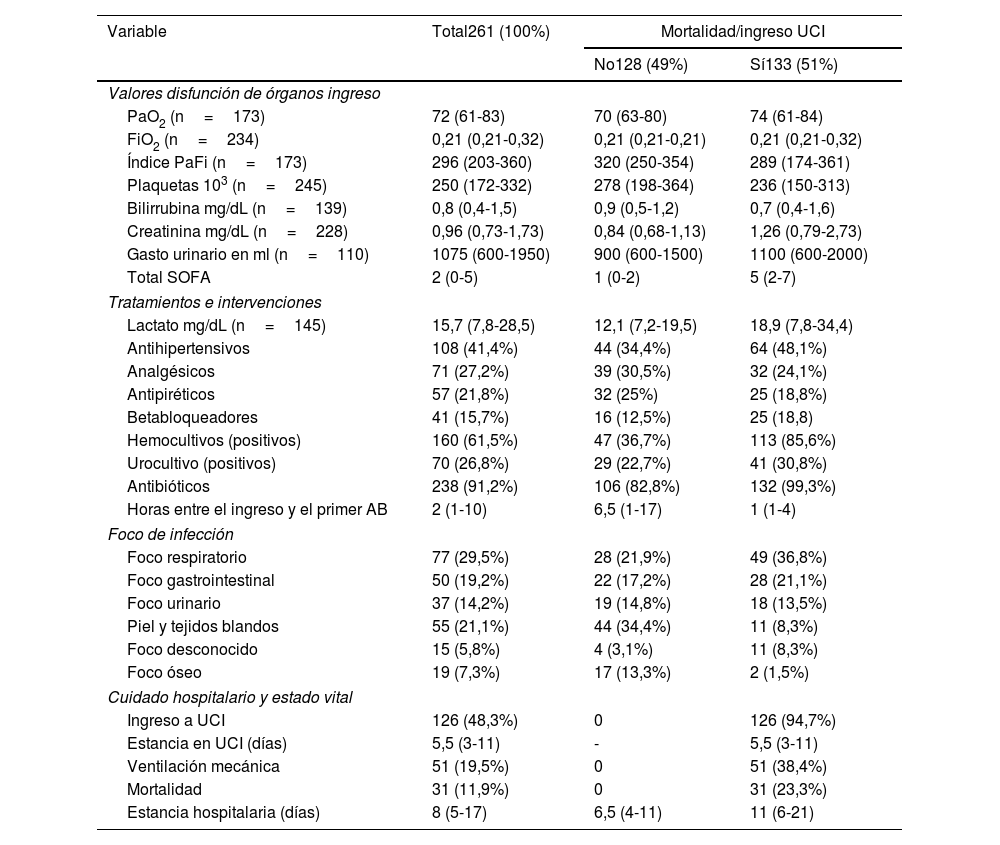
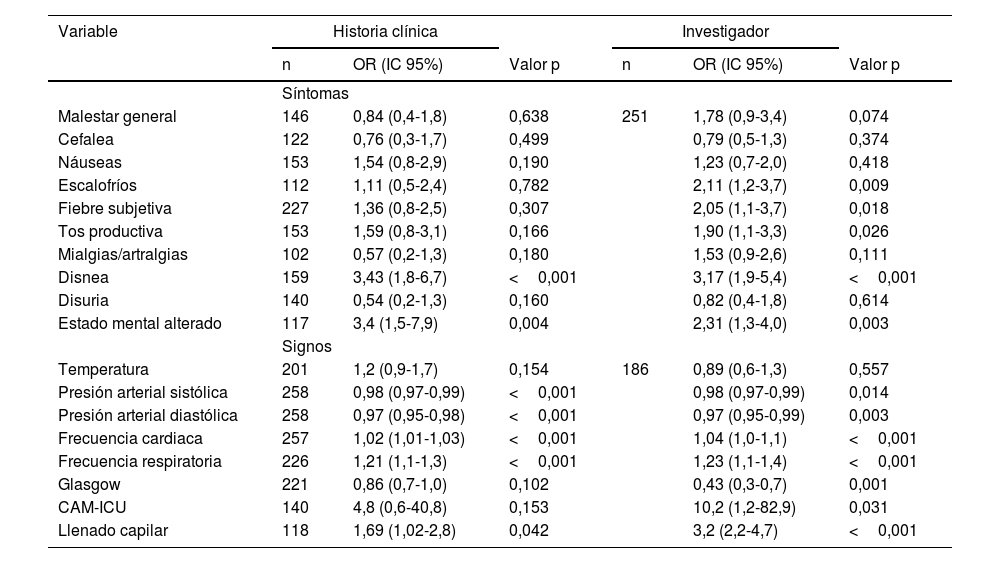
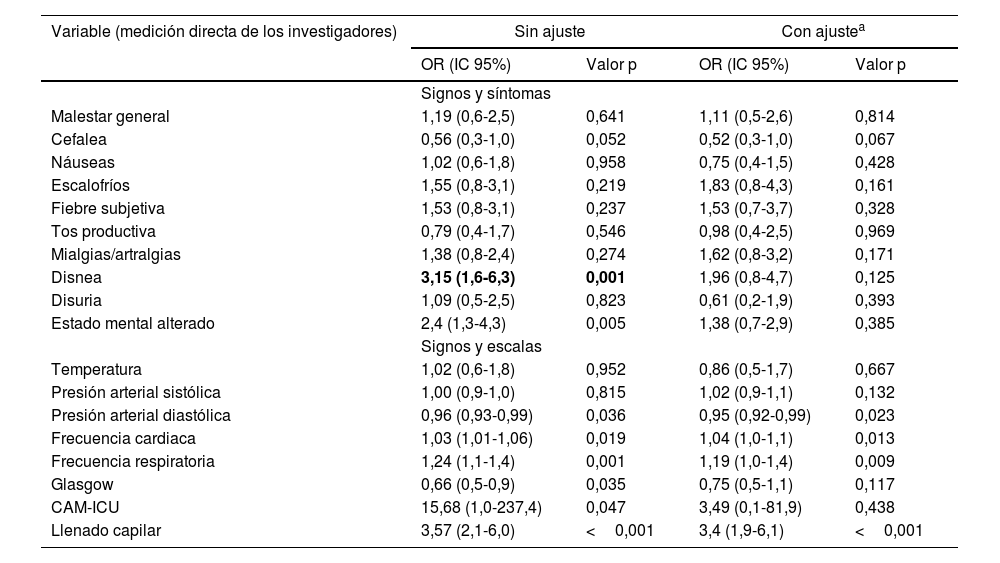
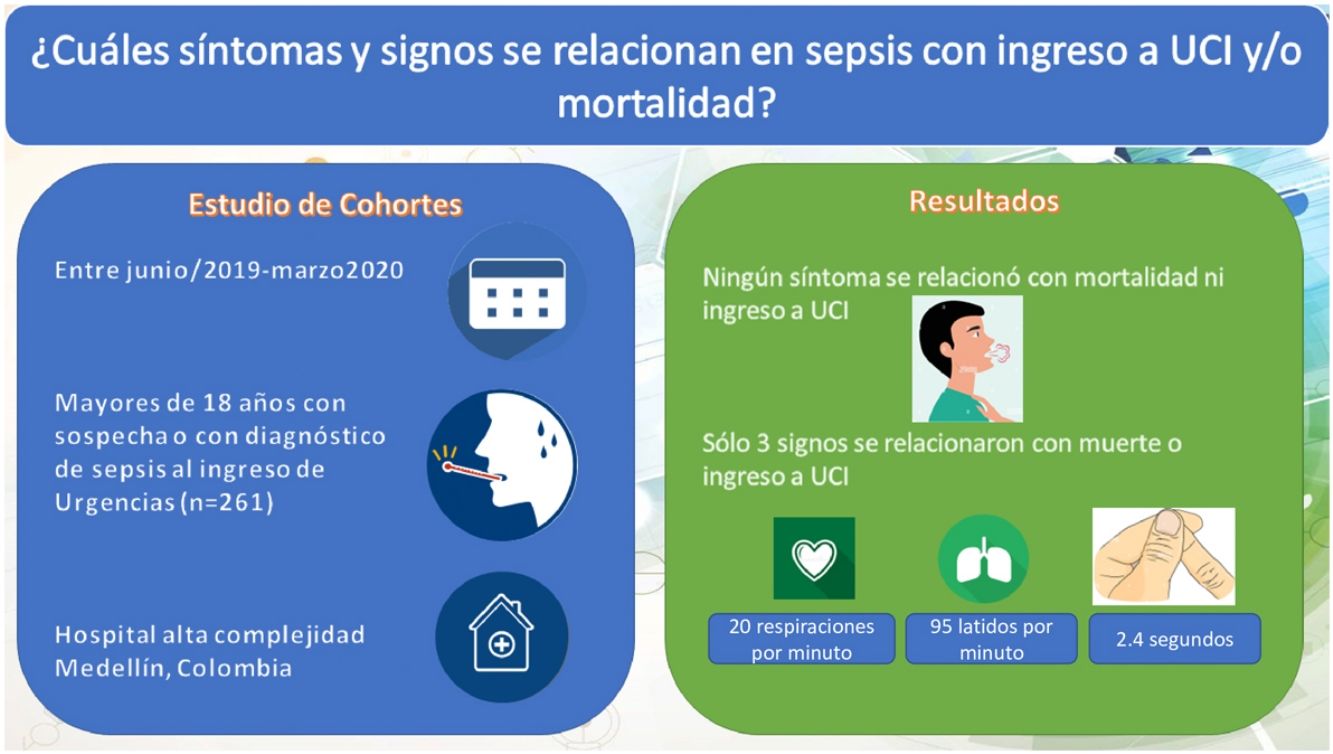
ResultadosDe 1005 pacientes elegibles se incluyeron 261; en los cuales, al aplicar un modelo de regresión logística ajustado, se encontró que se asociaron con el desenlace de mortalidad o ingreso a unidad de cuidados intensivos la frecuencia cardiaca (OR de 1,04 con IC 95% de 1,04-3,7), la frecuencia respiratoria (OR de 1,19 con IC 95% de 1,0-1,4) y el tiempo de llenado capilar (OR de 3,4 con IC 95% de 1,9-6,1).
ConclusionesLa frecuencia cardiaca, la frecuencia respiratoria y el llenado capilar se pueden comportar como factores predictores tempranos de ingreso a unidad de cuidados intensivos y mortalidad en casos con sospecha de sepsis.
To identify the first symptoms and signs of patients with suspected infection or sepsis and their association with the composite outcome of admission to the intensive care unit or mortality.
DesignProspective cohort study between June 2019 and March 2020.
SettingHospital Universitario San Vicente Fundación, Colombia.
PatientsOver 18 years of age with suspicion or confirmation of sepsis, which required hospitalization.
InterventionsNone.
Main variables of interestSymptoms and signs associated with infection, with their time of evolution, specified in the study.
ResultsFrom 1005 eligible patients, 261 were included. After multivariable adjustment with a logistic regression model, the main factors for intensive care unit admission or mortality were heart rate (OR 1.04 with 95% CI 1.04-3.7), respiratory rate (OR 1.19 with 95% CI 1.0-1.4) and capillary refill time (OR 3.4 with 95% CI 1.9-6.1).
ConclusionsHeart rate, respiratory rate, and capillary refill may behave as early predictors of intensive care unit admission and mortality in cases of sepsis.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora