Modified Harris Hip Score (HHS) is one of the most used scales in the assessment of patients with hip pathology. Although a Spanish cross-cultural adaptation has been recently published, there are many studies supporting its validity yet.
Therefore, the aim of this study is to validate the newly adapted Spanish version of the HHS (ES-EHM), comparing it with the WOMAC scale.
Materials and methodsThe ES-EHM scale was applied to 100 patients who underwent a total hip replacement, in three different situations: (1) prior to surgery (pre-surgical ES-EHM), (2) after surgery, with at least 2 years of follow up (after surgery ES-EHM), and (3) 6 months after the postsurgical registration (final ES-EHM). WOMAC questionnaire was also applied once.
We analysed data of scale main score, pain score, function-related score as well as the mean of pre-surgical, postsurgical and final postsurgical ES-EHM scale, in both the ES-EHM and the WOMAC scales.
Parameters of reliability, validity and sensitivity to change were obtained.
ResultsClinically relevant improvement was observed (46.55 points) when comparing pre-surgical and post-surgical ES-EHM scores. However, no differences between postsurgical and final ES-EHM were detected. Even so, strong correlation was obtained between the following: (1) postsurgical ES-EHM and final ES-EHM scores, (2) ES-EHM and WOMAC scores, and (3) pain and function-related parameters of ES-EHM and WOMAC scores.
Standardised response mean (SRM) was 2.99, test–retest reliability expressed by the intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.90 and Cronbach index 0.95.
ConclusionsThe Spanish cross-cultural adaptation of the EHM scale shows to be reliable, valid and sensitive to change. Thus, the Spanish medical staff will be able to apply the ES-EHM scale with good scientific support.
La escala de Harris modificada (EHM) es una de las herramientas más utilizadas para valorar pacientes con patología de cadera. A pesar de contar con una adaptación transcultural al español realizada por Lara et al., no cuenta con estudios que sustenten su validez. Se pretende obtener una validación de la versión adaptada de la EHM (ES-EHM), comparándola con la escala WOMAC.
Materiales y métodosLa ES-EHM se aplicó a 100 pacientes operados de prótesis total de cadera: (1) previamente a la cirugía (ES-EHM prequirúrgica), (2) dos años tras la cirugía (ES-EHM posquirúrgica) y (3) seis meses después de la aplicación de la ES-EHM posquirúrgica (ES-EHM final). Se aplicó también, en una ocasión, el cuestionario WOMAC. Se compararon las medias de la ES-EHM prequirúrgica, posquirúrgica y final, así como la totalidad y los parámetros de dolor y función de la ES-EHM con la escala WOMAC. Se obtuvieron parámetros de fiabilidad, validez y sensibilidad al cambio.
ResultadosAl comparar la ES-EHM prequirúrgica y la posquirúrgica, se observó una mejoría clínicamente relevante (46,54 puntos). Al comparar la ES-EHM posquirúrgica y la final, no se detectaron diferencias. Se obtuvo una correlación fuerte entre: (1) la ES-EHM posquirúrgica y la ES-EHM final, (2) ES-EHM y WOMAC y (3) parámetros de dolor y función de la ES-EHM y la WOMAC. El índice de respuesta media estandarizada fue de 2,99, la fiabilidad test-re-test representada por el coeficiente de correlación intraclase de 0,90 y el índice de consistencia interna alfa de Cronbach de 0,95.
ConclusionesLa adaptación transcultural de la ES-EHM muestra ser fiable, válida y sensible al cambio. Por lo tanto, el personal médico de la población española podrá aplicar la ES-EHM con el respaldo científico y la certeza de estar midiendo los parámetros deseados.
The Harris scale is one of the most widely used tools to assess functional capacity and symptomatology in a patient with hip disease.1–3 Its initial version was published in 1969, which contemplated information provided by both the patient and the physician. Subsequently, the modified Harris scale (MHS) was developed, which supplies only subjective, patient-reported data.4
By assessing various activities of daily living, the MHS makes it possible to evaluate the impact of hip joint symptomatology on the person's quality of life.2,4 Specifically, the scale evaluates: pain, limp, use of external supports for walking, tolerated walking distance, ability to put on socks and shoes, ability to remain seated, and ability to use public transport.4 Based on the patient's reported responses, a score of out of 100 points is obtained. The results are deemed: poor (<70), fair (70–79), good (80–89), and excellent (90–100).1,3
The original English-language version of the MHS was validated by Söderman and Malchau.5 Moreover, the MHS has been translated into several languages: Portuguese, Greek, Italian, Slovenian, Arabic, and Turkish.2,3,6–9 All of these versions have been statistically validated and their reliability corroborated. There is also a translated version adapted for the Brazilian population; however, there are no studies that back up its validity.8
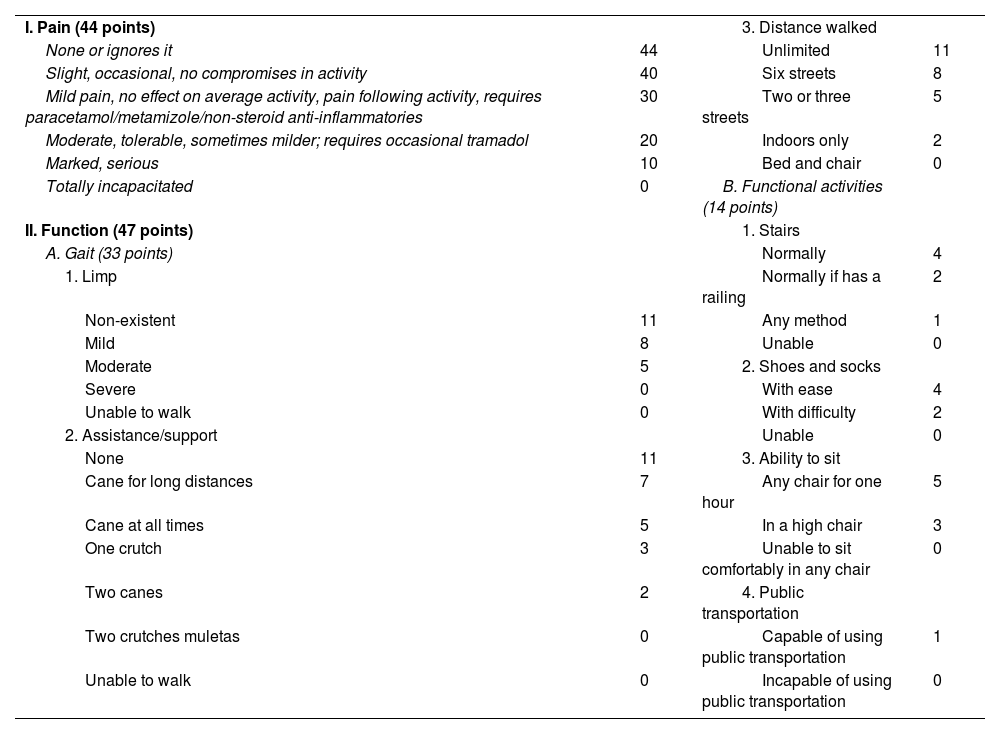
As for the Spanish language, the MHS has been translated and adapted cross-culturally by Lara et al.1 (Table 1). In addition, Navarro Collado et al. reported [on] a validation. However, a translation of the original version published in 1944 was used in this validation, and not a cross-cultural adaptation.10 Moreover, this validation uses the MOS-SF-46 questionnaire, which is not specific to bone and joint pathology.10
Cross-cultural adaptation of the modified Harris scale for the Spanish population (ES-EHM).
| I. Pain (44 points) | 3. Distance walked | ||
| None or ignores it | 44 | Unlimited | 11 |
| Slight, occasional, no compromises in activity | 40 | Six streets | 8 |
| Mild pain, no effect on average activity, pain following activity, requires paracetamol/metamizole/non-steroid anti-inflammatories | 30 | Two or three streets | 5 |
| Moderate, tolerable, sometimes milder; requires occasional tramadol | 20 | Indoors only | 2 |
| Marked, serious | 10 | Bed and chair | 0 |
| Totally incapacitated | 0 | B. Functional activities (14 points) | |
| II. Function (47 points) | 1. Stairs | ||
| A. Gait (33 points) | Normally | 4 | |
| 1. Limp | Normally if has a railing | 2 | |
| Non-existent | 11 | Any method | 1 |
| Mild | 8 | Unable | 0 |
| Moderate | 5 | 2. Shoes and socks | |
| Severe | 0 | With ease | 4 |
| Unable to walk | 0 | With difficulty | 2 |
| 2. Assistance/support | Unable | 0 | |
| None | 11 | 3. Ability to sit | |
| Cane for long distances | 7 | Any chair for one hour | 5 |
| Cane at all times | 5 | In a high chair | 3 |
| One crutch | 3 | Unable to sit comfortably in any chair | 0 |
| Two canes | 2 | 4. Public transportation | |
| Two crutches muletas | 0 | Capable of using public transportation | 1 |
| Unable to walk | 0 | Incapable of using public transportation | 0 |
To ensure a proper understanding of a patient-reported outcome tool, it is not enough to have a translation. Rather, it must also be adapted into terms that are understandable to the society in which it is intended to be used.1,11,12 Hence, the present study is of particular interest in that it attempts to scientifically validate the only cross-cultural adaptation of the MHS for the Spanish population (ES-EHM). To this end, the ES-EHM is compared with the WOMAC scale, which is the scale that has the most validation studies.10,13,14
MethodsStudy designObservational study that included patients between 30 and 80 years of age who had undergone total hip replacement surgery and who had more than two years of evolution. Therefore, subjects at either ends of the age range (less than 30 and more than 80 years old) and who were in their first two post-surgery years were excluded from participation in the study. Using a prospective database of a tertiary hospital, 100 patients meeting the inclusion criteria described above were randomly selected.
For the purposes of this study, the Modified Harris Scale adapted to the Spanish population (ES-EHM)1 was used. The selected group were administered the ES-EHM on three occasions: (1) prior to surgery (pre-surgical ES-EHM), (2) 2 years post-surgery (post-surgical ES-EHM), collected at the beginning of the investigation (2020), and (3) 6 months after the application of the post-surgical ES-EHM (final ES-EHM). Furthermore, the same patients were administered the WOMAC questionnaire on one occasion, at the same time as the final ES-MHS. All questionnaires were administered by a single doctor of the team.
All patients involved were informed about their participation in the study and the intention to be published, maintaining their anonymity at all times. The patients involved gave their consent.
Statistical analysisReliability analysisInternal consistency: This was measured by means of Cronbach's alpha index. Consistency is assumed to exist when the value is greater than 0.8.8
Floor effect and ceiling effect: The percentage of participants with a minimum and maximum score on the post-surgical ES-MHE was calculated.
Intra-observer reliability: The questionnaire was administered on two occasions, six months apart. The means of each parameter and the total post-surgical and final ES-MHE score were compared.
To measure the concordance between the two measurements, test–retest reliability was assessed by means of the intraclass correlation coefficient. A coefficient of between 0.81 and 1 indicates a strong correlation; between 0.61 and 0.80, very good; between 0.41 and 0.60, good; between 0.21 and 0.40, fair, and less than 0.21 indicates poor correlation.8
Validity analysisCriterion validity: The results of the ES-EHM and the WOMAC scales were compared. The WOMAC scale consists of 24 questions answered by the patient that are divided into 3 categories: pain (5 questions), stiffness (2 questions), and physical function (17 questions).6 The patient rates each item, assigning a score of 0–4 to each item. The patient provides a score from 0 to 4 for each item. The final score is the sum of the results of each section, obtaining a maximum of 96 points; the higher the score, the greater the pain, stiffness, and the worse their physical function.5 The Harris scale was categorised into its “pain” and “function” components in order to be able to compare the same parameters of the WOMAC scale.
The correlation between both scales was attained by means of Spearman's correlation coefficient and by comparing the means obtained using Student's t test for paired data.
Sensitivity to change analysisSensitivity to change: Pre-surgical and post-surgical outcomes were compared. The ability of the ES-MHE to detect change was also quantified by means of the standardised mean response. This index is calculated by dividing the mean change by the standard deviation of the change; a value of greater than 0.80 is interpreted as a high sensitivity to change.7
All the statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS® v.27.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
ResultsReliability analysisInternal consistency: Cronbach's alpha internal consistency index was 0.95.
Floor effect and ceiling effect: Nineteen out of 100 patients reported the maximum score for all parameters of the ES-EHM, obtaining a score of 100. None of the participants were found to have a floor effect, i.e., a score equal to 0.
Intra-observer reliability: When comparing the post-surgery ES-MHE values with the final ES-MHE scores, question by question, there were no statistically significant differences, except for the question “ability to sit” (mean difference of .25, p value=.07) (Table 2). The intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.90 (strong correlation).
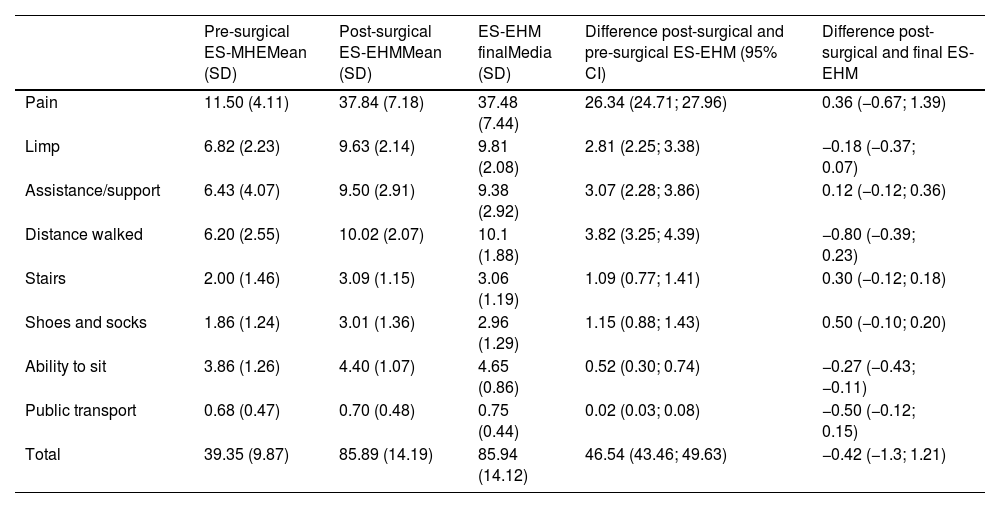
Comparison of means between pre-surgical, post-surgical and final administration of the Modified Harris Scale (ES-EHM).
| Pre-surgical ES-MHEMean (SD) | Post-surgical ES-EHMMean (SD) | ES-EHM finalMedia (SD) | Difference post-surgical and pre-surgical ES-EHM (95% CI) | Difference post-surgical and final ES-EHM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | 11.50 (4.11) | 37.84 (7.18) | 37.48 (7.44) | 26.34 (24.71; 27.96) | 0.36 (−0.67; 1.39) |
| Limp | 6.82 (2.23) | 9.63 (2.14) | 9.81 (2.08) | 2.81 (2.25; 3.38) | −0.18 (−0.37; 0.07) |
| Assistance/support | 6.43 (4.07) | 9.50 (2.91) | 9.38 (2.92) | 3.07 (2.28; 3.86) | 0.12 (−0.12; 0.36) |
| Distance walked | 6.20 (2.55) | 10.02 (2.07) | 10.1 (1.88) | 3.82 (3.25; 4.39) | −0.80 (−0.39; 0.23) |
| Stairs | 2.00 (1.46) | 3.09 (1.15) | 3.06 (1.19) | 1.09 (0.77; 1.41) | 0.30 (−0.12; 0.18) |
| Shoes and socks | 1.86 (1.24) | 3.01 (1.36) | 2.96 (1.29) | 1.15 (0.88; 1.43) | 0.50 (−0.10; 0.20) |
| Ability to sit | 3.86 (1.26) | 4.40 (1.07) | 4.65 (0.86) | 0.52 (0.30; 0.74) | −0.27 (−0.43; −0.11) |
| Public transport | 0.68 (0.47) | 0.70 (0.48) | 0.75 (0.44) | 0.02 (0.03; 0.08) | −0.50 (−0.12; 0.15) |
| Total | 39.35 (9.87) | 85.89 (14.19) | 85.94 (14.12) | 46.54 (43.46; 49.63) | −0.42 (−1.3; 1.21) |
SD: standard deviation; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
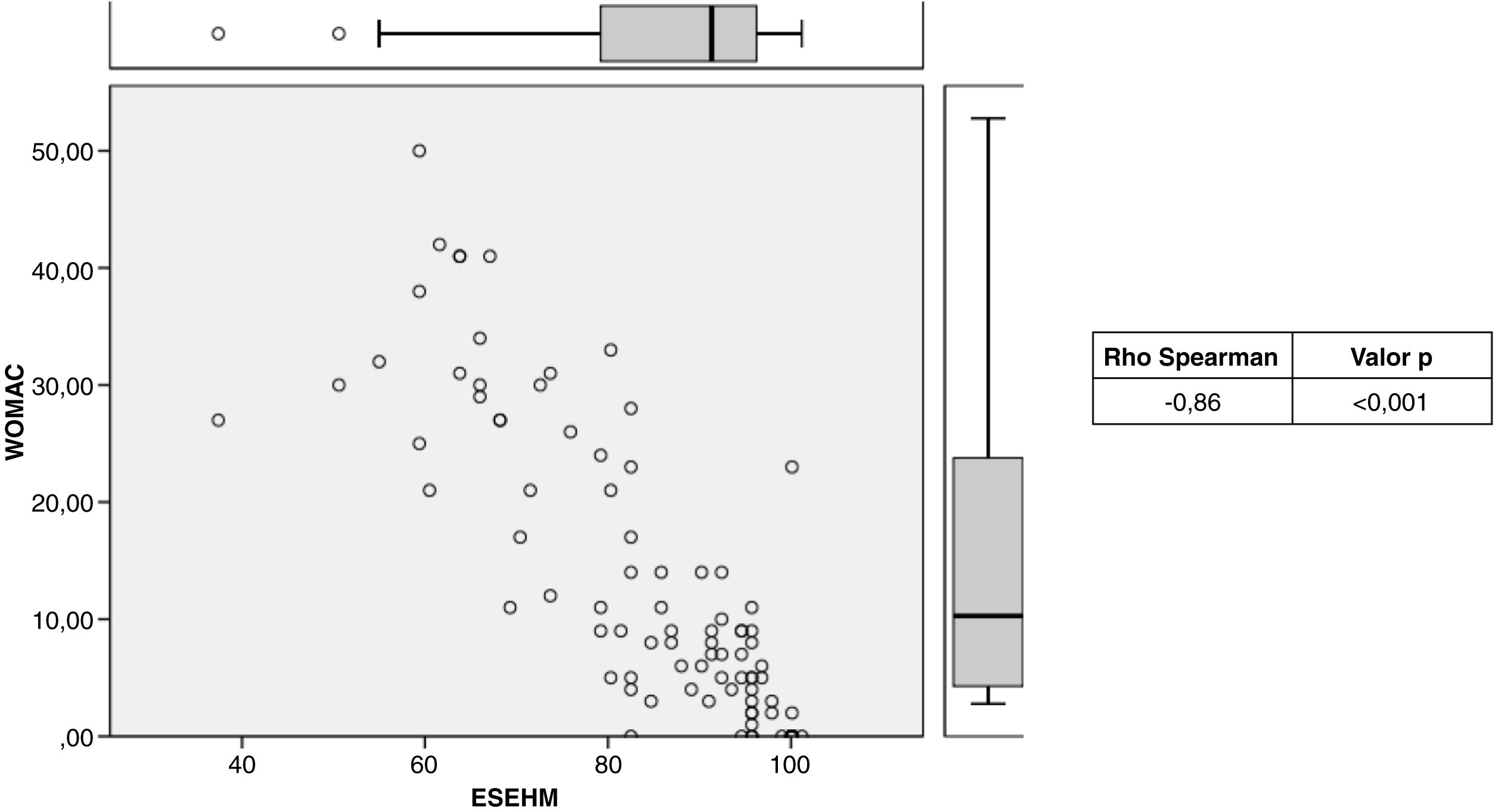
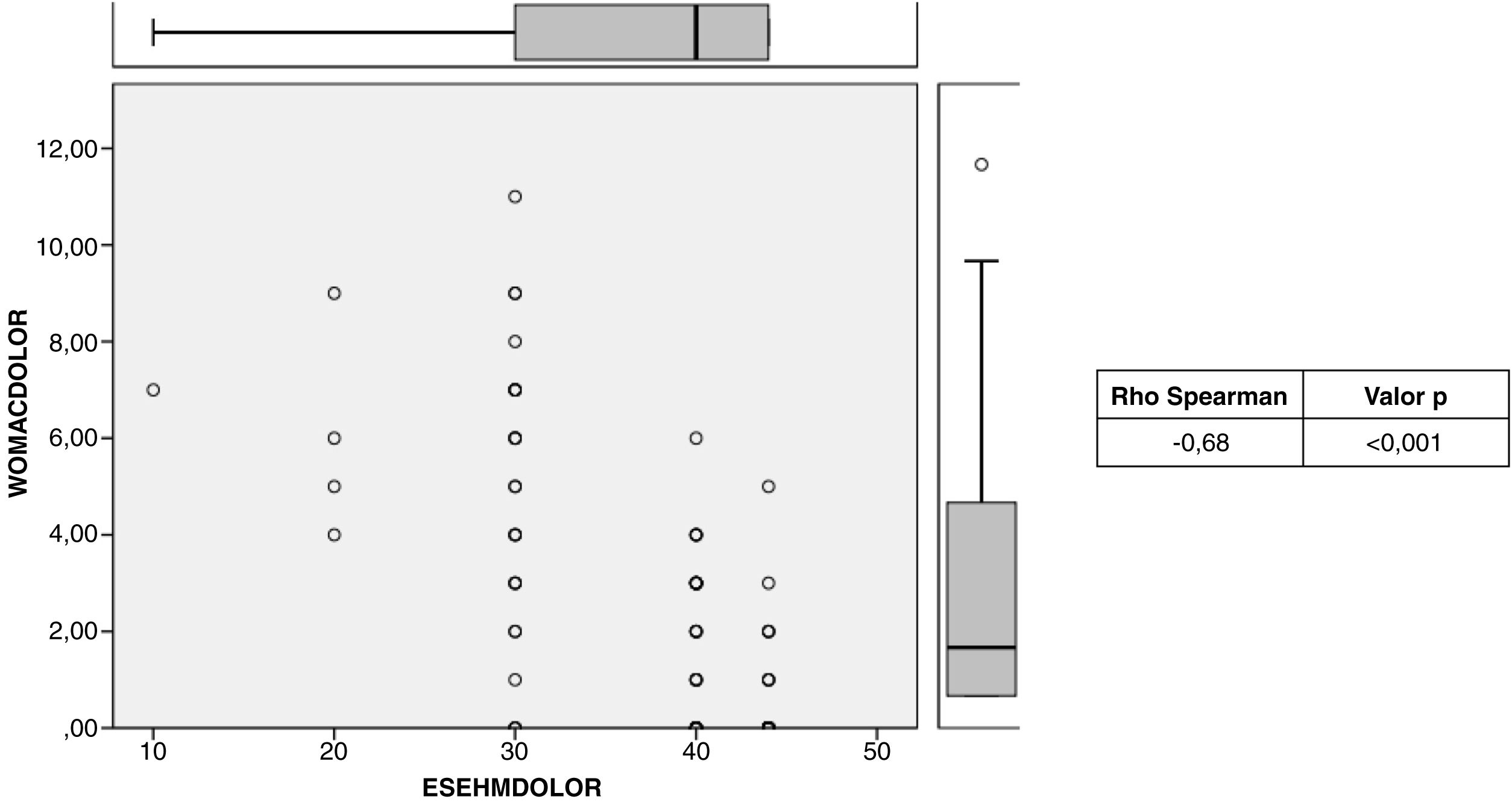
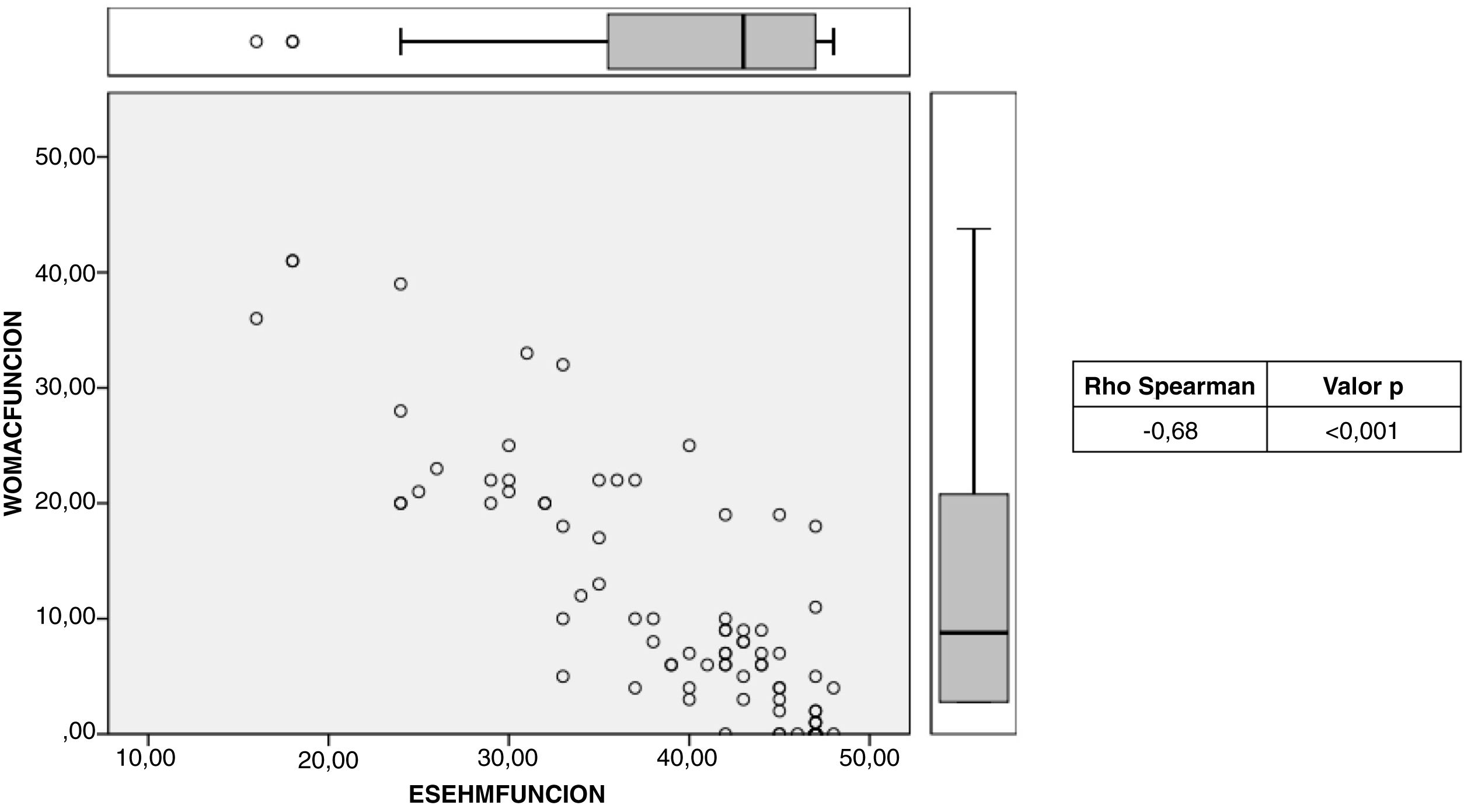
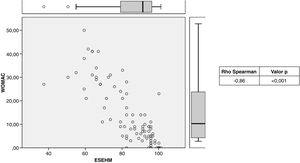
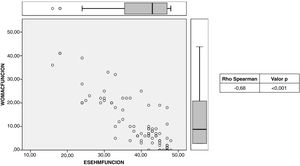
Criterion validity: The means of the WOMAC scale were as follows: pain, 2.28; function, 9.32, and total, 11.9, while those of the post-surgical ES-EHM were: 37.80, 40.40, and 85.90, respectively. When comparing the two scales, a statistically significant Spearman correlation index of −0.86 was obtained (Fig. 1). Inverse correlation was also evident when comparing the pain and function parameters of both scales, with correlation indices of −0.98 and −0.85, respectively (Figs. 2 and 3).
Sensitivity to change: The mean pre-surgical total ES-MHE score was 39.35; the mean post-surgical total score was 85.89, and the mean final score was 85.94 (Table 2). On comparison of the pre-surgical ES-MHE and post-surgical ES-MHE, a statistically significant improvement of 46.55 points was noted. This statistically significant difference was maintained when each of the scale parameters was compared. Conversely, no differences were detected between the post-surgical ES-EHM and final ES-EHM scales (Table 2).
The mean standardised response rate was 2.99, i.e., a high degree of sensitivity to change was evident.
DiscussionThe importance of cross-cultural adaptation of scales used as medical assessment tools resides in the possible differences in how people express themselves based on the society in which they are immersed.1,8 These subtle differences can impact patients’ understanding and thereby change the psychometric properties of the scale to be used.8 Similarly, it is important for any tool to be statistically backed up to validate its usefulness. Thus, the EHM has been adapted and validated for the Portuguese, Greek, Italian, Slovenian, Arabic, and Turkish languages.2,3,6–9 Meanwhile, the cross-cultural adaptation of the modified Harris scale for the Spanish population has proven to be reliable, valid, and sensitive to change.
In terms of reliability, the Cronbach's index of 0.95 is superior to that demonstrated by the Slovenian (0.94), Italian (0.81), and Turkish (0.76) versions.8,15 Therefore, it can be concluded that the ES-EHM has good internal correlation.12 Contrary to the findings of Navarro et al.10 and Çelik et al., the ES-EHM does indeed exhibit a ceiling effect. The intraclass correlation index obtained is lower than the Slovenian validation (0.98) yet higher than that reported by Hinman et al. (0.76) in their study demonstrating the validity of the original HHS for use in patients with femoroacetabular impingement.8,16
To verify criterion validity, the WOMAC scale was considered, inasmuch as it has been adapted for use in the Spanish population and has been validated since 2002.13 It should be noted that unlike the HHS, the WOMAC scale yields a better result at lower scores; therefore, an inverse relationship is expected when comparing the two scales.5 A strong inverse correlation was evidenced (Spearman=−0.86), similar to the correlation displayed by the Slovenian version (Spearman=−0.88). The magnitude of correlation was maintained when the pain and function parameters were compared separately (Spearman=−0.98 and −0.85, respectively). The magnitude of correlation between the pain and function parameters between the ES-EHM and the WOMAC is greater than that found by Navarro et al. between the EHM and the MOS-SF-36 scale (Spearman=0.70 and 0.55, respectively).
Singh et al. demonstrated that to define a minimal clinically relevant improvement, there must be a change of between 16 and 18 points on the HHS, while when the difference in score is greater than 40, there is a moderate degree of improvement.17 This confirms that the ES-MHE is sensitive to change, bearing in mind that the difference between the pre- and post-surgical scores was 46 points. This is further corroborated by the high standardised mean response rate obtained (2.99). As with the Turkish version by Çelik et al., the ES-EHM proved to be consistent over time given that no difference was detected in the scores obtained separated by 6 months.6
As to the limitations of the study, in order to ascertain the reliability of the HHS, the optimal time interval between the 2 assessments has been determined to be between 7 days and 4 weeks.6,16 In the present study, the interval was 6 months in an attempt to prevent patients from becoming familiar with and remembering their answers from the first assessment. Furthermore, the fact that the scales were administered by a single doctor on the team did not enable us to obtain an inter-observer correlation coefficient.
ConclusionThe present study substantiates the usefulness of the cross-cultural adaptation of the modified Harris scale (ES-EHM) as a tool for the Spanish population, with scientific support in terms of its reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change. Thus, medical personnel will be able to administer the ES-EHM, not only in the Spanish population, but also in the Spanish-speaking community, as long as they do not have a version adapted to their own style of expression. All this with the scientific backing and the certainty of measuring the parameters intended.
Level of evidenceLevel of evidence iii.
Consent to participate and consentAll patients involved were informed of their participation in the study and the [authors’] intention of being published, while at all times maintaining their anonymity. The subjects involved provided their consent.
FundingThis research has not received specific support from public sector agencies, the commercial sector, or non-profit organisations.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.