To evaluate the range of motion (ROM) of the knee in patients with severe post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis after being treated with arthroscopic fibroarthrolysis (AFA) and manipulation under anesthesia (MUA).
MethodsCase series of patients with severe post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis who underwent AFL+MUA in a national referral center. The primary outcome to be assessed was ROM before and after surgery and then at 3-month intervals until a minimum follow-up of one year was completed.
Results51 patients were included. The main injuries preceding the stiffness were tibial plateau fracture (37.3%), distal femur fracture (27.5%), and femoral shaft fracture (15.7%). Forty-five patients had severe flexion deficits with a median preoperative flexion of 70°. Intraoperative flexion significantly improved to 110°. Significant loss of flexion was observed at 3 and 6 months, however, patients regained ROM in the 9 and 12-month follow-ups. At discharge, 80% of the patients achieved flexion of 90° or more. There were 4 intraoperative complications and 3 reinterventions were performed.
ConclusionAFA+MUA can help patients with severe post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis to recover ROM in most cases. However, this procedure is not without risks and complications, therefore, careful consideration should be given to its indication and execution.
Evaluar el rango de movimiento (ROM) de la rodilla en los pacientes con artrofibrosis postraumática severa de la rodilla después de ser tratados con fibroartrolísis artroscópica (FAA) y movilización bajo anestesia (MBA).
MétodosSerie de casos de pacientes con artrofibrosis postraumática severa de la rodilla sometidos a una FAA+MBA en un centro nacional de referencia. El resultado primario a evaluar fue el ROM antes y después de la cirugía y luego a intervalos de 3 meses hasta completar un seguimiento mínimo de un año.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 51 pacientes. Las principales lesiones precedentes a la rigidez fueron fractura de platillo tibial (37,3%), de fémur distal (27,5%) y de diáfisis femoral (15,7%). Cuarenta y cinco pacientes tenían un déficit de flexión severo con una flexión preoperatoria mediana de 70°. La flexión intraoperatoria mejoró significativamente a 110°. Se observó una pérdida significativa de flexión a los 3 y 6 meses, sin embargo, los pacientes recuperaron ROM en los seguimientos de 9 y 12 meses. Al momento del alta, el 80% de los pacientes alcanzó una flexión de 90° o más. Hubo 4 complicaciones intraoperatorias y se realizaron 3 reintervenciones.
ConclusiónLa FAA+MBA pueden ayudar a los pacientes con artrofibrosis de rodilla postraumática severa a recuperar el ROM en la mayoría de los casos. Sin embargo, este procedimiento no está exento de riesgos y complicaciones, por lo tanto, se debe ser cuidadoso en su indicación y ejecución.
Arthrofibrosis is a common complication that occurs after intra-articular knee trauma, with a reported incidence of up to 14.5%. This incidence is significantly higher compared to its incidence after ACLR (4%) or TKA (5.3%).1–10 However, there are few studies that specifically focus on the condition of post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis and its arthroscopic treatment.
The available literature suggests some association with distal femur fractures, tibial plateau, and patella, but further research is required to understand the underlying mechanisms.11–14
Conservative management of arthrofibrosis usually involves aggressive physical therapy. However, its effectiveness is limited, especially in cases of post-traumatic arthrofibrosis.3 Therefore, arthroscopic intra-articular lysis of adhesions, also known as arthroscopic fibroarthrolysis (AFA), along with manipulation under anesthesia (MUA), has become increasingly important.4,15–17 Lysis of adhesions allows surgeons to apply less force during manipulation, which is particularly important since MUA alone can lead to an increasing risk of complications such as intraoperative fracture, hemarthrosis, postoperative scarring, and chondral damage. As a result, some authors do not recommend MUA as an isolated treatment option.18 Consequently, AFA and MUA have gained increasing importance.4,15,17,16
Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the ROM after AFA and MUA in patients with post-traumatic arthrofibrosis of the knee over a mid-term follow-up. By assessing the effectiveness of these procedures, this study will provide healthcare professionals with a better understanding of the available treatment options for improving the ROM of patients with this condition.
Material and methodsStudy design and patientsA case series study was conducted on patients who experienced severe knee arthrofibrosis following a traumatic injury and were treated with AFA and MUA at a referral trauma center. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee, and all patients provided written consent. Clinical records of patients who had undergone AFA and MUA due to severe knee arthrofibrosis between May 2019 and December 2020 were reviewed. Demographic information, including sex, age, body mass index (BMI), tobacco use, comorbidities, involved side, and primary diagnosis, was retrieved. Severe arthrofibrosis of the knee was defined as a loss of extension of 10° or more and flexion of 90° or less. Prior to the AFA & MUA procedure, patients underwent a minimum of three months of standard physical therapy with five sessions per week. The therapy regimen included knee mobilization and muscle strengthening to prevent implant failure.
The study included adult patients with severe knee arthrofibrosis caused by femur fractures (shaft or distal), patellar fractures, or tibia fractures (plateau, shaft, or spines). Patients with spinal cord injury or unresolved osteoarticular infection and those who did not provide consent were excluded.
The primary outcome was to evaluate the range of motion (ROM) before and after surgery. ROM was measured every three months until one year of follow-up. Only the measures performed by an orthopedic knee surgeon using a goniometer were considered. Measurements were made by stabilizing the femur and then moving the tibia through its entire available range of motion until reaching the end feel. The goniometer was aligned by touching the relevant bone landmarks and following the femoral and tibial diaphysis. Then the measurement in maximum extension and flexion were recorded. This process was repeated 2 times and the average was calculated and registered.
The secondary outcomes aimed to analyze the association between the timing of the procedure and the final range of motion. Additionally, the number of patients with resolved arthrofibrosis at the final follow-up, compared to the total number of patients included, was evaluated. Intraoperative complications at the time of AFA or MUA such as refractures, new fractures, patellar or quadriceps tendon rupture, chondral damage, ligamentous or vascular injuries were analyzed. We also evaluated the need for reintervention, defined as the need for secondary procedures after AFA and MUA, up to the final follow-up.
Surgical and postoperative protocolThe AFA and MUA procedure was conducted using general or regional anesthesia. A femoral catheter was inserted into the operated limb. The surgical procedure began by creating anterolateral and anteromedial arthroscopic portals. Additional portals, such as superomedial, superolateral, posteromedial, or posterolateral, were used as required. Adherence lysis was performed in the patellofemoral and anterior compartment, as well as in the medial and lateral gutters, using an arthroscopic shaver and radiofrequency ablation. In some cases, a Steinmann pin was used to mechanically release thick adherences in the suprapatellar pouch. The intercondylar notch was then debrided, and the posterior capsule was released if necessary. MUA was performed using the proximal tibia as the primary lever during manipulation, with care taken not to generate torque using the distal tibia or foot. Force was gradually applied, with a frequency of 3–4 manipulations of 10–30s each. Final ROM was measured using a sterile universal long-arm goniometer. Limiting the risk of postoperative hematoma is important because it's resorption increases the risk of stiffness recurrence.18 However, intra-articular drains and topical/systemic tranexamic acid were not routinely used. An attempt was made to achieve thorough hemostasis using a radiofrequency ablator when the tourniquet was deflated in all patients. A mild compressive bandage and cryotherapy were also used for the first 48h.
Following the surgery, all patients received physical therapy treatment while hospitalized, which included passive, assisted, and active mobilization exercises, as well as soft tissue management and muscle strengthening exercises. As per the protocol, all patients used a continuous passive mobilization device (CPM) for 12h a day for 3 days. After being discharged from the hospital, patients attended physical therapy sessions 5 days a week, for at least 6 weeks.
Statistical analysisDescriptive and inferential statistical analyses were conducted. As there were upper and lower ROM limits present, we treated the ROM as an asymmetrical variable. We calculated rates, median, interquartile range (IQR 25–75), and absolute change for each variable as needed. To analyze the absolute change in ROM, we used the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test. Then, we performed scatter plots and calculated Spearman's correlation to determine the relationship between the final ROM and the timing of the procedure. We carried out the statistical analysis using Stata IC 16.1v (StataCorp. 2019. Stata Statistical Software: Release 16, College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC). A significance level of α=0.05 and power of 1−β=0.2 were predefined for this study. Since this was a descriptive study, we did not perform a sample size calculation.
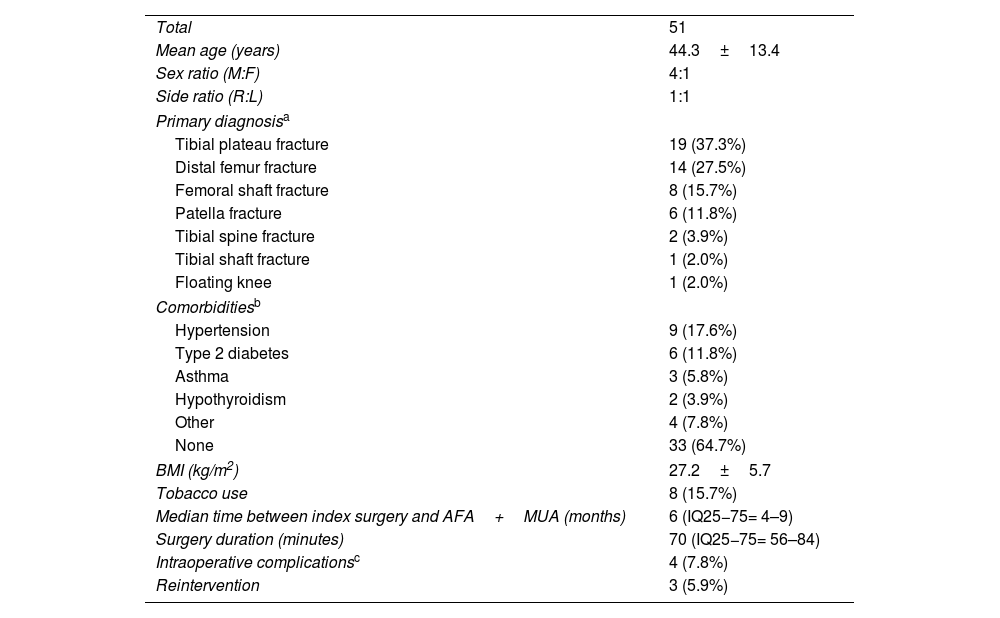
ResultsGeneral resultsThere were 76 patients who suffered from post-traumatic knee stiffness and underwent AFA and MUA procedures between 2019 and 2020. Out of the 76 patients, 25 were excluded, as shown in Fig. 1, leaving 51 patients for analysis. The demographics of the patients are presented in Table 1.
Demographic data of included patients.
| Total | 51 |
| Mean age (years) | 44.3±13.4 |
| Sex ratio (M:F) | 4:1 |
| Side ratio (R:L) | 1:1 |
| Primary diagnosisa | |
| Tibial plateau fracture | 19 (37.3%) |
| Distal femur fracture | 14 (27.5%) |
| Femoral shaft fracture | 8 (15.7%) |
| Patella fracture | 6 (11.8%) |
| Tibial spine fracture | 2 (3.9%) |
| Tibial shaft fracture | 1 (2.0%) |
| Floating knee | 1 (2.0%) |
| Comorbiditiesb | |
| Hypertension | 9 (17.6%) |
| Type 2 diabetes | 6 (11.8%) |
| Asthma | 3 (5.8%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 2 (3.9%) |
| Other | 4 (7.8%) |
| None | 33 (64.7%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.2±5.7 |
| Tobacco use | 8 (15.7%) |
| Median time between index surgery and AFA+MUA (months) | 6 (IQ25−75= 4–9) |
| Surgery duration (minutes) | 70 (IQ25−75= 56–84) |
| Intraoperative complicationsc | 4 (7.8%) |
| Reintervention | 3 (5.9%) |
There were 45 patients who presented with a severe flexion deficit, with a median preoperative flexion of 70°. Following the surgical intervention, intraoperative flexion improved significantly to 110°, resulting in an overall improvement of 40° (p<0.01). However, at the three-month and six-month follow-ups, a significant loss of flexion was observed compared to the intraoperative flexion achieved. Nevertheless, the patients regained flexion range at nine and twelve-month follow-ups, as shown in Fig. 2. At the last follow-up, the median range of motion had improved by 40°, and this improvement was not found to be statistically different compared to the intraoperative range of motion achieved (p=0.13), meaning that both measures were comparable. At discharge, 80% of the patients achieved a flexion of 90° or more. Yet, three patients required reintervention, which is discussed in Section “Intraoperative complications and reinterventions”.
Extension deficitAmong 7 patients with extension deficit, the median pre-operative extension was 10°, which significantly improved to 0° intraoperatively (Δ 10°, p<0.031). The range of extension showed no significant change at three, six, nine, and twelve months follow-up compared to intraoperative; see Fig. 3. At the final follow-up, the median range of extension was 0°, representing a final improvement of 10°. All patients demonstrated improvement in their extension deficit and did not require any reintervention.
Timing of AFA and MUA, and ROMThe association between the timing of the AFA and MUA, and the ROM is presented in Table 2.
Spearman correlation between time of AFA & MUA and ROM.
| Spearman correlation | |
|---|---|
| Flexion | |
| Preoperative | r=0.135 |
| Intraoperative | r=−0.199 |
| 3 month | r=−0.238 |
| 6 month | r=−0.329 |
| 9 month | r=−0.438 |
| 12 month | r=−0.255 |
| Extension | |
| Preoperative | r=−0.037 |
| Intraoperative | r=0.182 |
| 3 month | r=−0.004 |
| 6 month | r=0.016 |
| 9 month | r=0.261 |
| 12 month | r=0.376 |
r=Spearman correlation coefficient.
There were four intraoperative complications among three patients and three reinterventions, as shown in Table 1. The intraoperative complications included two proximal metaphyseal tibial fractures in one patient during two different surgeries, one avulsion fracture of the anterior tibial tuberosity, and one partial ACL tear that was less than 10%.
The patient who experienced the proximal tibia fractures was 36 years old with no comorbidities and initially suffered a Fraser IIC floating knee and patellar fracture. Six months after the definitive osteosynthesis, the patient underwent the first AFA and MUA procedure. During this procedure, an incomplete anterior metaphyseal fracture was detected by intraoperative fluoroscopy, leading to immediate fixation with a 4.5mm medial tibial plate. Despite the medical intervention, the patient could not improve postoperative ROM beyond 0–35° after five months. Therefore, a new AFA and MUA procedure was performed, resulting in an improvement in the patient's ROM to 0–95° intraoperatively. However, the patient suffered a new anterolateral proximal tibia fracture during the MUA, which was treated with a 3.5mm LCP proximal tibia plate. At the six-month follow-up, the patient presented with a ROM of 0–85°.
The patient who had a fracture in the distal femur and patella underwent a procedure 10 months after the index surgery. However, during the AFA & MUA procedure, the patient suffered from an anterior tibial tuberosity avulsion, which was treated immediately with 2 cannulated 4.5 screws. A knee immobilizer was placed during the next month to support the affected area. Before the procedure, the patient's range of motion was between 0° and 40°. But after the procedure, the final range of motion decreased to 0–20°. The patient had comorbidities such as pancreatic cancer 10 years prior to the accident and alcoholism, which was associated with caloric malnutrition at the time of AFA and MUA. Due to the patient's comorbidities, it was decided not to reoperate.
Finally, a 23-year-old female with no underlying medical conditions, sustained a partial ACL tear of less than 10%. She did not exhibit any instability and, as a result, reconstruction was deemed unnecessary. This patient achieved 140° flexion at the final follow-up.
Regarding reinterventions, three patients required a second procedure of AFA and MUA. One patient who had a proximal tibia fracture during the surgery was discussed earlier in this section. He resulted in a final range of motion (ROM) of 0–85°. However, the other two patients who underwent reintervention lost their intraoperative improvement at 3 months follow-up, and were scheduled for a second AFA and MUA. Their ROM at the final follow-up was 0–100° and 0–110°, respectively.
DiscussionSeveral techniques have been described for the treatment of knee stiffness, alongside AFA & MUA, including isolated MUA and quadricepsplasty. Sassoon et al. evaluated MUA in a case series of 22 patients, reporting an average recovery of 64° of range of motion (ROM) at mobilization and an average final improvement of 51° of ROM at a 7-month follow-up with no complications,19 which is consistent with our results. However, other investigators have reported less favorable outcomes with MUA alone, with 9 complications out of 48 procedures.20 On top of that, to perform a MUA without directly assess the intraarticular space can be a risky procedure,5,21 and therefore it is usually not done alone.
Regarding the treatment with AFA and MUA, Gittings et al. described the intraoperative and postoperative ROM changes in post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis patients treated with AFA & MUA. Their case series of 14 patients revealed an improvement in flexion ROM from 72° preoperatively to 127° intraoperatively, resulting in a mean improvement of 55° (76%) of flexion ROM. However, they presented a significant flexion loss at the mean final follow-up of 4.5 months with a mean of 104°.4 Similarly, Kim and Joo found that the post-traumatic knee stiffness subgroup treated with AFA & MUA improved their preoperative ROM from 69.3° to 117.4° (59%) at the final follow-up.16
Our findings are similar to those described in previous studies.4,16 Both groups – those with flexion and extension deficits - showed initial improvement, achieving significantly higher ROM compared to the pre-operative status, which was maintained at one-year follow-up. Furthermore, 80% and 100% of patients achieved better flexion or extension ROM, respectively. This result may be associated with better functionality and higher patient satisfaction parameters, although this outcome was not directly assessed in our study.
Interestingly, patients with extra-articular injuries such as diaphyseal femur or tibia fractures regain ROM with AFA considering that it is an intra-articular procedure. It has to be notice, that tibial and femoral shaft fractures were all treated with anterograde and retrograde nails, respectively. Previous studies have shown that knee stiffness can be a complication when a retrograde femoral nail is used, as a consequence of the intraarticular procedure.22 In addition, it has been previously stated that just as pure intra-articular stiffness can be complicated over time by quadriceps contracture; pure extra-articular stiffness might be complicated as well by intra-articular adhesions and capsule and ligament contractures,18 hence an intra-articular treatment could improve their ROM deficit; as observed in this investigation.
Physical therapy is critical in preventing disease recurrence. AFA & MUA should not be recommended in the absence of a rigorous post-operative rehabilitation program.23 Although we cannot establish the impact of post-operative support, we believe that the results we obtained would not persist without intensive physical therapy. We used CPMD as part of the post-operative protocol for 3 days to ensure early mobilization (1–9 days).
Complications related to AFA and MUA are common and include hemarthrosis due to proximity to geniculate vessels,24 residual stiffness, infections, embolism, iatrogenic fractures, loss of fracture fixation, and chondral injuries.3 In our series, 3 patients experienced intraoperative complications: one patient suffered 2 proximal tibia fractures in separate procedures, another presented a tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture, and another had an ACL iatrogenic partial injury (less than 10% of the total ACL diameter).
One of the significant concerns while performing AFA and MUA is the possibility of a new fracture or a refracture. To prevent this, we confirm bone healing with computed tomography before the procedure. In theory, a time window of at least 3 months allows for substantial fracture healing before MUA, thereby decreasing the risk of fixation compromise.19
It has been suggested that the results of AFA and MUA may not be as satisfactory if it is delayed after the initial procedure. Early intervention could prevent muscle contracture and further formation and maturation of extracellular matrix. Therefore, the recommendation is to perform AFA and MUA between 3 and 6 months after the index procedure. However, there is some controversy as some studies have shown that AFA & MUA could be delayed even up to 7 months without affecting the results. In our study, we found that the relationship between the timing of AFA and MUA and range of motion at the final follow-up was acceptable, but it was not consistent throughout the follow-up period. While it seems plausible that time could negatively impact the results of AFA and MUA, we do not have enough data to support this statement.
The strength of this study lies in the substantial number of patients included, which makes it one of the largest patient series with post-traumatic arthrofibrosis. We were able to obtain this large patient number because they were referred to our trauma center, which primarily treats injuries resulting from trauma across the country.
However, this study has several limitations that require attention. Considering its descriptive nature and the lack of a control group, all conclusions drawn are based solely on the intervention itself and not on alternative management options. Therefore, comparative studies must be conducted to determine whether this is the best treatment option for this population. Finally, the subgroup with extension deficit was small in size, and conclusions regarding the procedure's effectiveness in this subgroup may be biased.
ConclusionOur study suggests that arthroscopic fibroarthrolysis and manipulation under anesthesia can help patients with post-traumatic knee arthrofibrosis recover range of motion in most cases. However, it is important to note that this procedure is not without risks and complications, so careful consideration and attention should be paid to the prescription and surgical process.
Level of evidenceLevel of evidence iii.
Ethical considerations- 1.
Has your work involved animal testing?:
No
- 2.
Do patients or human subjects intervene in your work?:
Yes
- 3.
If the answer is yes, please confirm that the authors have the informed consent of the patients.:
Yes
- 4.
Does your work include a clinical trial?:
No
- 5.
Are all the data shown in the figures and tables included in the manuscript included in the results and conclusions section?:
Yes
We declare that the authors of this work have no conflicts of interest to declare.
This research has not received specific aid from public sector agencies, commercial sectors or non-profit entities.