En nuestro estudio el objetivo fue investigar la contribución de los hallazgos de la tomografía por emisión de positrones (PET)/tomografía computarizada (TC) en la diferenciación no invasiva entre el derrame pleural (DP) de origen benigno (DPB) y maligno (DPM) en pacientes diagnosticadas de un carcinoma de ovario (CO).
Material y métodoSe incluyeron en el estudio a 32 pacientes diagnosticadas de CO con DP. Se efectuó análisis comparativo entre el DPB y el DPM para los siguientes parámetros: SUVmáx. del DP, índice objeto/fondo (TBRp: target/background ratio) del DP, dividiendo el SUVmáx. del DP por el SUVmedio del flujo sanguíneo mediastínico (MBP: medistinal blood pool), engrosamiento pleural, adenopatías supradiafragmáticas, DP unilateral o bilateral, diámetro del DP, edad de la paciente y niveles de CA125.
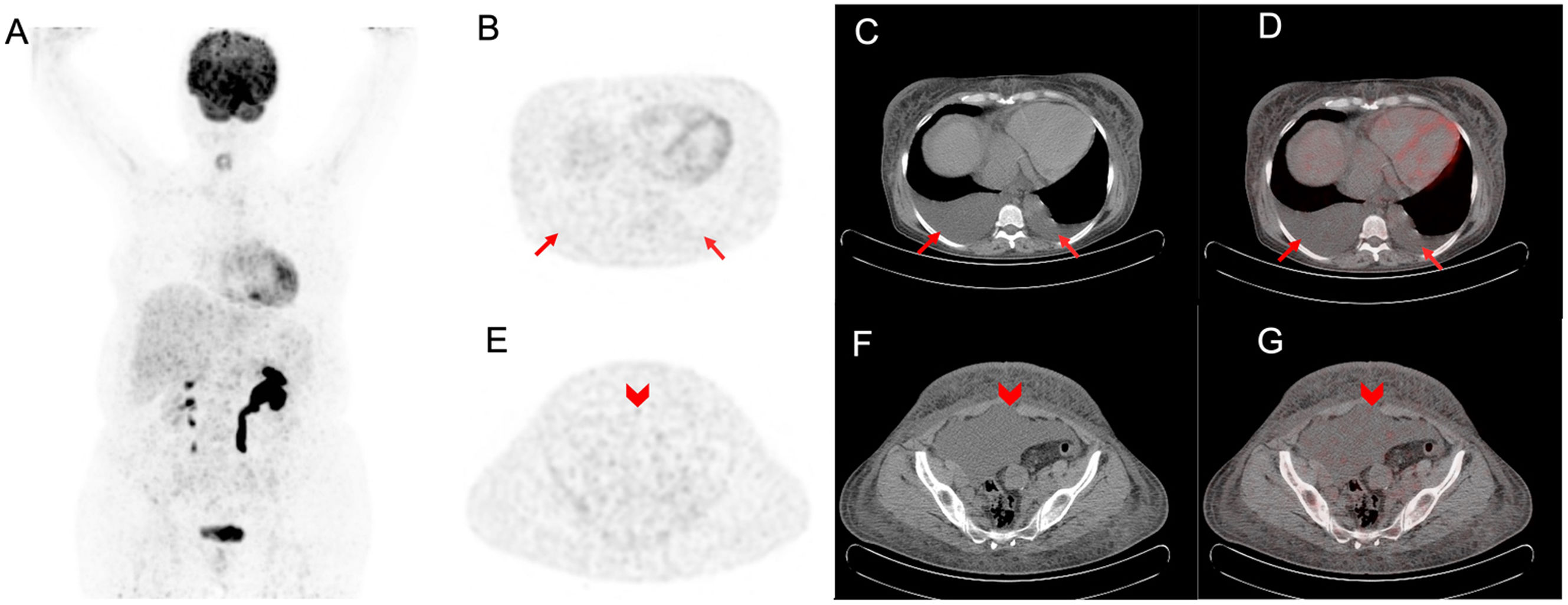
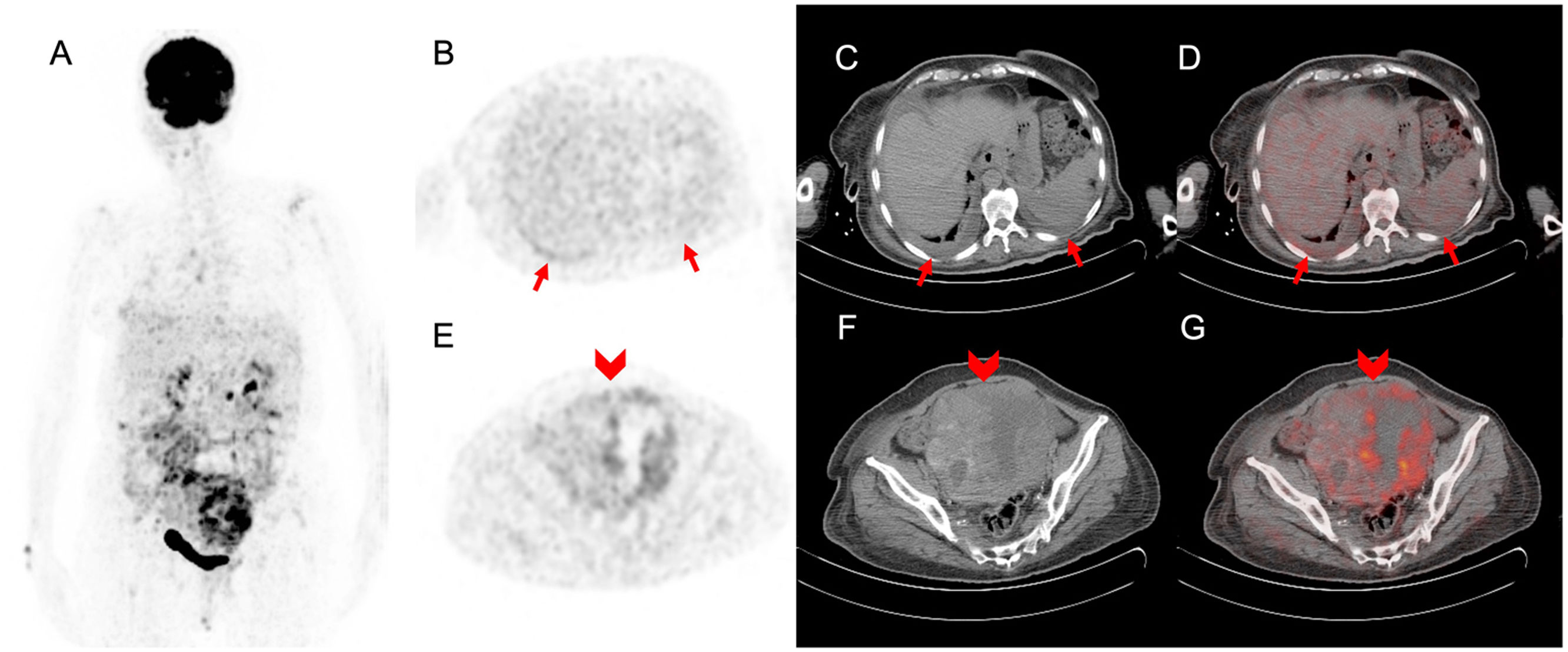
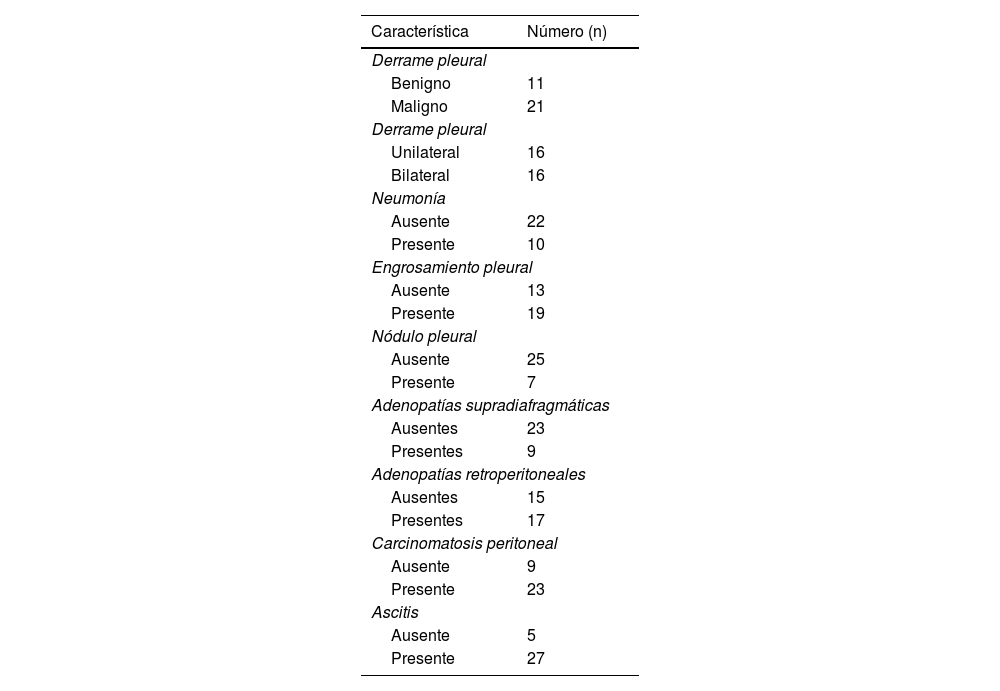
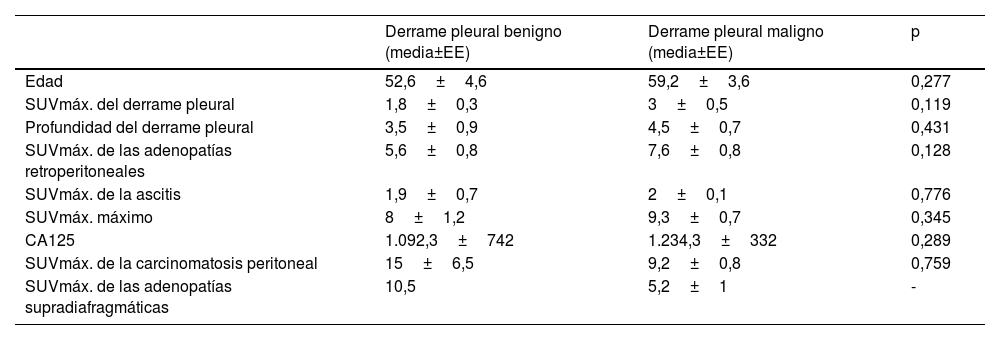
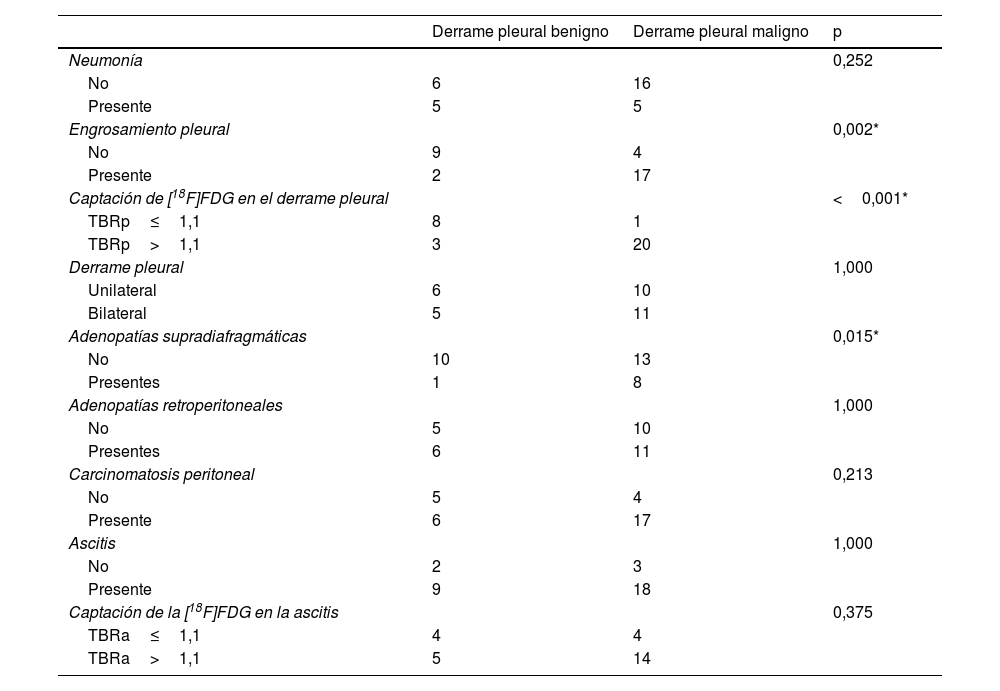
ResultadosLa edad media de las 32 pacientes fue de 57±2,8 años. Se observó mayor frecuencia significativa de un TBRp>1,1, engrosamiento pleural y ganglios linfáticos supradiafragmáticos en el DPM respecto al DPB. Aunque no se detectó ningún nódulo pleural en las pacientes con DPB, estos estuvieron presentes en 7 pacientes con DPM. En la distinción DMP-DBP la sensibilidad del TBRp fue del 95,2% y la especificidad del 72,7%, la sensibilidad del engrosamiento pleural fue del 80,9%, y la especificidad del 81,8%, la sensibilidad de los ganglios linfáticos supradiafragmáticos fue del 38% y la especificidad del 90,9%, y la sensibilidad del nódulo pleural fue del 33,3% y la especificidad del 100%. No hubo diferencias significativas entre los 2 grupos respecto al resto de factores.
ConclusiónEl engrosamiento pleural y el valor de TBRp determinados en la PET/TC pueden contribuir a la diferenciación entre DMP y DBP, especialmente en aquellas pacientes con CO en estadio avanzado y mal estado general, o que no son tributarias de ser sometidas a tratamiento quirúrgico.
The present study investigates the ability of non-invasive contribution of positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) to distinguish between benign pleural effusions (BPE) and malignant pleural effusions (MPE) in patients diagnosed with ovarian carcinoma (OC).
Material and methodIncluded in the study were 32 OC patients with a PE diagnosis. The cases with BPE and MPE were compared in terms of the PE maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), PE SUVmax/mean standardized uptake (SUVmean) value of the mediastinal blood pool (TBRp), the presence of pleural thickening, the presence of supradiaphragmatic lymph node, unilateral or bilateral PE, pleural effusion diameter, patient age and CA125 value.
ResultsThe mean age of the 32 patients was 57±2.8 years. TBRp>1.1, pleural thickening and supradiaphragmatic lymph node were observed significantly more frequently in the MPE than the BPE cases. While no pleural nodules were detected in patients with BPE, they were present in 7 of the patients with MPE. The rates of distinction between the MPE and BPE cases were as follows: the sensitivity of the TBRp value was 95.2% and specificity was 72.7%; the sensitivity of pleural thickness was 80.9% and specificity was 81.8%; the sensitivity of supradiaphragmatic lymph node was 38% and specificity was 90.9%; and the sensitivity of the pleural nodule was 33.3% and specificity was 100%. There were no significant differences between two groups in any other factors.
ConclusionPleural thickening and TBRp values ascertained through PET/CT may aid the distinction between MPE-BPE, especially in patients with advanced stage OC with a poor general condition, or those who cannot undergo surgery.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora