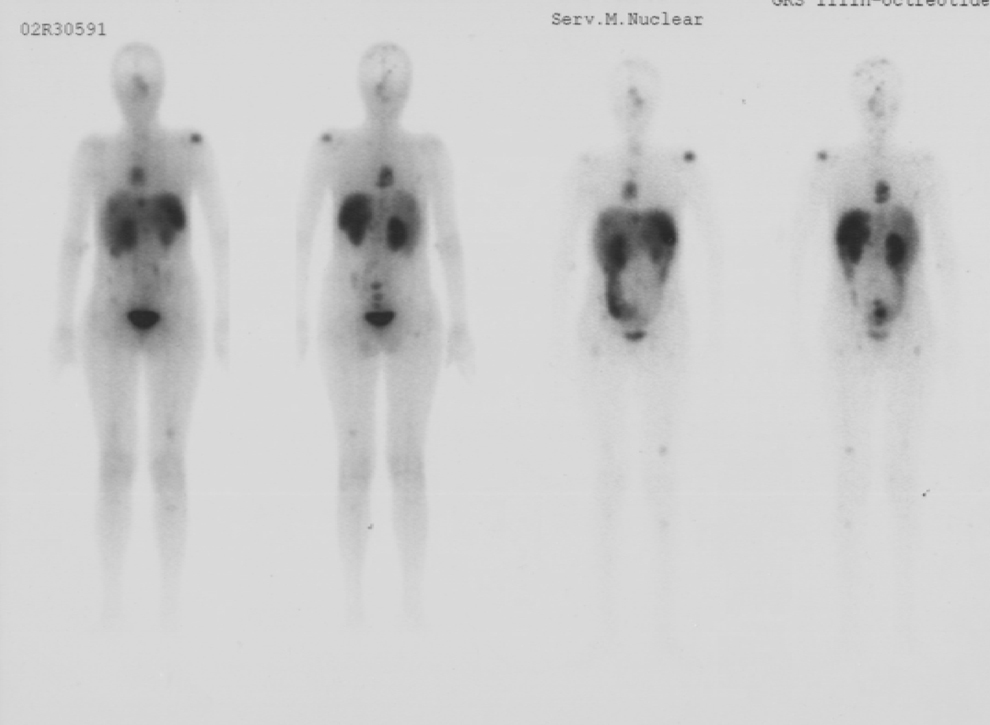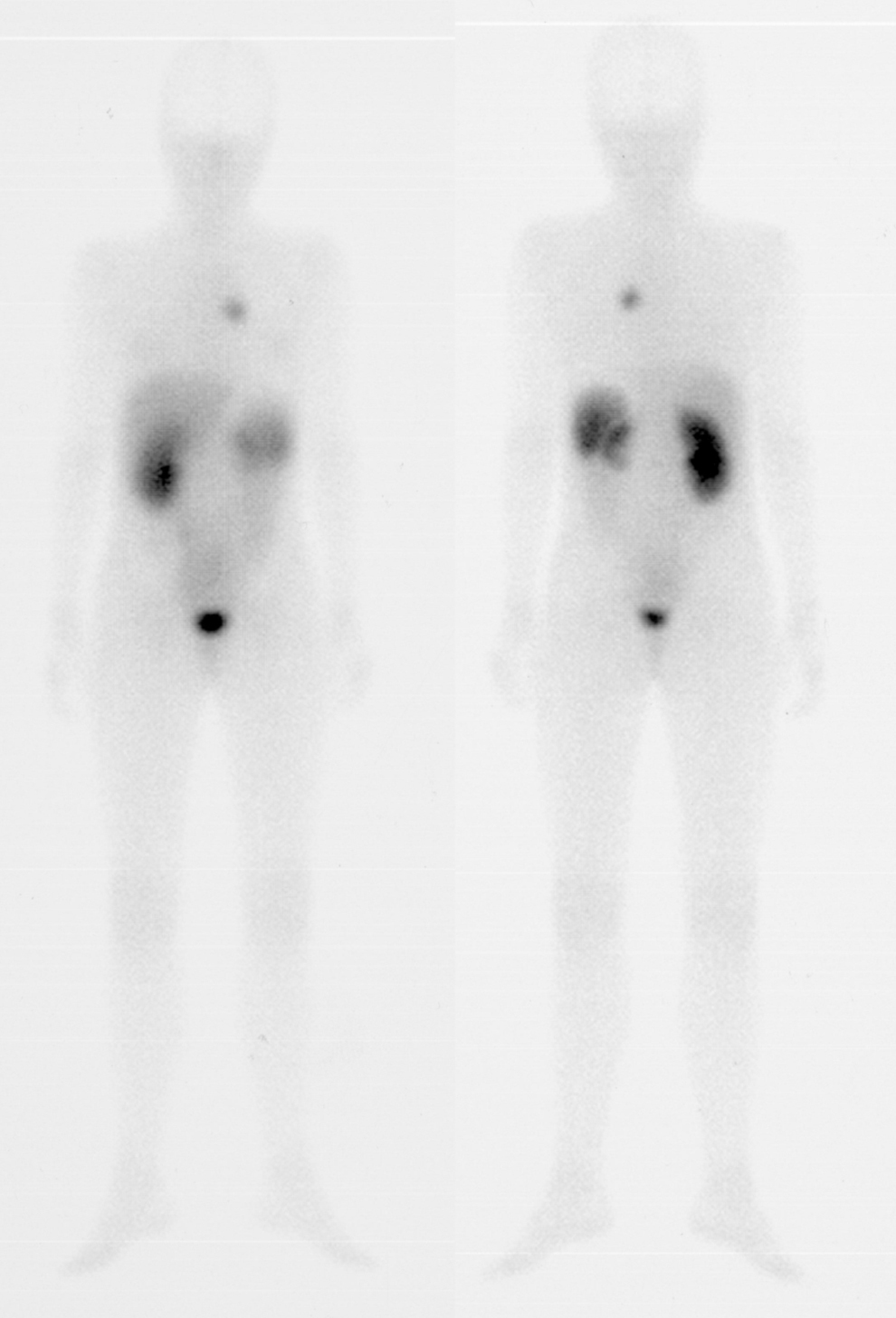El tumor carcinoide es una rara neoplasia de origen neuroendocrino con localizaciones diversas, siendo las más frecuentes en la edad pediátrica el apéndice y el pulmón. La gammagrafía con 111In-DTPA-d-Phe1-octreótido ha supuesto un considerable avance en el diagnóstico de extensión de pacientes con tumor carcinoide. Presentamos tres pacientes pediátricos con carcinoide bronquial (CB) explorados con gammagrafía con análogos de la somatostatina (GRSS).
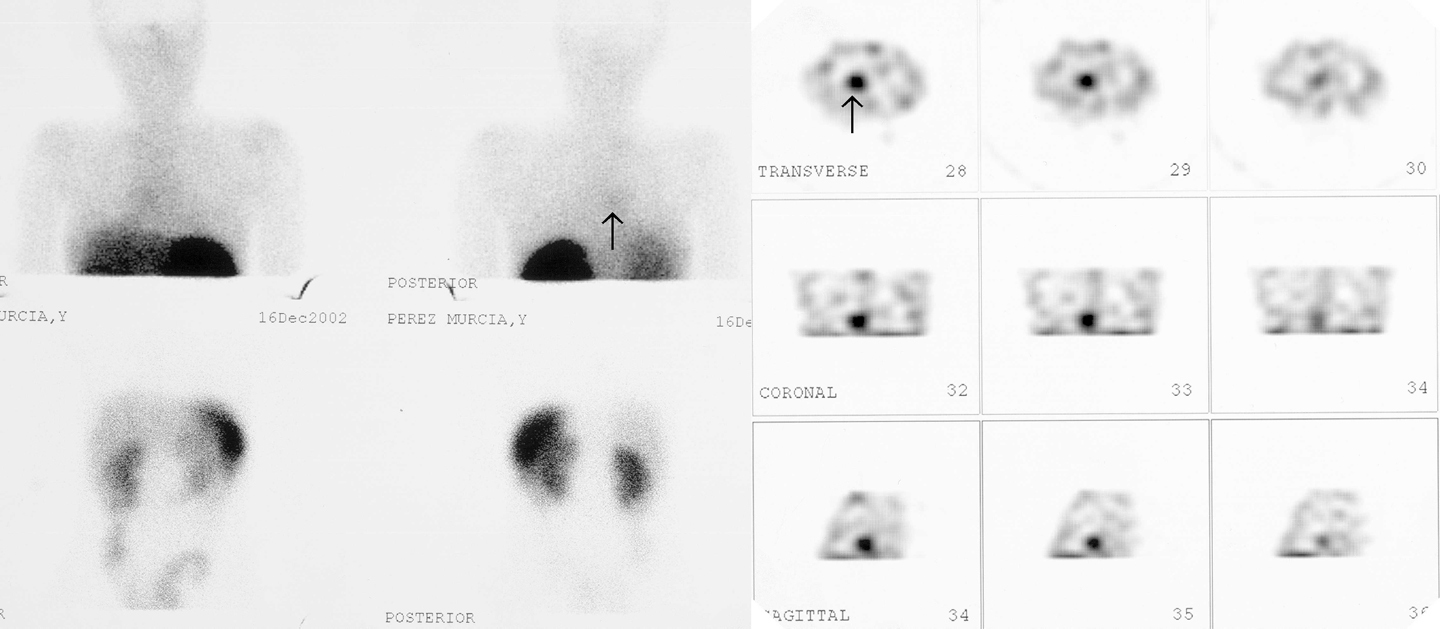
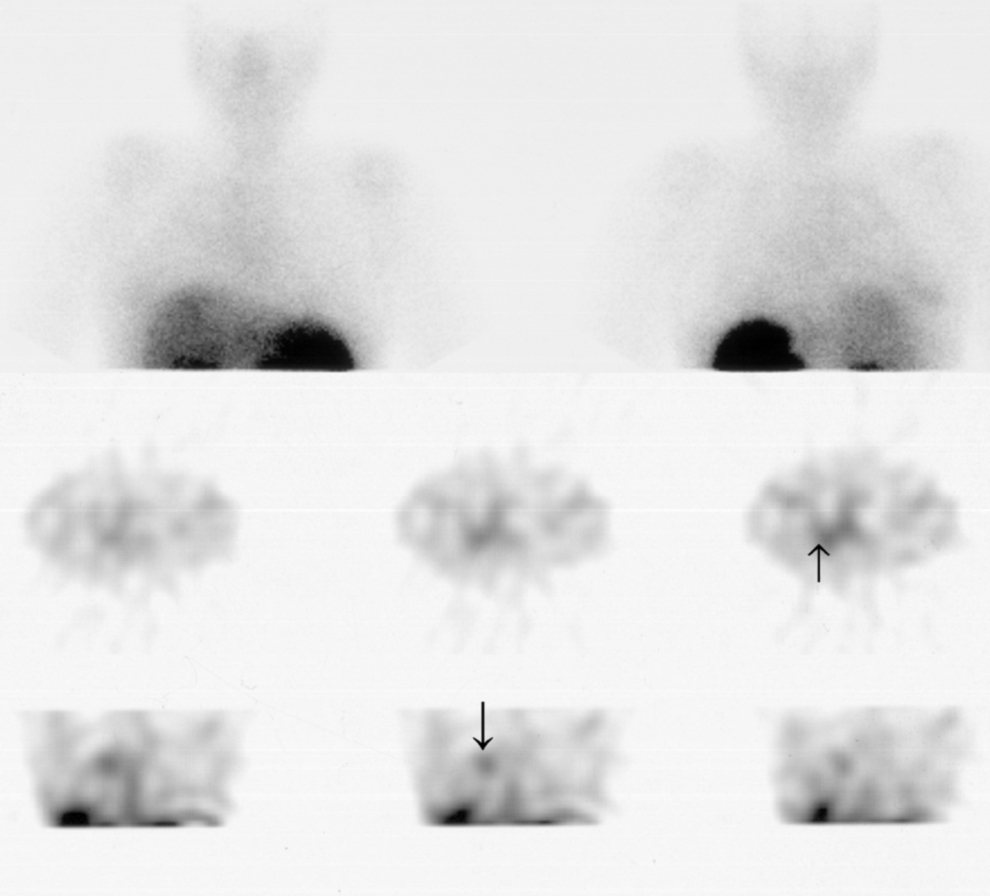
Casos clínicosLa primera paciente (9 años) fue estudiada mediante GRSS tras cirugía por tumoración carcinoide en el lóbulo inferior derecho (LID), que objetivó resto tumoral (más evidente en el estudio tomográfico). Nuevos estudios de control con GRSS demostraron el aumento de tamaño del resto tumoral, la existencia de metástasis óseas, hepáticas y otro foco pulmonar de forma más precoz que las otras técnicas de imagen realizadas.
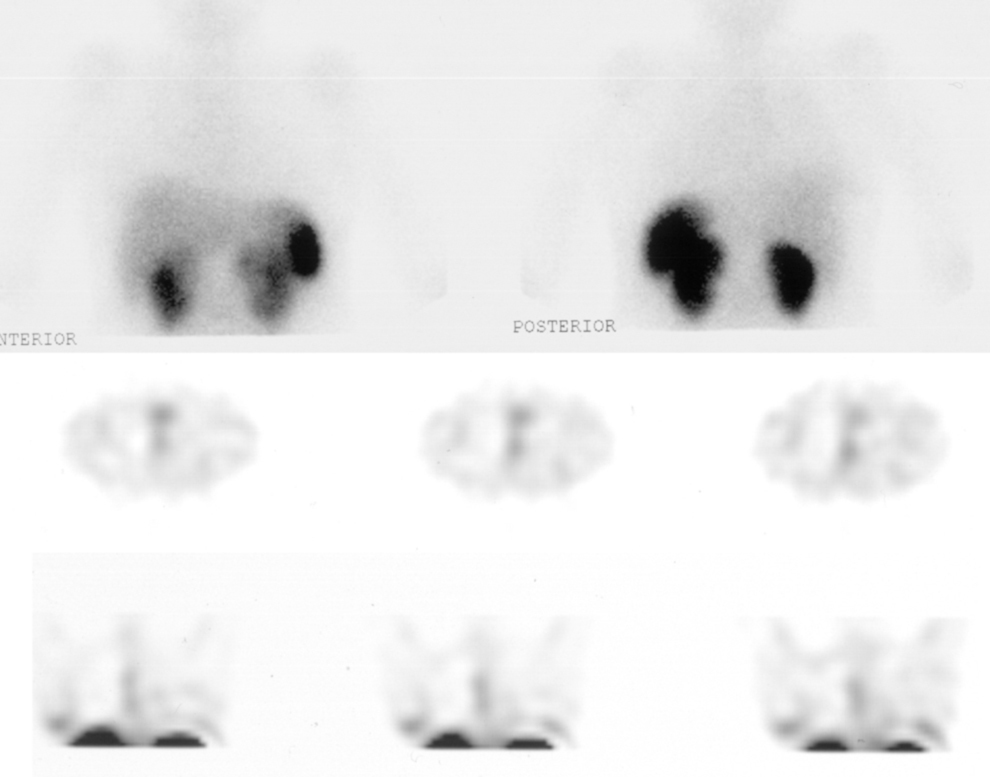
La segunda paciente (10 años) acudió por tumoración endobronquial en el lóbulo inferior izquierdo (LII) junto con atelectasia del lóbulo superior izquierdo y enfisema del LII. Las técnicas de imagen radiológicas planteaban el diagnóstico diferencial entre tumor carcinoide endobronquial o granulomas de células plasmáticas o a cuerpo extraño. La GRSS mostró un depósito anormal de actividad en el hemitórax izquierdo compatible con tumoración carcinoide. No se visualizaron otras áreas sugestivas de metástasis. Tras la cirugía (resección endobronquial), los nuevos controles con GRSS mostraron ausencia de enfermedad.
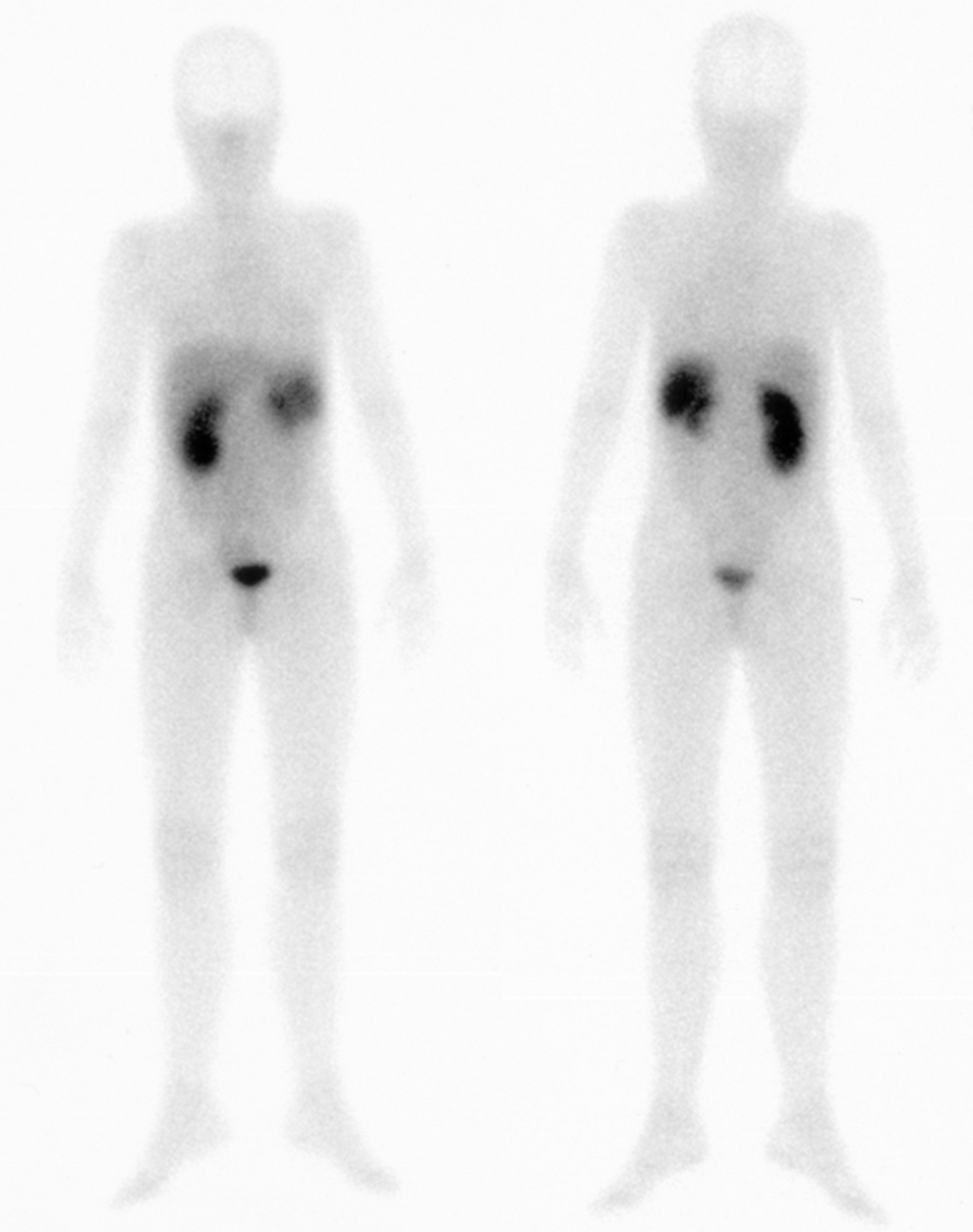
El tercer paciente (12 años) acudió tras lobectomía (lóbulo superior derecho) por CB. La GRSS no mostró áreas anormales de actividad. En un control posterior (3 meses) se visualizó un depósito de actividad en el tercio medio del hemitórax derecho, tras lo que se realizó lobectomía (LID y lóbulo medio), que objetivó pequeños restos de carcinoide neuroendocrino. Los controles posteriores fueron negativos.
ConclusiónLa GRSS ha demostrado gran utilidad en el diagnóstico, el seguimiento y la estadificación de los pacientes pediátricos portadores de tumoraciones carcinoides neuroendocrinas.
Carcinoid tumor is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm with different locations, the most frequent ones during the pediatric age being the appendix and lung. Scintigraphy with 111In-DTPA-d-Phe1-octreotide has led to an importance advance in the diagnosis of extension in carcinoid tumor patients. We present three pediatric patients with bronchial carcinoid studied with somatostatin analogue scintigraphy (SSRS).
Clinical casesThe first patient (9 years) was studied using the SSRS after surgery due to carcinoid tumor in the right lower lobe in which tumor remains was observed (this being clearer in the tomography study).
The second patient (10 years) presented due to endobronchial tumor in the left lower lobe together with atelectasis of the LUL and emphysema of the LLL. Radiology imaging techniques suggested the differential diagnosis between the endobronchial carcinoid tumor or plasma cells or foreign body gramuloma. The SSRS showed an abnormal deposit of activity in the left hemithorax consisted with carcinoid tumor. No other areas suggesting metastasis were observed. After the surgery (endobronchial resection), new controls with SSRS showed absence of disease.
The third patient (12 years) came after a lobectomy (RUL) due to bronchial carcinoid. The SSRS did not show any abnormal areas of activity. In the subsequent control (3 months), a deposit of activity was observed in the middle third of the right hemithorax, after which a lobectomy was performed (RLL and ML) that showed small remains of neuroendocrine carcinoid. Subsequent controls were negative.
ConclusionThe SSRS has demonstrated great utility in the diagnosis, follow-up and staging of pediatric patients, carriers of neuroendocrine carcinoid tumors.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora