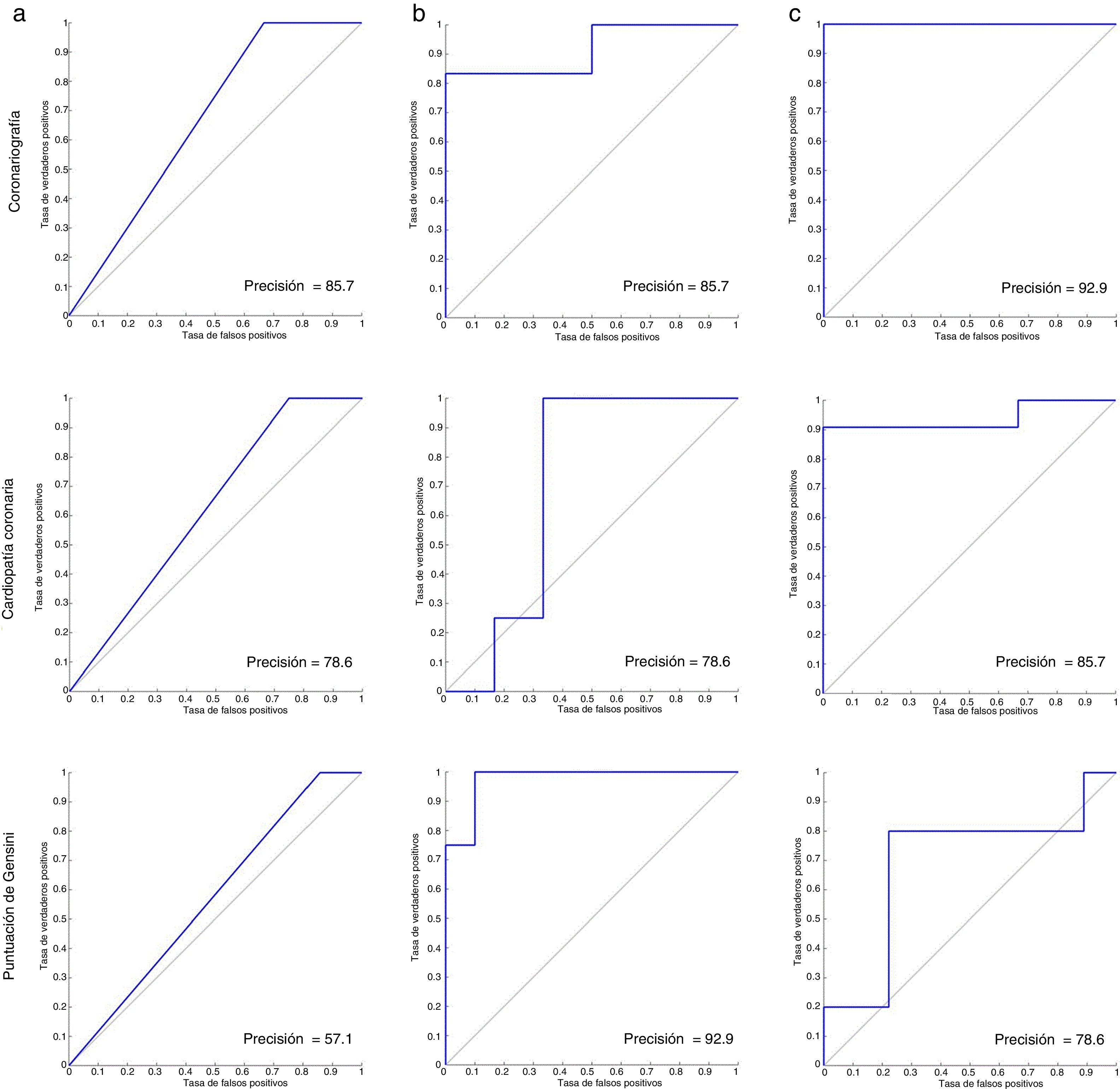
La precisión diagnóstica de la imagen de perfusión miocárdica (IPM) no es óptima para predecir el resultado de la angiografía. El objetivo del presente estudio es investigar la aplicación de la red neuronal artificial (RNA) para integrar los datos clínicos con el resultado y la cuantificación de la IPM.
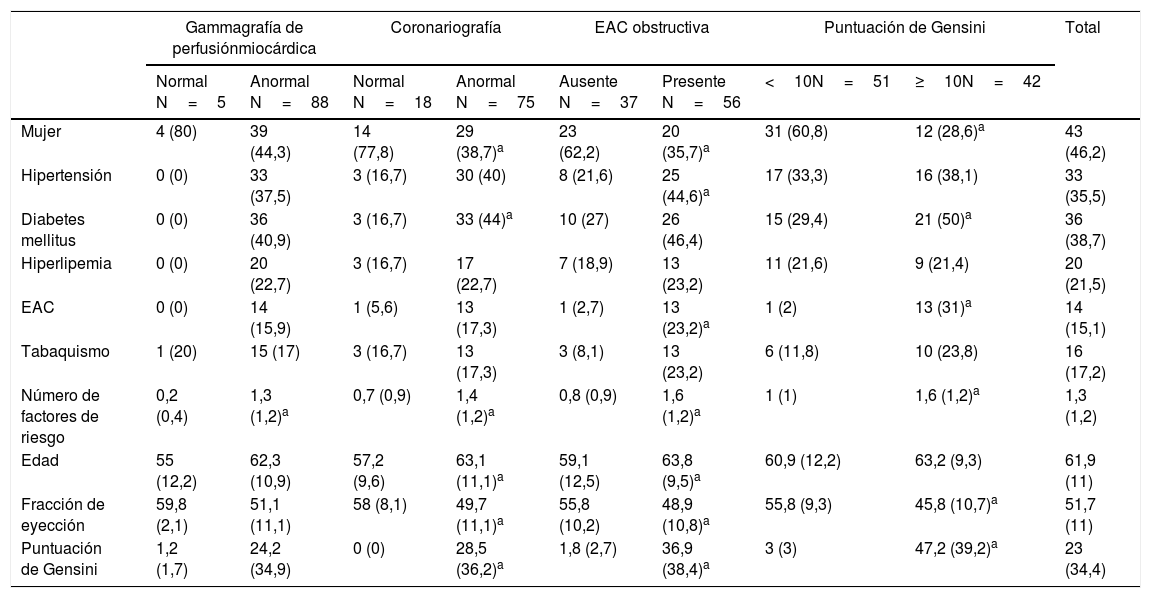
MétodosDe 923 pacientes con IPM, se reclutaron 93 que se sometieron a angiografía. Se recogieron los datos clínicos, incluidos los factores de riesgo cardíaco, y se registraron los resultados de la IPM y la angiografía coronaria. Se calculó la cuantificación de las gráficas polares IPM (es decir, los recuentos de 20 segmentos de cada una de las gráficas polares de esfuerzo y de reposo) y la puntuación de Gensini de las angiografías. La RNA fue diseñada integrando datos clínicos y de cuantificación para predecir el resultado de la angiografía (normal vs. anormal), la enfermedad coronaria no obstructiva u obstructiva (EAC) y la puntuación de Gensini (≥10 y <10). Las RNA fueron diseñadas para predecir los resultados de la angiografía usando diferentes combinaciones de datos como sigue: informes de IPM, la cuantificación de 40 segmentos de diagramas polares de esfuerzo y reposo, y la cuantificación de estos 40 segmentos además de la edad, el sexo y el número de factores de riesgo. Se comparó el rendimiento diagnóstico de la IPM con diferentes RNA.
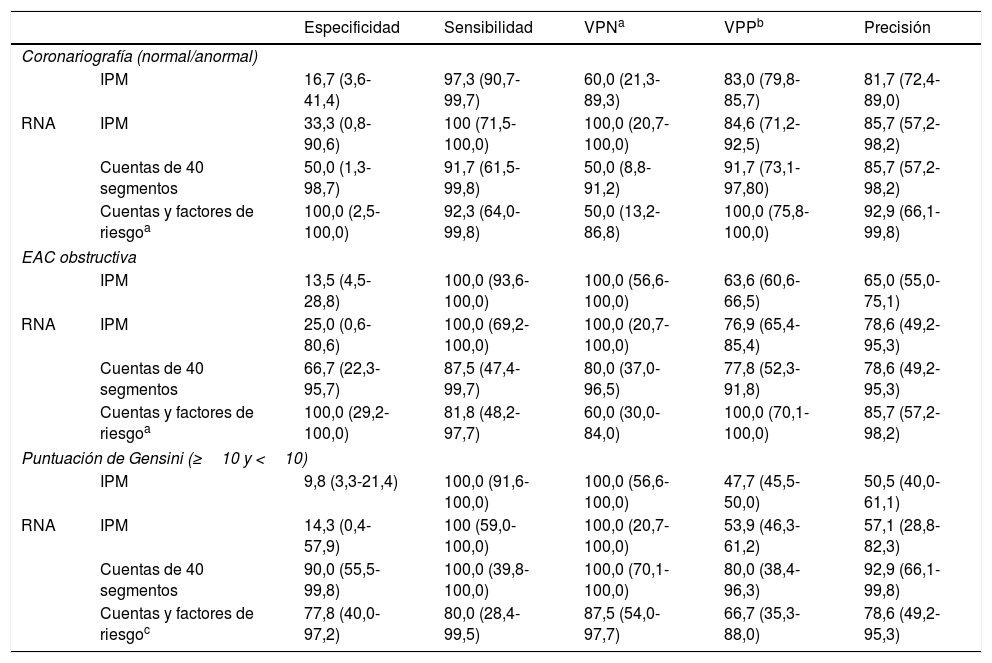
ResultadosLa precisión de la IPM para predecir el resultado de la angiografía, la EAC obstructiva y la puntuación de Gensini aumentó del 81,7 al 92,9%, del 65,0 al 85,7% y del 50,5 al 92,9%, respectivamente, mediante la RNA con cuantificación y factores de riesgo clínicos.
ConclusiónLa precisión diagnóstica de la IPM podría mejorarse mediante la RNA, utilizando datos clínicos y de cuantificación.
Diagnostic accuracy of myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is not optimal to predict the result of angiography. The current study aimed at investigating the application of artificial neural network (ANN) to integrate the clinical data with the result and quantification of MPI.
MethodsOut of 923 patients with MPI, 93 who underwent angiography were recruited. The clinical data including the cardiac risk factors were collected and the results of MPI and coronary angiography were recorded. The quantification of MPI polar plots (i.e. the counts of 20 segments of each stress and rest polar plots) and the Gensini score of angiographies were calculated. Feed-forward ANN was designed integrating clinical and quantification data to predict the result of angiography (normal vs. abnormal), non-obstructive or obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), and Gensini score (≥10 and <10). The ANNs were designed to predict the results of angiography using different combinations of data as follows: reports of MPI, the counts of 40 segments of stress and rest polar plots, and the count of these 40 segments in addition to age, gender, and the number of risk factors. The diagnostic performance of MPI with different ANNs was compared.
ResultsThe accuracy of MPI to predict the result of angiography, obstructive CAD, and Gensini score increased from 81.7% to 92.9%, 65.0% to 85.7%, and 50.5% to 92.9%, respectively by ANN using counts and clinical risk factors.
ConclusionThe diagnostic accuracy of MPI could be improved by ANN, using clinical and quantification data.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora