Definitive staging for cervical (CC) and endometrial cancer (EC) takes place once surgery is performed. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of PET/CT in detecting lymphatic metastasis in patients with CC and EC using dual-time-point imaging (DPI), taking the histopathological results of sentinel lymph node (SLN) and lymphadenectomy as the reference.
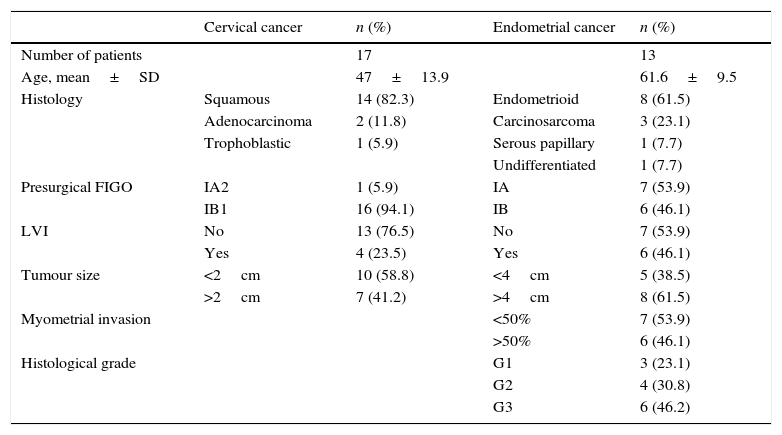
Material and methodsA prospective study was conducted on 17 patients with early CC, and 13 patients with high-risk EC. The patients had a pre-operative PET/CT, MRI, SLN detection, and lymphadenectomy, when indicated. PET/CT findings were compared with histopathological results.
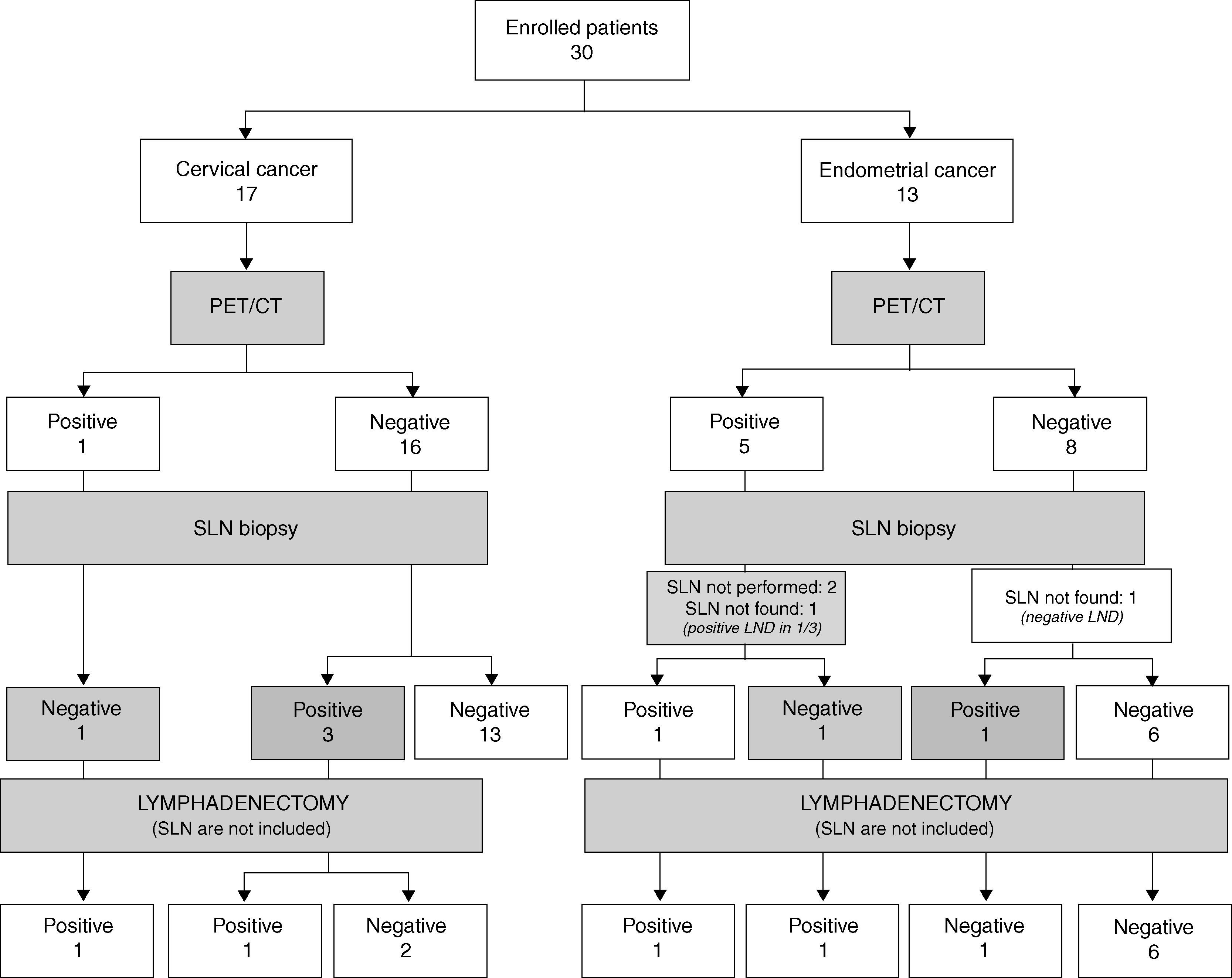
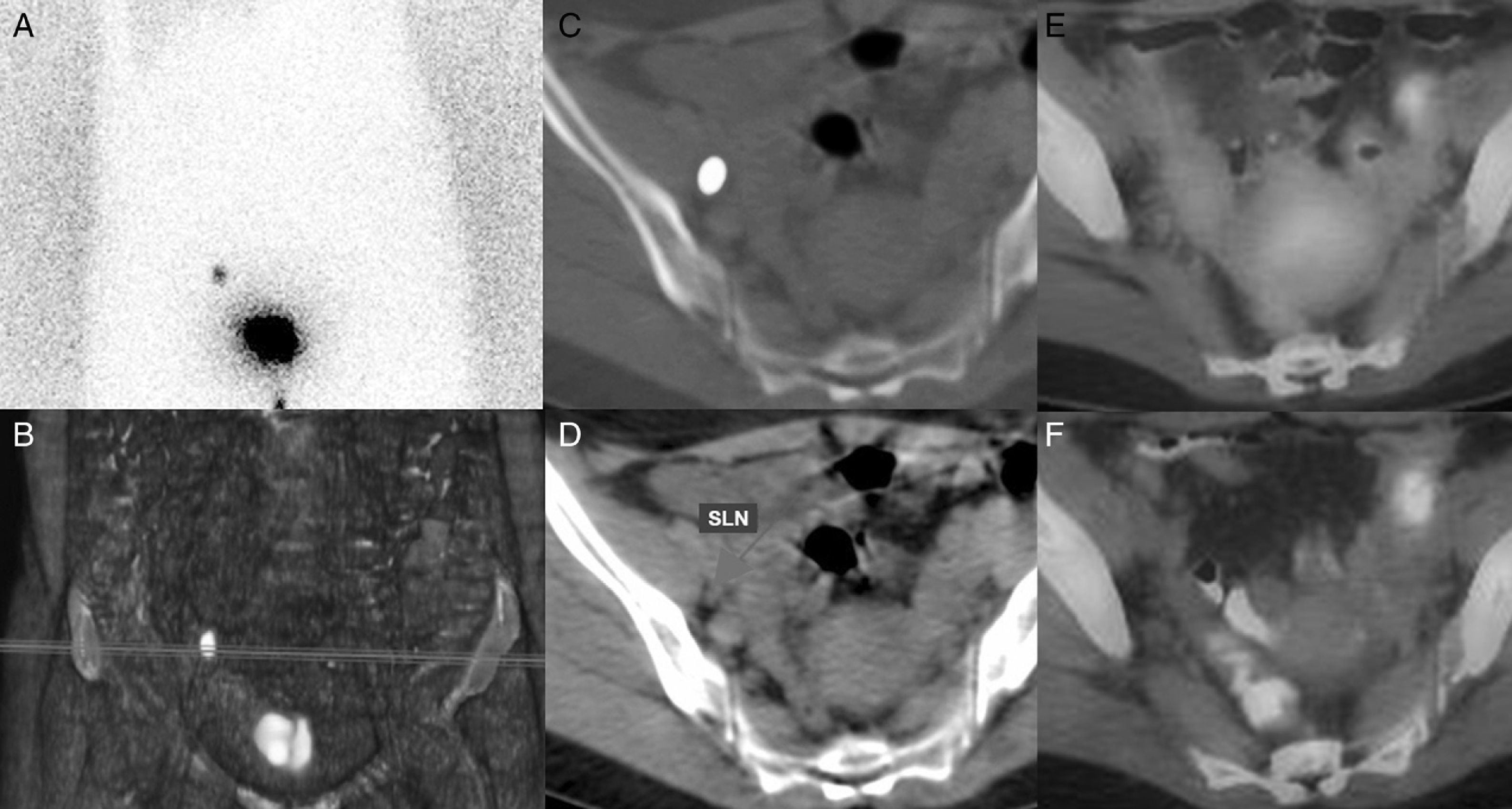
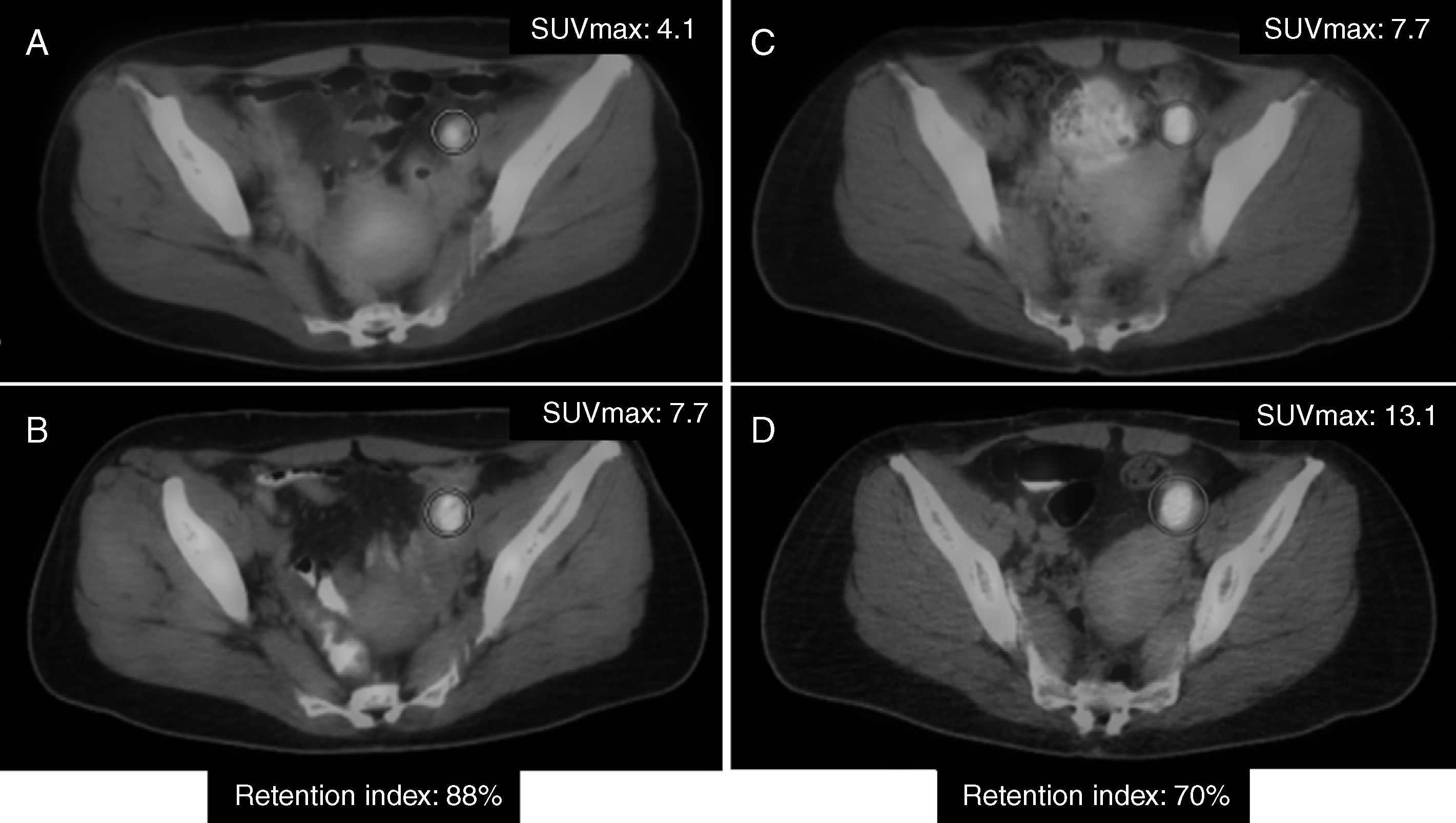
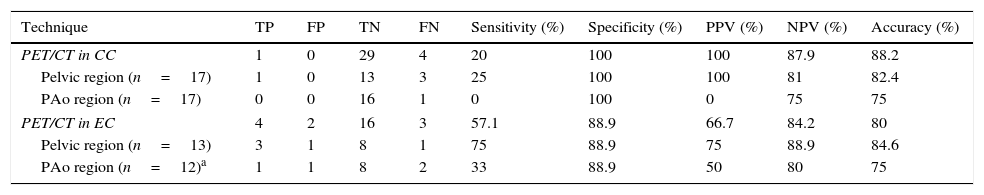
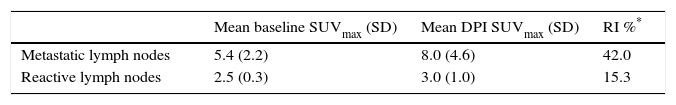
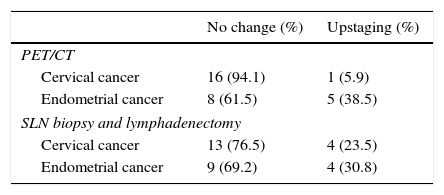
ResultsIn the pathology study, 4 patients with CC and 4 patients with EC had lymphatic metastasis. PET/CT showed hypermetabolic nodes in 1 patient with CC, and 5 with EC. Four of these had metastasis, one detected in the SLN biopsy. Four patients who had negative PET/CT had micrometastasis in the SLN biopsy, 1 patient with additional lymph nodes involvement. The overall patient-based sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy of PET/CT to detect lymphatic metastasis was 20.0%, 100.0%, 100.0%, 87.9%, and 88.2%, respectively, in CC, and 57.1%, 88.9%, 66.7%, 84.2% and 80.0%, respectively, in EC. DPI showed higher retention index in malignant than in inflammatory nodes, although no statistically significant differences were found.
ConclusionsPET/CT has low sensitivity in lymph node staging of CC and EC, owing to the lack of detection of micrometastasis. Thus, PET/CT cannot replace SLN biopsy. Although no statistically significant differences were found, DPI may help to differentiate between inflammatory and malignant nodes.
La estadificación definitiva del cáncer de cérvix (CC) y de endometrio (CE) tiene lugar tras la cirugía. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la utilidad de la PET/TC para la detección de metástasis ganglionares en el CC y en el CE con imagen dual-time-point (DPI), considerando como gold standard la histopatología del ganglio centinela (GC) y la linfadenectomía.
Material y métodosDiecisiete pacientes con CC inicial y 13 con CE de alto riesgo fueron incluidas prospectivamente. Preoperatoriamente se realizó una PET/TC, RM, detección del GC y linfadenectomía en los casos indicados. Se comparó la PET/TC con la histopatología.
ResultadosEn el estudio anatomopatológico, 4 pacientes con CC y 4 con CE tuvieron metástasis ganglionares. La PET/TC mostró ganglios hipermetabólicos en una paciente con CC y en 5 con CE. Cuatro de ellas tenían metástasis, una detectada en el GC. Cuatro pacientes con PET/TC negativa presentaron micrometástasis en el GC, una paciente con ganglios adicionales infiltrados. La sensibilidad, especificidad, valor predictivo positivo y negativo y la exactitud diagnóstica de la PET/TC para detectar metástasis ganglionares fueron 20,0; 100,0; 100,0; 87,9 y 88,2% para el CC, y 57,1; 88,9; 66,7; 84,2 y 80,0% para el CE. La DPI mostró un índice de retención superior en ganglios infiltrados respecto a los inflamatorios, sin hallar diferencias estadísticamente significativas.
ConclusionesLa PET/TC tiene baja sensibilidad para estadificar el CC y CE por la incapacidad de detectar micrometástasis y, por tanto, no sustituye la detección del GC. Aunque no hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas, la DPI podría ayudar a diferenciar ganglios inflamatorios de tumorales.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora