To compare sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp) and predictive value of Deauville score (DS) vs ΔSUVmax in iPET and ePET, in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), and follicular lymphoma (FL).
MethodRetrospective longitudinal multicentre study including 138 patients (46 DLBCL, 46 HL, 46 FL), on whom three 18F-FDG PET/CT were performed: baseline (bPET), mid-treatment or interim (iPET), and end-treatment (ePET). Visual (DS) and semi-quantitative (ΔSUVmax) parameters were determined for iPET and ePET. Predictive value was determined in relation to disease-free interval (DFI).
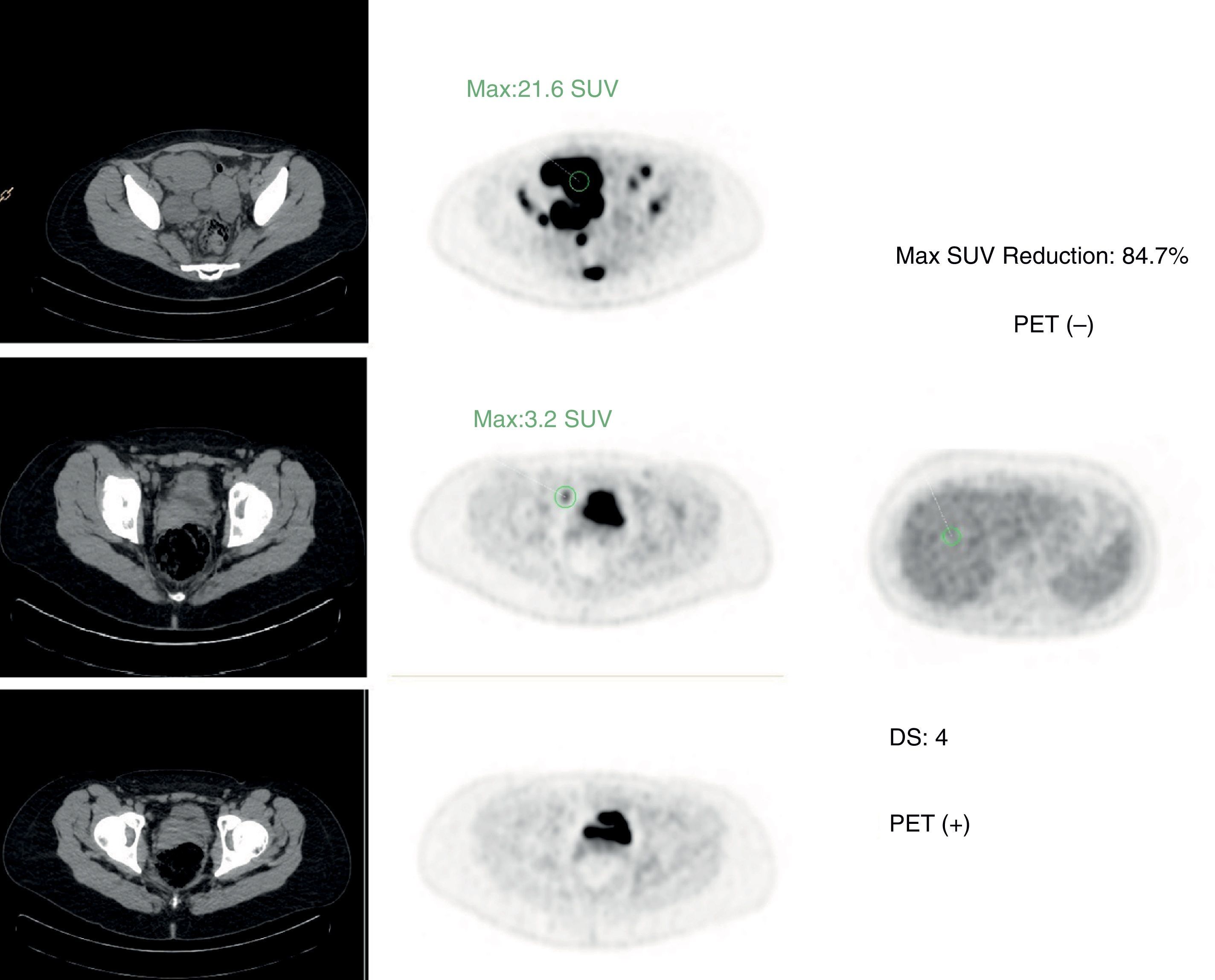
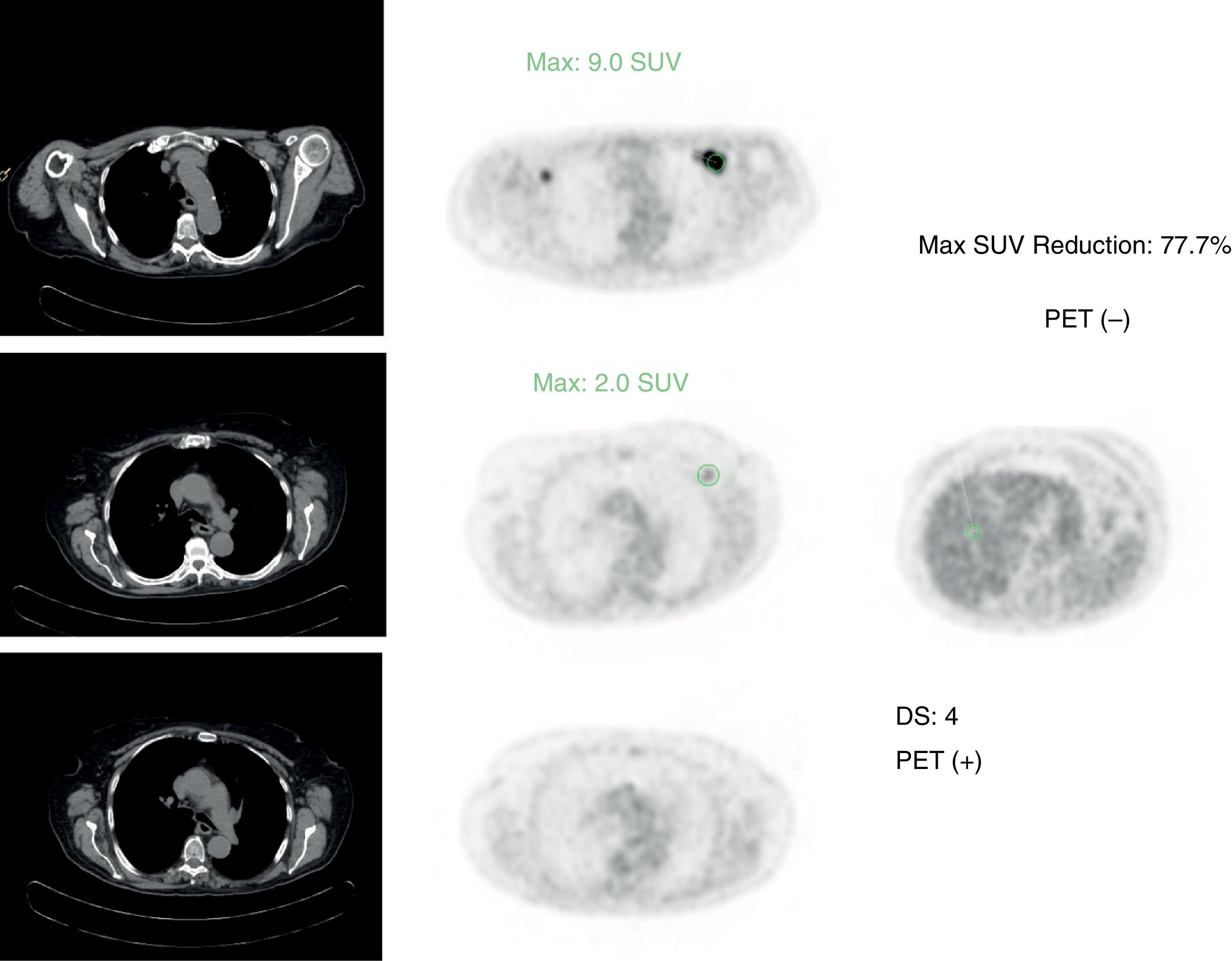
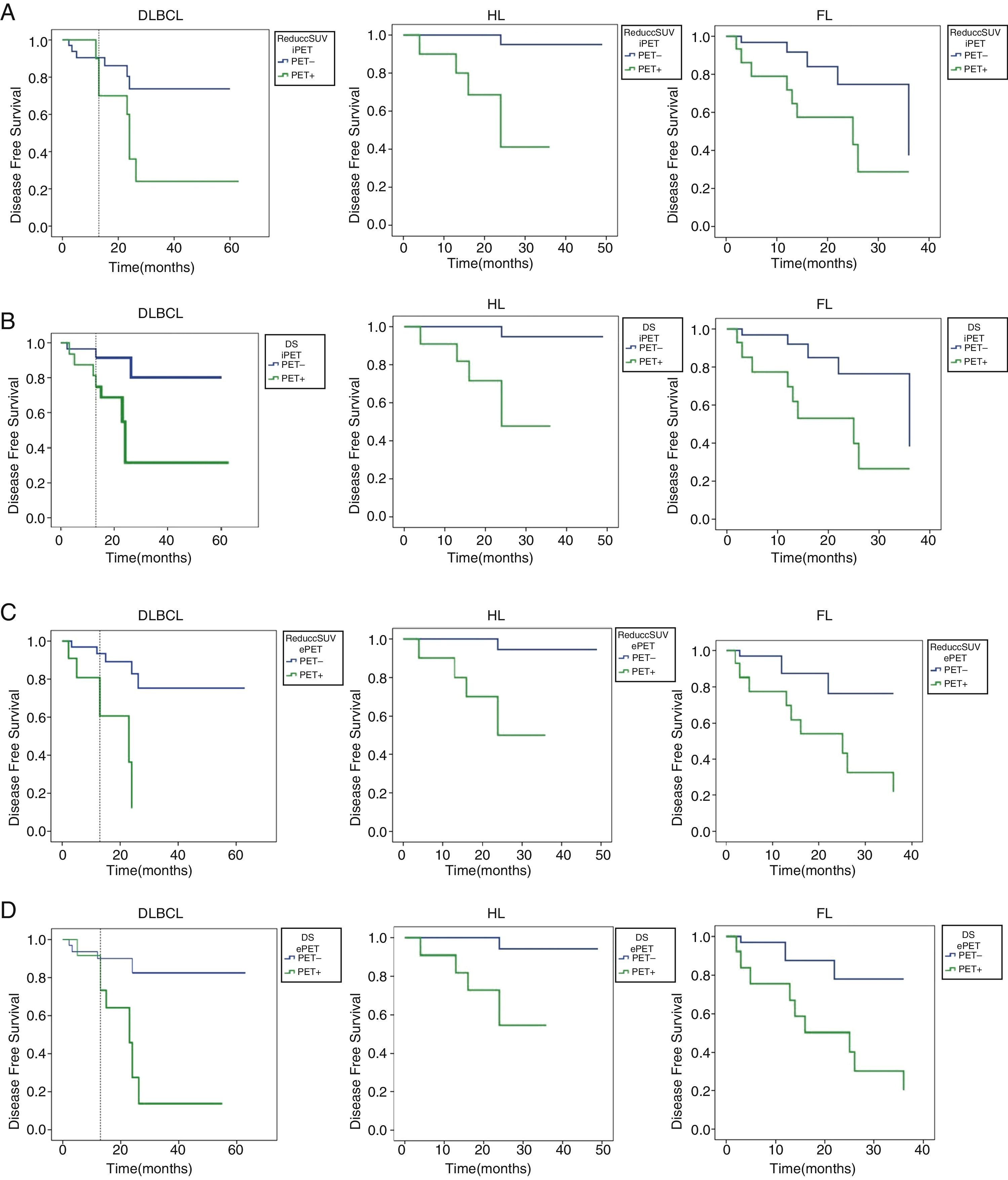
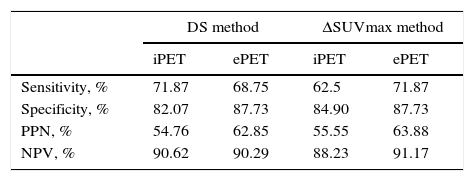
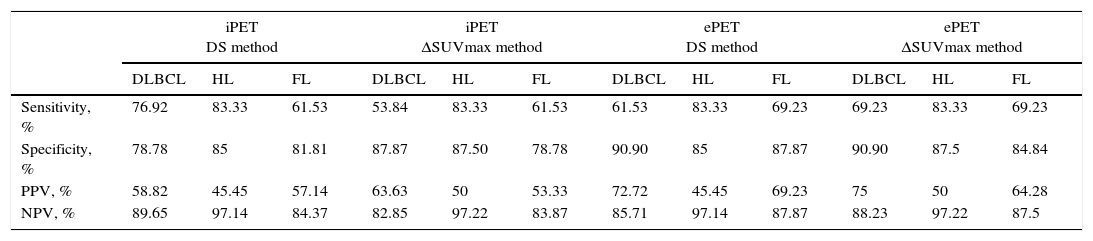
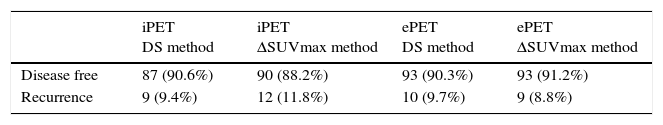
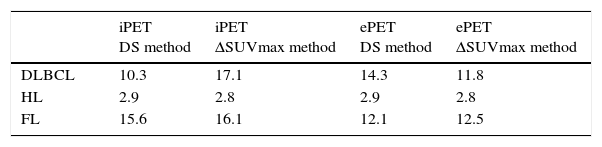
ResultsStatistical analysis. iPET for DLBCL, HL, and FL: (1) Se of DS: 76.92%; 83.33%; 61.53%; Sp: 78.78%; 85%; 81.81%; (2) Se of ΔSUVmax: 53.84%; 83.33%; 61.53%; Sp: 87.87%; 87.50%; 78.78%. ePET for DLBCL, HL and FL: (1) Se of D: 61.53%; 83.33%; 69.23%; Sp: 90.90%; 85%; 87.87%; (2) Se of ΔSUVmax: 69.23%; 83.33%; 69.23%; Sp: 90.90%; 87.50%; 84.84%. Predictive assessment. iPET study: (1) in DLBCL, DS resulted in 10.3% recurrence of negative iPET, and 17.1% in ΔSUVmax at DFI; (2) in HL, both parameters showed a 2.8% recurrence of negative iPET; (3) in FL, DS resulted in 15.6% recurrence of negative iPET, and 16.1% in ΔSUVmax 16.1%, with no statistical significance. ePET study: (1) in DLBCL, DS resulted in 14.3% recurrence of negative ePET, and 11.8% in ΔSUVmax at DFI; (2) in HL and FL, both methods showed 2.8% and 12.5% recurrence in negative ePET.
ConclusionsDS and ΔSUVmax did not show significant differences between DLBCL, HL and FL. Furthermore, their predictive values did not show significant differences between HL and FL. In DLBCL, DS was higher in iPET, and ΔSUVmax in ePET.
Comparar sensibilidad, especificidad y valor pronóstico de Deauville score (DS) versus ΔSUVmax, tanto en «interim» PET (iPET) como en «end» PET (ePET), en pacientes con linfoma difuso de células grandes B (LDCGB), linfoma de Hodgkin (LH), linfoma folicular (LF).
MétodoEstudio multicéntrico retrospectivo longitudinal en 138 pacientes (46 LDCGB, 46 LH, 46 LF). Se realizaron 3 18F-FDG PET/TC: basal, iPET y ePET. En iPET y ePET se utilizaron 2 criterios de interpretación: visual (DS) y semicuantitativo (ΔSUVmax). Se estableció el valor pronóstico en relación con el intervalo libre de enfermedad.
ResultadosAnálisis estadístico. Del iPET por subtipos histológicos (LDCGB, LH y LF): 1) DS obtuvo sensibilidad 76,92/83,33/61,53%; especificidad 78,78/85/81,81%, respectivamente; 2) ΔSUVmax obtuvo una sensibilidad del 53,84/83,33/61,53%; especificidad del 87,87/87,50/78,78%. Del ePET por subtipos histológicos: 1) DS obtuvo sensibilidad del 61,53/83,33/69,23%; especificidad del 90,90/85/87,87%; 2) ΔSUVmax obtuvo sensibilidad del 69,23/83,33/69,23%; especificidad del 90,90/87,5/84,84%. Evaluación pronóstica. Estudio iPET: en LDCGB el DS obtuvo que 10,3% con iPET negativo recidivó durante el intervalo libre de enfermedad y 17,1% con ΔSUVmax; en LH ambos métodos obtuvieron que 2,8% con iPET negativo recidivó; en LF el DS obtuvo que 15,6% con iPET negativo recidivó, con ΔSUVmax 16,1%, sin significación estadística para este método. Estudio ePET: en LDCGB el DS obtuvo que 14,3% con ePET negativo recidivó durante el intervalo libre de enfermedad, respecto al 11,8% con ΔSUVmax; en LH y LF ambos métodos obtuvieron que 2,8 y 12,5%, respectivamente, con ePET negativo recidivó.
ConclusiónDS y ΔSUVmax no muestran diferencias significativas en LDCGB, LH, LF. El valor pronóstico del DS y ΔSUVmax no muestra diferencias significativas en LH y LF; en LDCGB el DS es superior en iPET y el ΔSUVmax en ePET.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora