To compare two different methods for the interpretation of interim PET/CT (PET/CT-i) in lymphomas, and to establish which one best predicts a complete metabolic response (CMR) in the PET/CT study at the end of treatment (PET/CT-et).
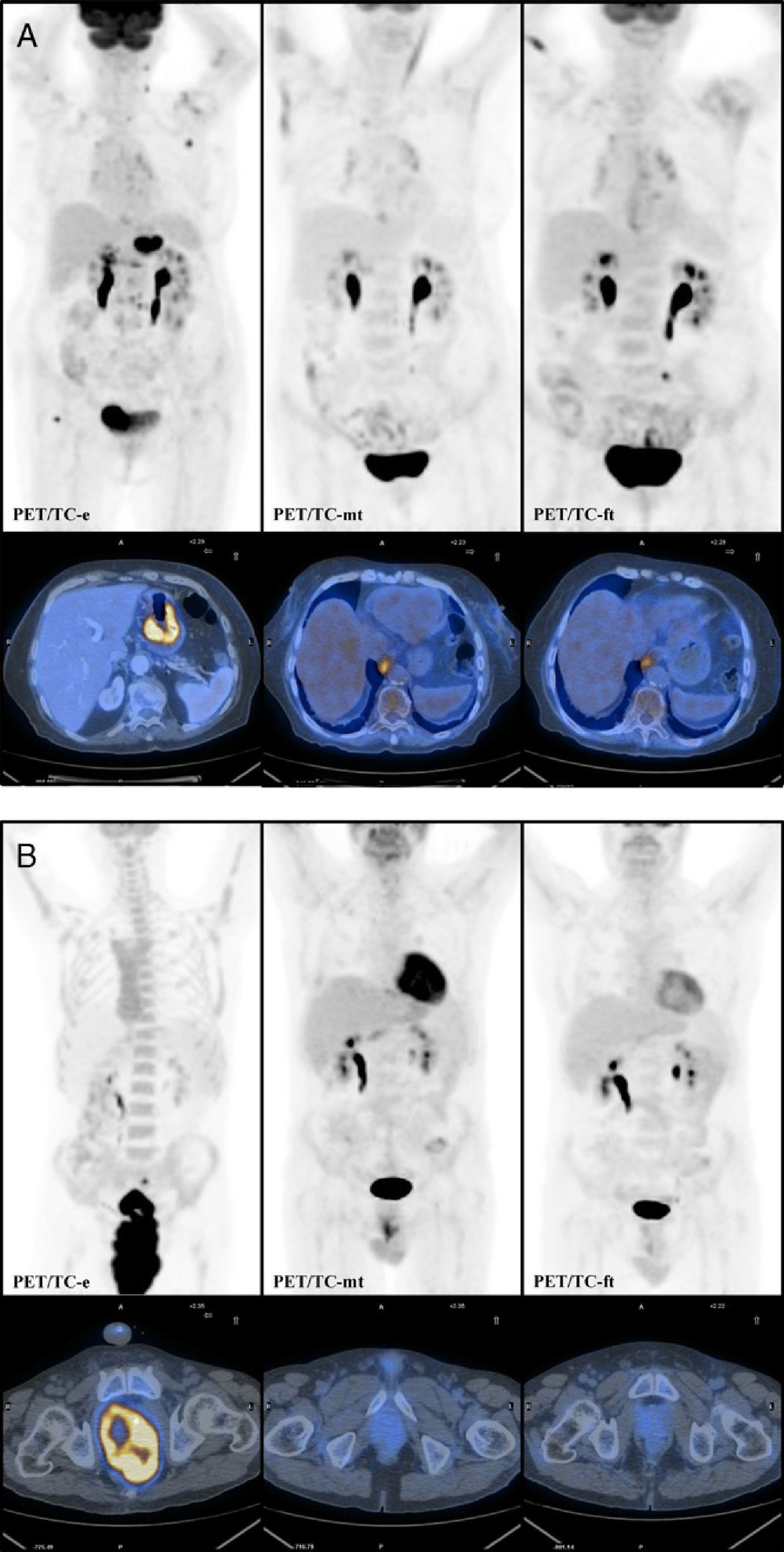
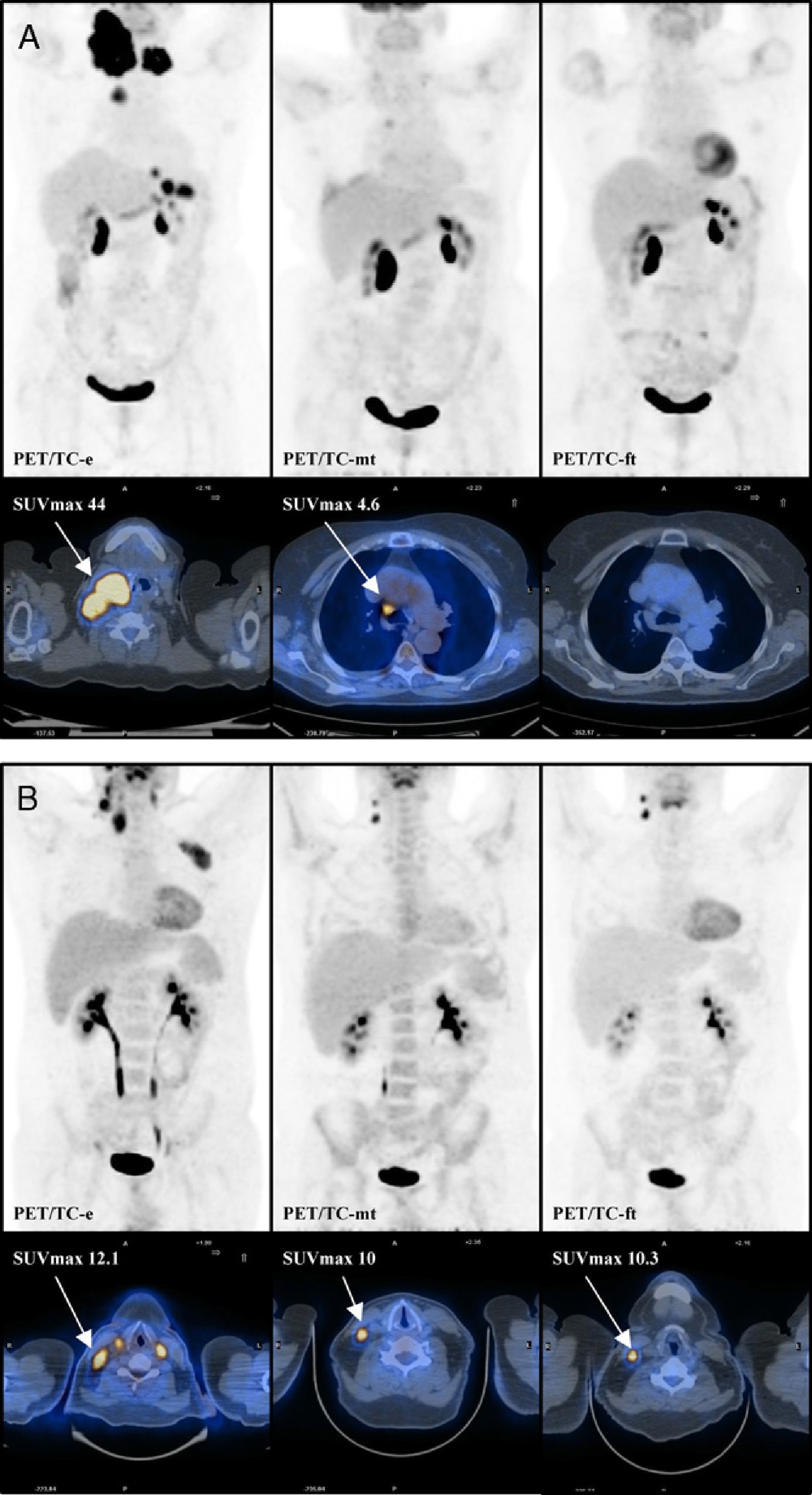
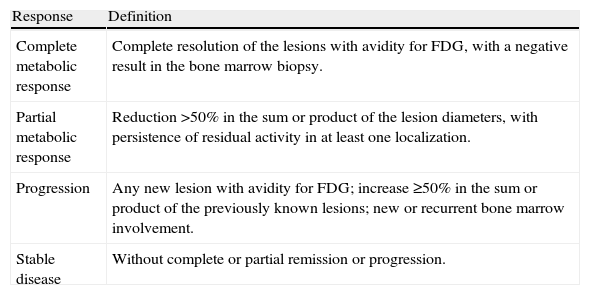
Materials and methodsRetrospective longitudinal analysis of the PET/CT studies for staging (PET/CT-s), PET/CT-i and PET/CT-et of 65 patients, 35 Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and 30 non-HL was performed. The PET/CT-i was performed between the second and fourth chemotherapy cycle. It was interpreted using two different criteria: qualitative criteria (5 point visual scale) and semiquantitative criteria (percentage difference between the lesion with more SUVmax in the PET/CT-s and PET/CT-i). We analyzed the likelihood of obtaining a CMR in the PET/CT-et according to the results obtained on the PET/CT-i with these two criteria.
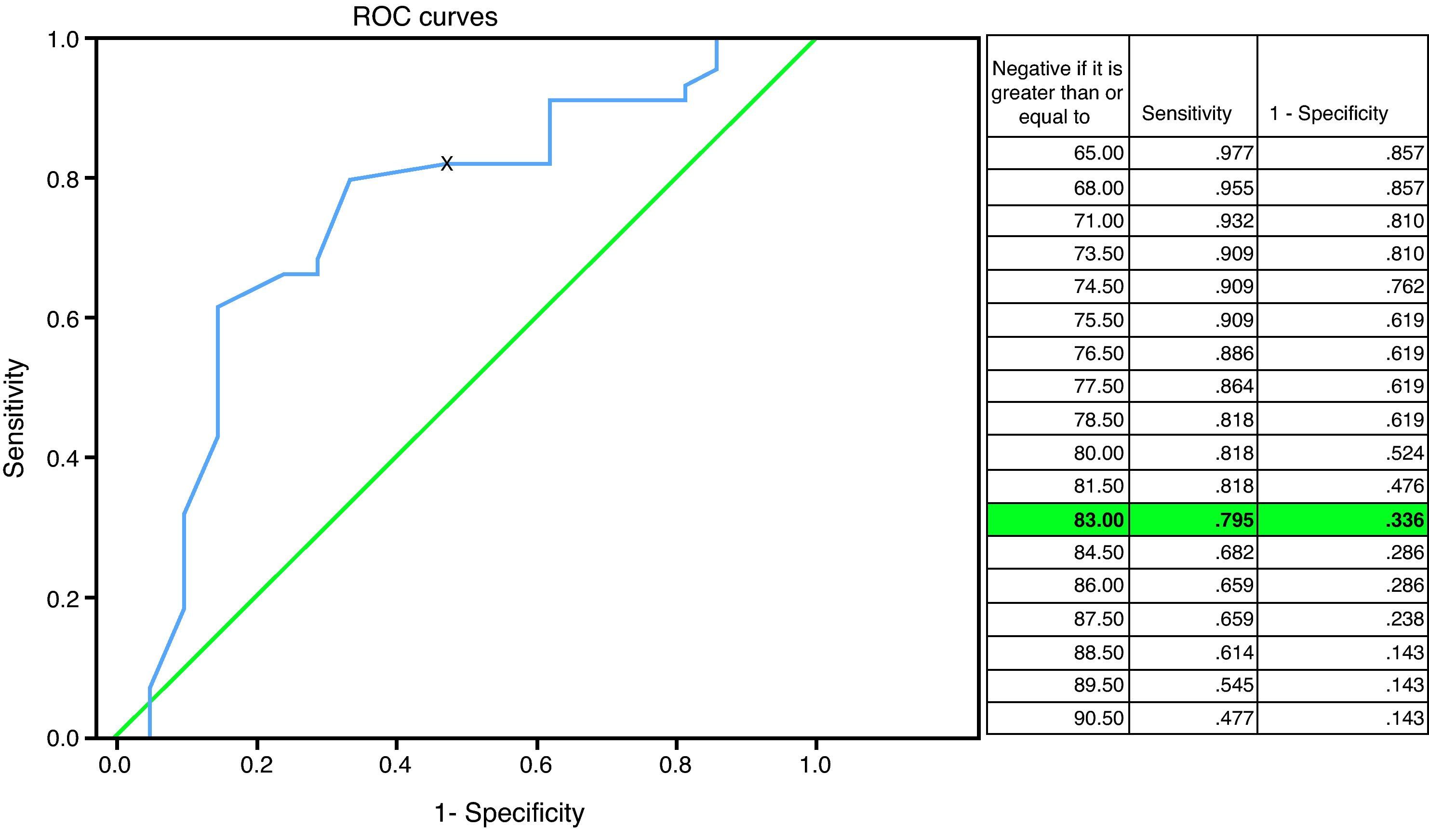
ResultsWe obtained sensitivity (S), specificity (Sp), positive predictive values (PPV), negative predictive values (NPV) and likelihood ratio (LR) for the qualitative/semiquantitative method of 91%/80%, 76.2%/67%, 88.9%/83.3%, 80%/60.9% and 32%/7.8%, respectively, to predict a CMR in the PET/CT-et. There were no statistically significant differences between the LR of both methods (p=0.1942).
ConclusionWe found clear differences in S, Sp, PPV and NPV between both interpretation criteria for the PET/CT-i to predict a CMR in the PET/CT-et. Nevertheless, we cannot confirm the superiority of the qualitative method over the semiqualitative method for this purpose as no statistically significance differences were found in their LR in our study.
Realizar una comparación entre 2 métodos para la valoración de la PET/TC a la mitad del tratamiento (PET/TC-mt) en linfomas, y establecer cuál de ellos predice con mayor precisión una respuesta metabólica completa (RMC) en la PET/TC al final del tratamiento (PET/TC-ft).
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo longitudinal de los estudios PET/TC de estadificación (PET/TC-e), PET/TC-mt y PET/TC-ft de 65 pacientes con linfoma, 35 linfoma de Hodgkin y 30 linfoma no Hodgkin. La PET/TC-mt fue realizada entre el segundo y cuarto ciclo de quimioterapia y se valoró utilizando 2 criterios de interpretación: criterio cualitativo (escala visual de 5 puntos), criterio semicuantitativo (porcentaje de diferencia entre el SUVmax de la lesión con mayor actividad metabólica en la PET/TC-e y la PET/TC-mt). Analizamos la probabilidad de obtener una RMC en la PET/TC-ft según la clasificación de la PET/TC-mt con estos 2 criterios.
ResultadosObtuvimos valores de sensibilidad (S), especificidad (E), valor predictivo positivo (VPP), valor predictivo negativo (VPN) y razón de probabilidad (RP) para el método cualitativo/semicuantitativo de 91/80%, 76,2/67%, 88,9/83,3%, 80/60,9% y 32/7,8% respectivamente, para predecir un RMC en la PET/TC-ft.
No encontramos diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre la RP del análisis cualitativo y semicuantitativo (p=0,1942).
ConclusiónEncontramos claras diferencias en la S, E, VPP y VPN entre ambos métodos de valoración de la PET/TC-mt para predecir una RMC en la PET/TC-ft. Sin embargo, al no encontrar diferencias estadísticamente significativas en la RP, no podemos afirmar que el método cualitativo sea superior al semicuantitativo para este fin.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora