Searching for online health information is a popular approach employed by patients to enhance their knowledge for their diseases. Recently developed AI chatbots are probably the easiest way in this regard. The purpose of the study is to analyze the reliability and readability of AI chatbot responses in terms of the most commonly applied radionuclide treatments in cancer patients.
MethodsBasic patient questions, thirty about RAI, PRRT and TARE treatments and twenty-nine about PSMA-TRT, were asked one by one to GPT-4 and Bard on January 2024. The reliability and readability of the responses were assessed by using DISCERN scale, Flesch Reading Ease(FRE) and Flesch-Kincaid Reading Grade Level(FKRGL).
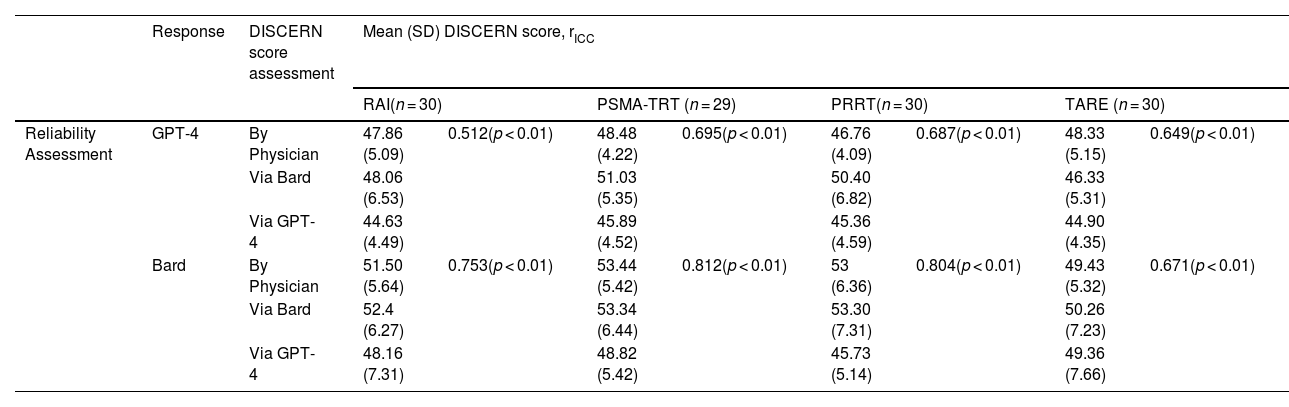
ResultsThe mean (SD) FKRGL scores for the responses of GPT-4 and Google Bard about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatmens were 14.57 (1.19), 14.65 (1.38), 14.25 (1.10), 14.38 (1.2) and 11.49 (1.59), 12.42 (1.71), 11.35 (1.80), 13.01 (1.97), respectively. In terms of readability the FRKGL scores of the responses of GPT-4 and Google Bard about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatments were above the general public reading grade level. The mean (SD) DISCERN scores assesses by nuclear medicine phsician for the responses of GPT-4 and Bard about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatments were 47.86 (5.09), 48.48 (4.22), 46.76 (4.09), 48.33 (5.15) and 51.50 (5.64), 53.44 (5.42), 53 (6.36), 49.43 (5.32), respectively. Based on mean DISCERN scores, the reliability of the responses of GPT-4 and Google Bard about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT, and TARE treatments ranged from fair to good. The inter-rater reliability correlation coefficient of DISCERN scores assessed by GPT-4, Bard and nuclear medicine physician for the responses of GPT-4 about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatments were 0.512(95% CI 0.296: 0.704), 0.695(95% CI 0.518: 0.829), 0.687(95% CI 0.511: 0.823) and 0.649 (95% CI 0.462: 0.798), respectively (p < 0.01). The inter-rater reliability correlation coefficient of DISCERN scores assessed by GPT-4, Bard and nuclear medicine physician for the responses of Bard about RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatments were 0.753(95% CI 0.602: 0.863), 0.812(95% CI 0.686: 0.899), 0.804(95% CI 0.677: 0.894) and 0.671 (95% CI 0.489: 0.812), respectively (p < 0.01). The inter-rater reliability for the responses of Bard and GPT-4 about RAİ, PSMA-TRT, PRRT and TARE treatments were moderate to good. Further, consulting to the nuclear medicine physician was rarely emphasized both in GPT-4 and Google Bard and references were included in some responses of Google Bard, but there were no references in GPT-4.
ConclusionAlthough the information provided by AI chatbots may be acceptable in medical terms, it can not be easy to read for the general public, which may prevent it from being understandable. Effective prompts using 'prompt engineering' may refine the responses in a more comprehensible manner. Since radionuclide treatments are specific to nuclear medicine expertise, nuclear medicine physician need to be stated as a consultant in responses in order to guide patients and caregivers to obtain accurate medical advice. Referencing is significant in terms of confidence and satisfaction of patients and caregivers seeking information.
La búsqueda de información de salud en línea es un enfoque popular empleado por los pacientes para mejorar sus conocimientos sobre sus enfermedades. Los chatbots de IA desarrollados recientemente son probablemente la forma más sencilla a este respecto. El propósito del estudio es analizar la confiabilidad y legibilidad de las respuesta de los chatbots de IA en relación con los tratamientos con radionúclidos más comúnmente aplicados en pacientes con cáncer.
MétodosLas preguntas básicas de los pacientes, treinta sobre los tratamientos RAI, PRRT y TARE y veintinueve sobre PSMA-TRT, se formularon una por una a GPT-4 y Bard en enero de 2024. La confiabilidad y legibilidad de las respuestas se evaluaron mediante la escala DISCERN y Flesch Reading Ease (FRE) y Flesch-Kincaid Reading Grade Level (FKRGL).
ResultadosLas puntuaciones medias (DE) de FKRGL para las respuestas de GPT-4 y Google Bard sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE fueron 14,57 (1,19), 14,65 (1,38), 14,25 (1,10), 14,38 (1,2) y 11,49. (1,59), 12,42 (1,71), 11,35 (1,80), 13,01 (1,97), respectivamente. En términos de legibilidad, las puntuaciones FRKGL de las respuestas de GPT-4 y Google Bard sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE estuvieron por encima del nivel de lectura del público general. Las puntuaciones DISCERN medias (DE) evaluadas por un médico de medicina nuclear para las respuestas de GPT-4 y Bard sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA TRT, PRRT y TARE fueron 47,86 (5,09), 48,48 (4,22), 46,76 (4,09), 48,33 (5,15) y 51,50 (5,64), 53,44 (5,42), 53 (6,36), 49,43 (5,32), respectivamente. Según las puntuaciones medias de DISCERN, la confiabilidad de las respuestas de GPT-4 y Google Bard sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE osciló de regular a buena. El coeficiente de correlación de confiabilidad entre evaluadores de las puntuaciones DISCERN evaluadas por GPT-4, Bard y el médico de medicina nuclear para las respuestas de GPT-4 sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE fueron 0,512 (IC del 95%: 0,296: 0,704), 0,695 (IC 95% 0,518: 0,829), 0,687 (IC 95% 0,511: 0,823) y 0,649 (IC 95% 0,462: 0,798), respectivamente (p < 0,01). El coeficiente de correlación de confiabilidad entre evaluadores de las puntuaciones DISCERN evaluadas por GPT-4, Bard y el médico de medicina nuclear para las respuestas de Bard sobre los tratamientos RAI, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE fueron 0,753 (IC del 95 %: 0,602: 0,863), 0,812 (IC 95% 0,686: 0,899), 0,804 (IC 95% 0,677: 0,894) y 0,671 (IC 95% 0,489: 0,812), respectivamente (p < 0,01). La confiabilidad entre evaluadores para las respuestas de Bard y GPT-4 sobre los tratamientos RAİ, PSMA-TRT, PRRT y TARE fue de moderada a buena. Además, rara vez se hizo hincapié en la consulta con un médico nuclear tanto en GPT-4 como en Google Bard y se incluyeron referencias en algunas respuestas de Google Bard, pero no hubo referencias en GPT-4.
ConclusiónAunque la información proporcionada por los chatbots de IA puede ser aceptable en términos médicos, puede que no sea fácil de leer para el público en general, lo que puede impedir que sea comprensible. Las indicaciones efectivas que utilizan "ingeniería rápida" pueden refinar las respuestas de una manera más comprensible. Dado que los tratamientos con radionúclidos son específicos de la experiencia en medicina nuclear, el médico en medicina nuclear debe figurar como consultor en las respuestas para guiar a los pacientes y cuidadores a obtener un asesoramiento médico preciso. Las referencias son importantes en términos de confianza y satisfacción de los pacientes y cuidadores que buscan información.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora