To study in detail the accuracy and repeatability of three commonly used methods for SUV estimation in solitary pulmonary nodules.
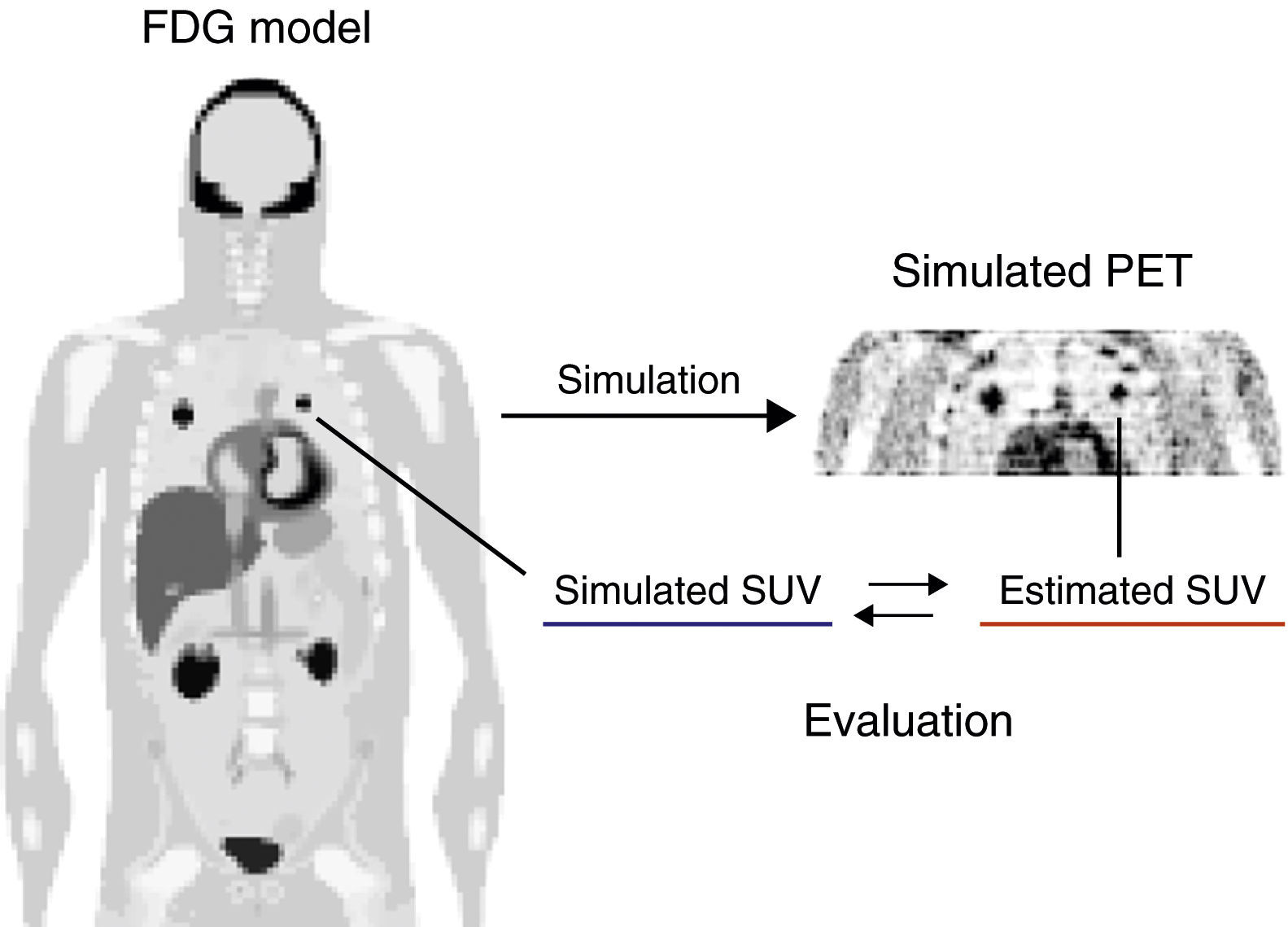
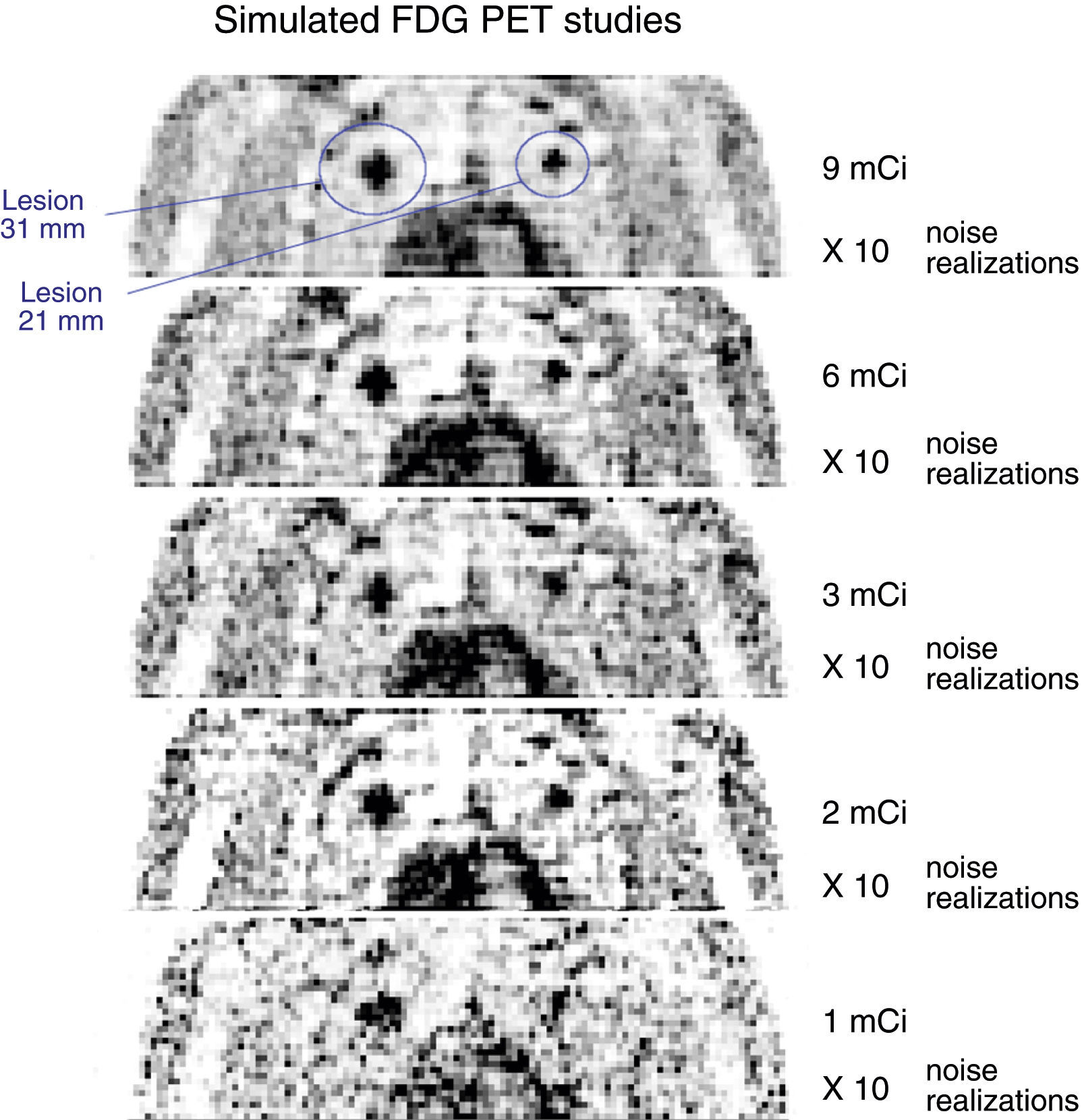
Material and methodsWe have designed a realistic framework based on simulated FDG-PET acquisitions from an anthropomorphic activity model that included solitary pulmonary nodules (different sizes) of well-known SUV. This framework enables us to compare the SUV values obtained from the reconstructed PET images with the real SUV values. Three commonly used methods (SUVmax, SUVmean and SUV50) were used to estimate the tumor activity.
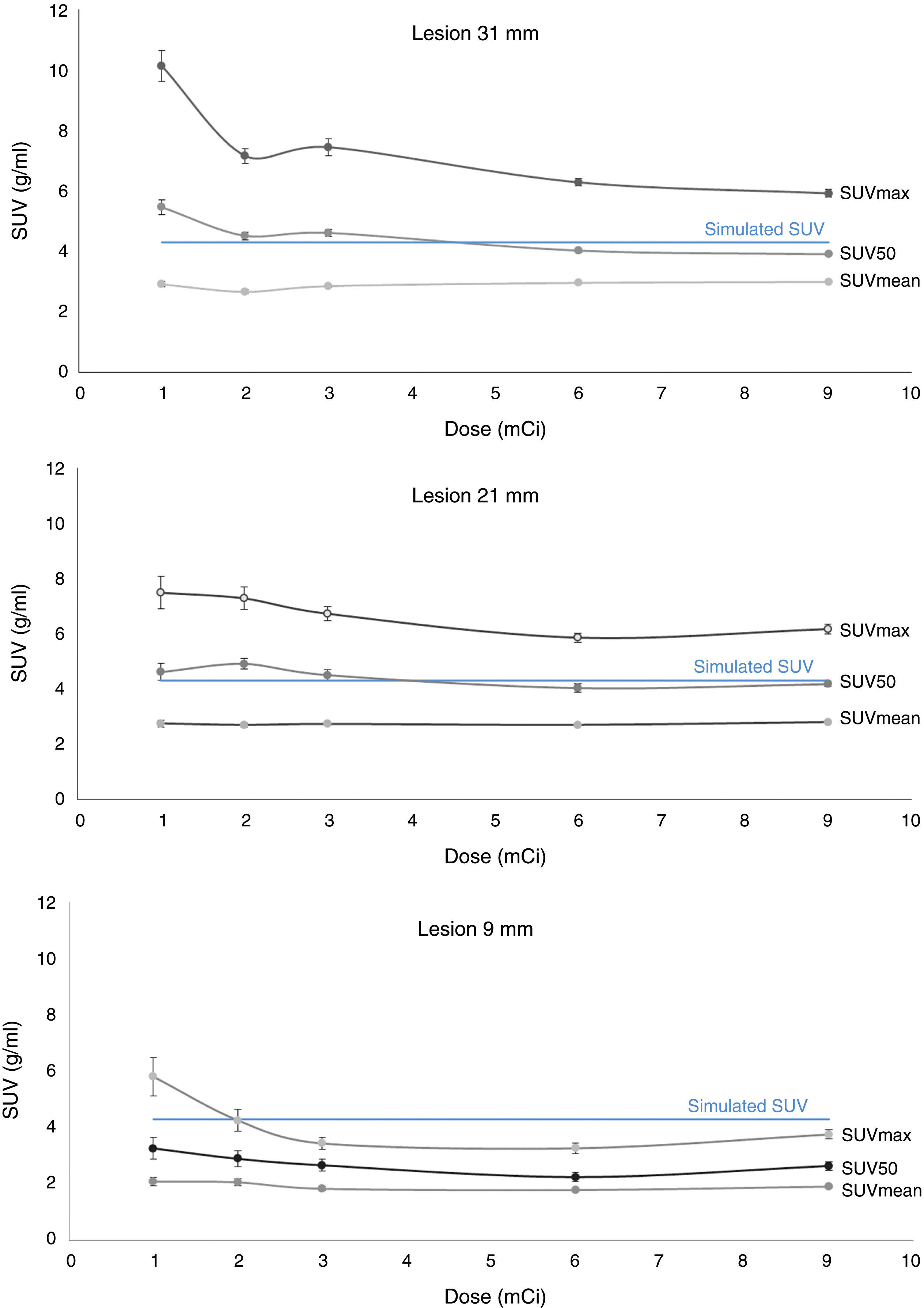
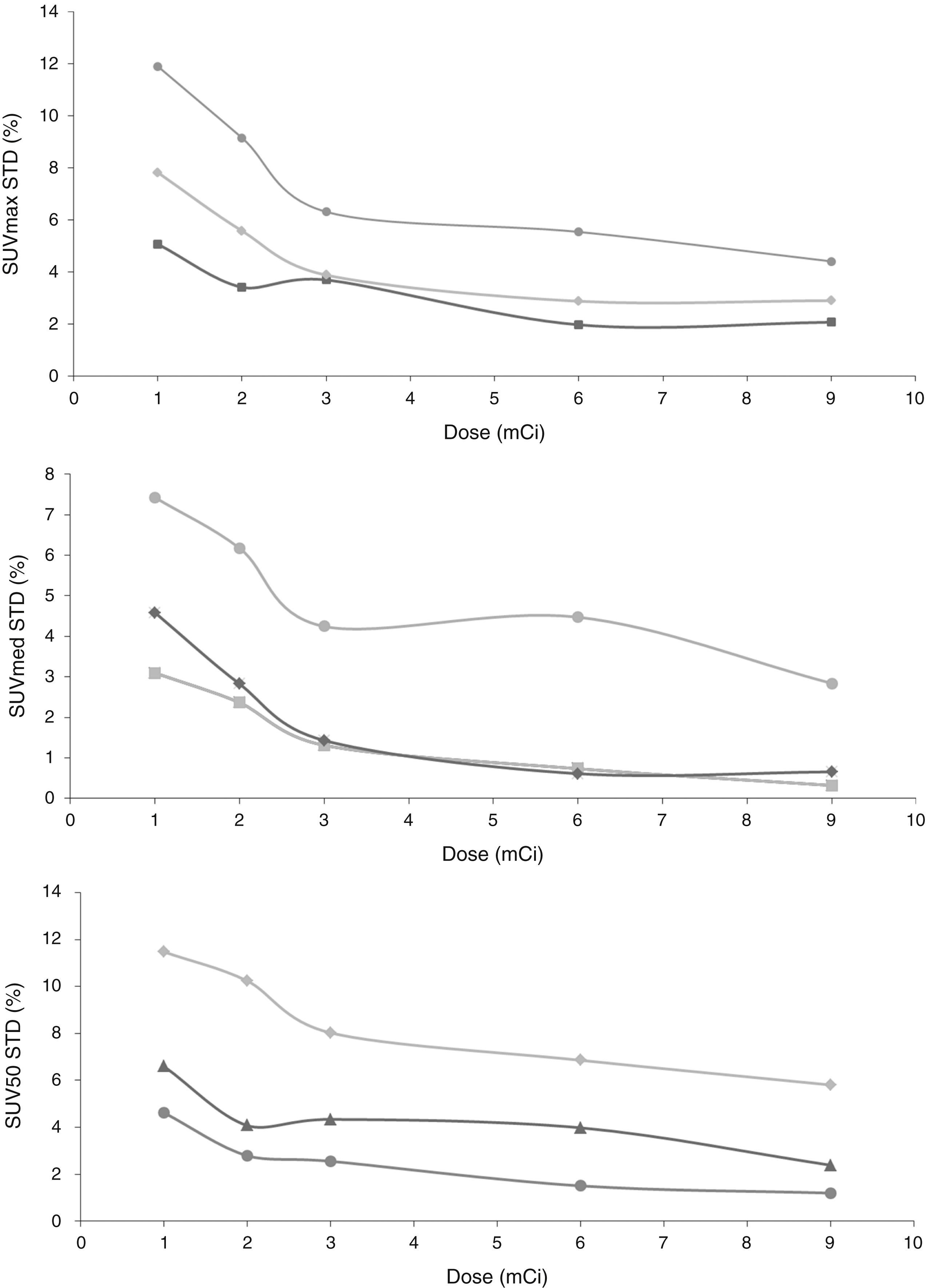
ResultsOur results showed the tumor activity was overestimated using SUVmax and clearly subestimated using SUVmean. Instead, the quantification of SUV50 showed great agreement with the simulated tumor activity and only slight subestimation was found for very small lesions. On the other hand, SUVmean showed better performance than SUV50 in terms of repeatability, providing variabilities below 5% for all tumor sizes and for injected doses as low as 111 MBq.
ConclusionsOur findings showed that SUV50 provided better performance for estimating accurately tumor SUV values in pulmonary nodules, but SUVmean showed better results in terms of repeatability.
estudiar en detalle la precisión y la repetitividad de tres métodos de uso común en la estimación del SUV de nódulos pulmonares solitarios.
Material y métodoshemos diseñado una metodología de trabajo basada en la simulación de adquisiciones de estudios PET-FDG a partir de modelos antropomórficos de actividad, que incluyen nódulos pulmonares de diferente tamaño y valor de SUV conocido. Esta metodología nos permite comparar el SUV estimado a partir de la imagen PET con el SUV teórico. La actividad del tumor fue estimada mediante tres métodos conocidos: SUVmax, SUVmean y SUV50.
Resultadosnuestros resultados muestran que, por un lado SUVmax sobreestima la actividad en el tumor, mientras SUV50 subestima el valor de actividad de manera muy significa. En cambio, la cuantificación de SUV50 mostró un buen acuerdo con los valores de SUV teóricos o simulados, y únicamente mostró una ligera subestimación para lesiones muy pequeñas. Por otro lado, SUVmean mostró un mejor comportamiento que SUV50 en términos de repetitividad, proporcionando variabilidades por debajo del 5% para todos los tamaños de lesión y para dosis inyectadas tan bajas como 111 MBq.
Conclusionesnuestros hallazgos mostraron que SUV50 proporciona el mejor comportamiento para estimar la actividad en nódulos pulmonares, pero SUVmean mostró mejores resultados en términos de repetitividad.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)