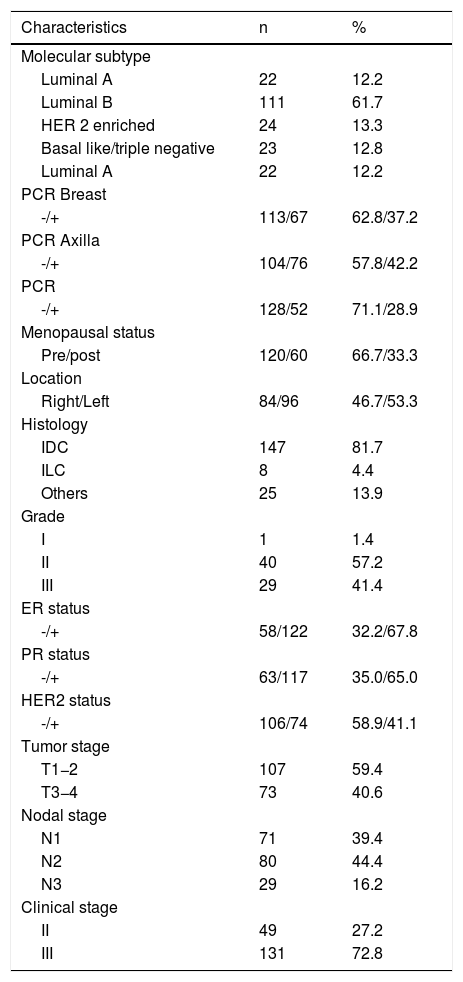
This study aimed to determine the prognostic role of baseline maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) obtained by pretreatment PET/CT and the change in SUVmax (ΔSUVmax [%]) in patients with axillary lymph node–positive breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
MethodsOne hundred and eighty patients with baseline SUVmax and 121 patients with SUVmax measurement after treatment were evaluated in the study. The baseline SUVmax value of the breast (SUVmaxBI) and axilla (SUVmaxAI) and the change in the SUVmax of the breast (ΔSUVmaxB) and axilla (ΔSUVmaxA) were measured. The optimal cut-off value of SUVmax and ΔSUVmax were determined by ROC curve analysis. Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated using Kaplan–Meier curves.
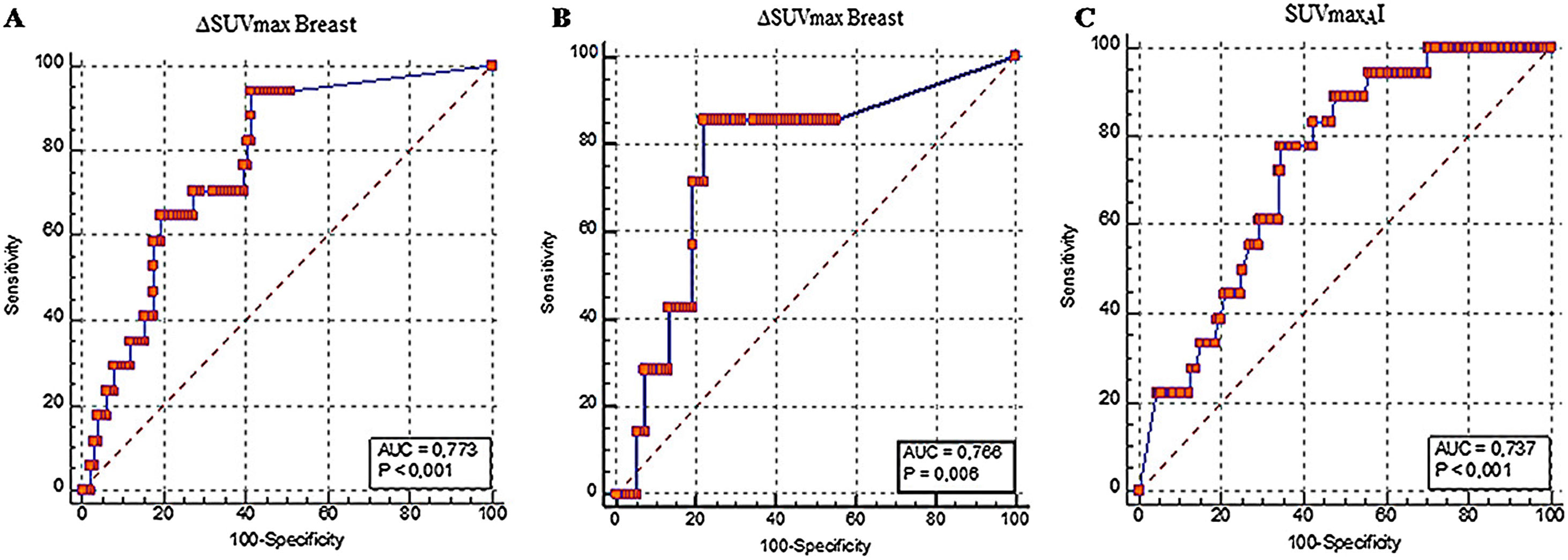
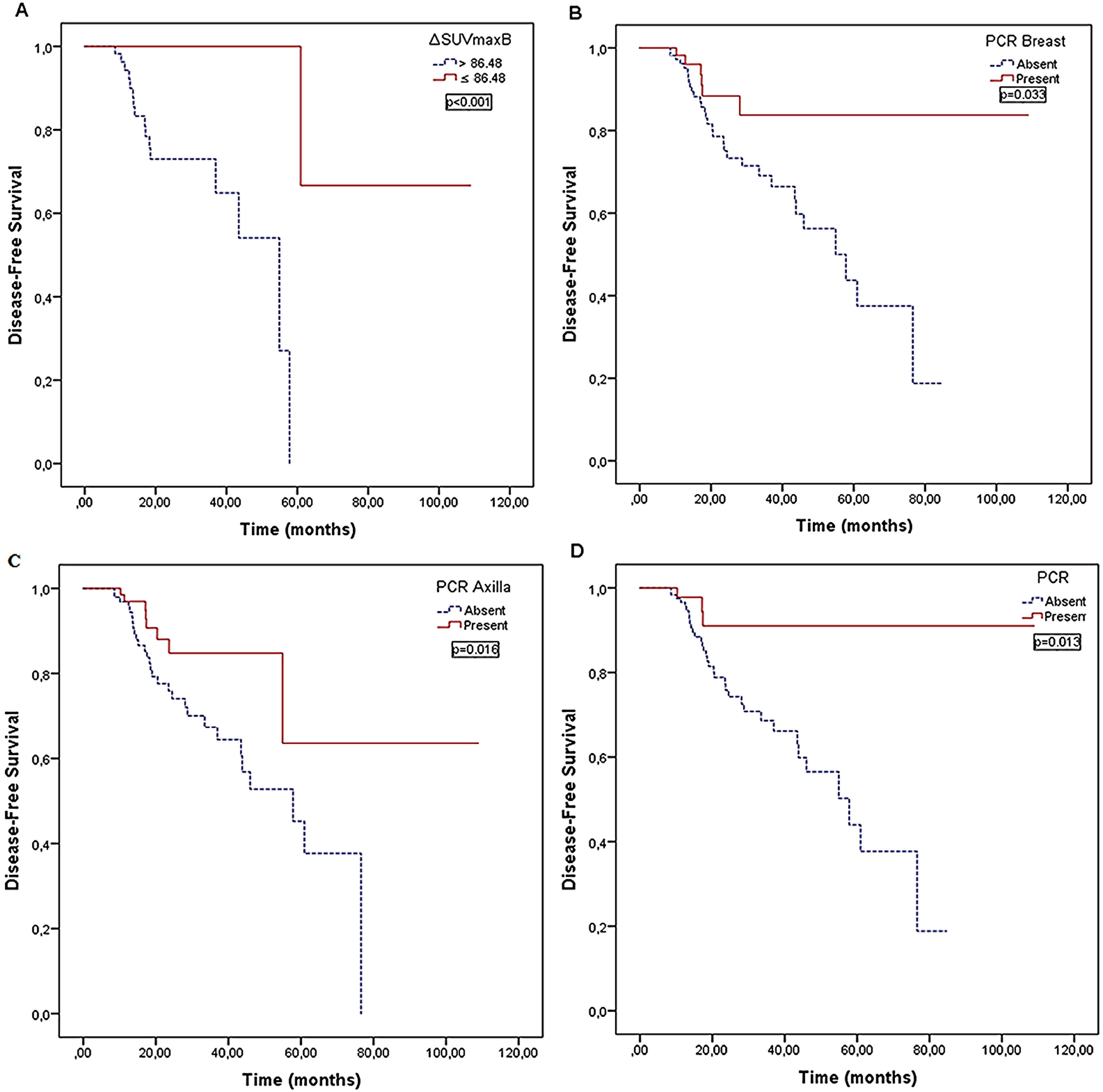
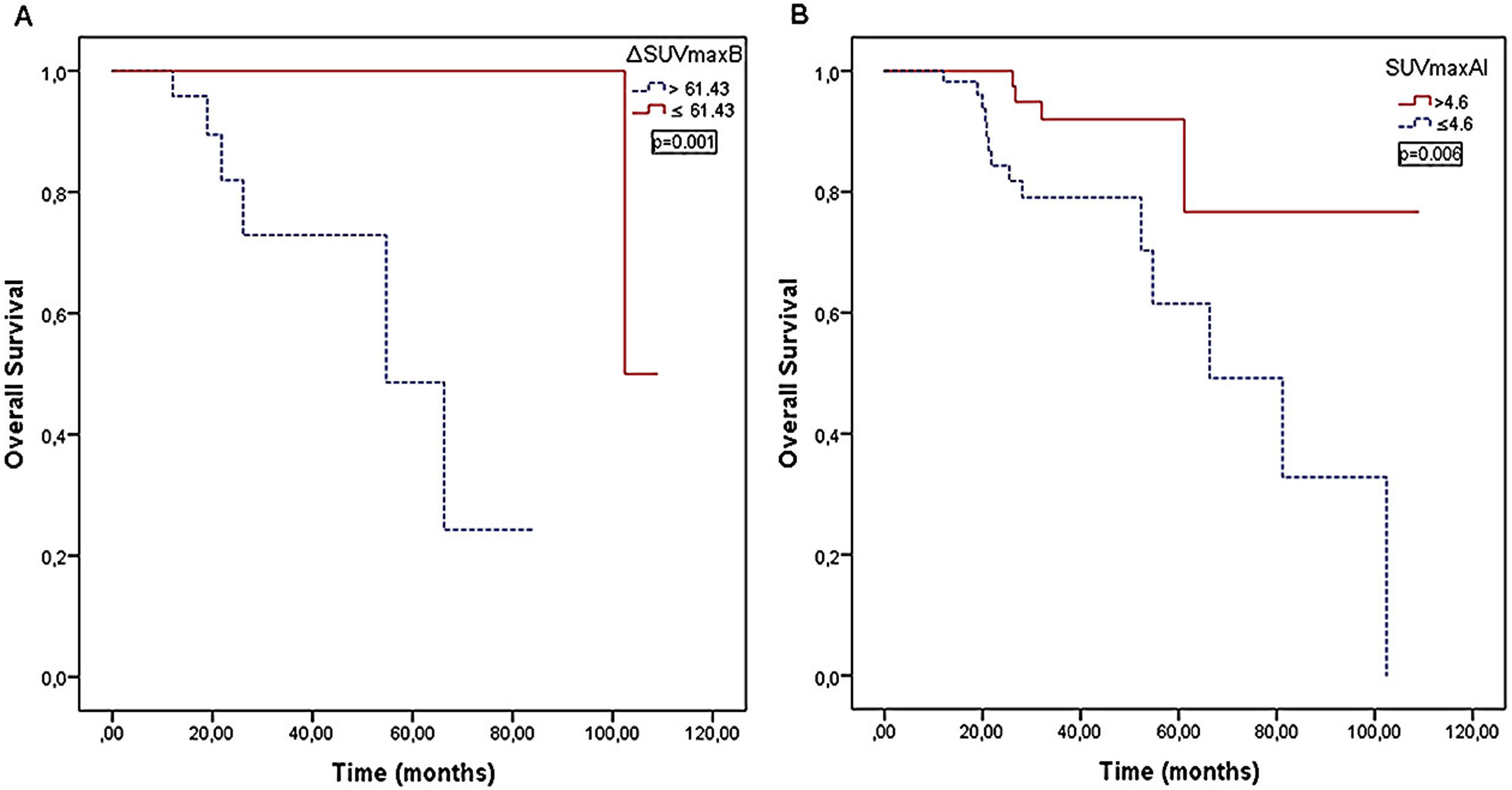
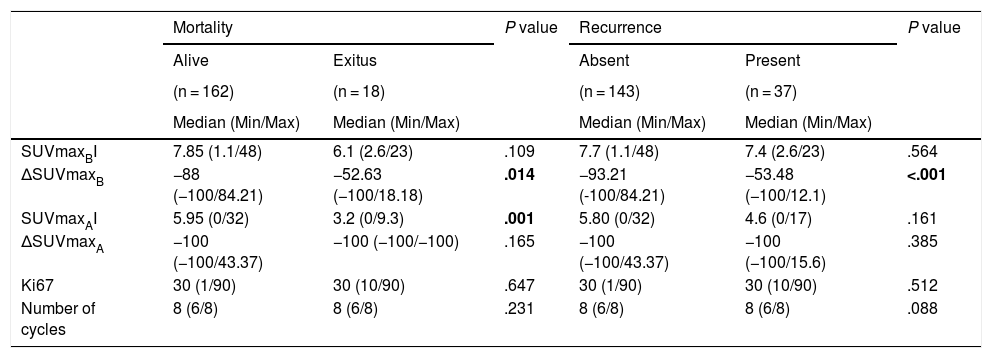
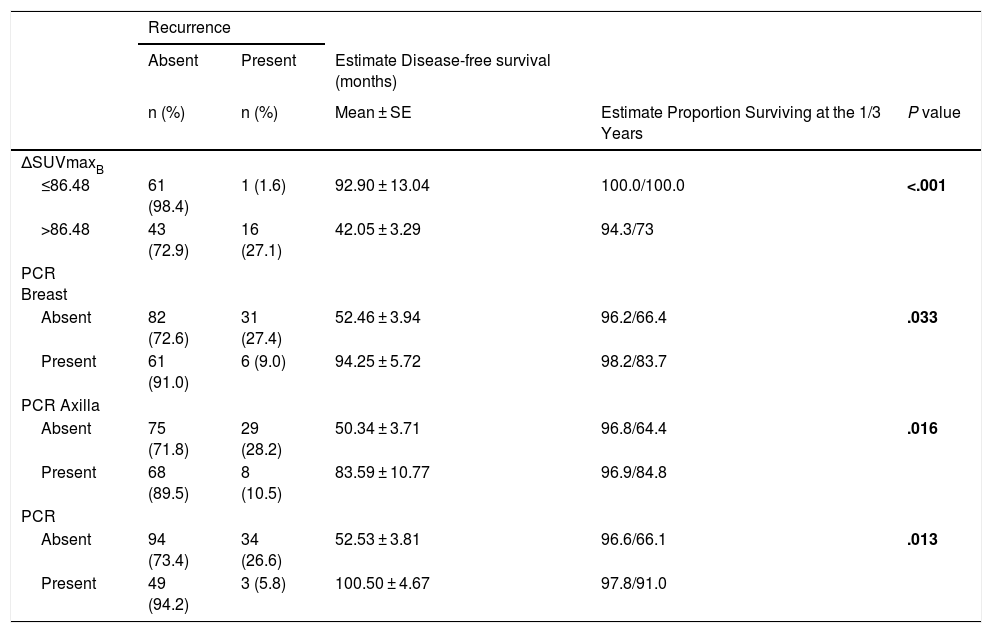
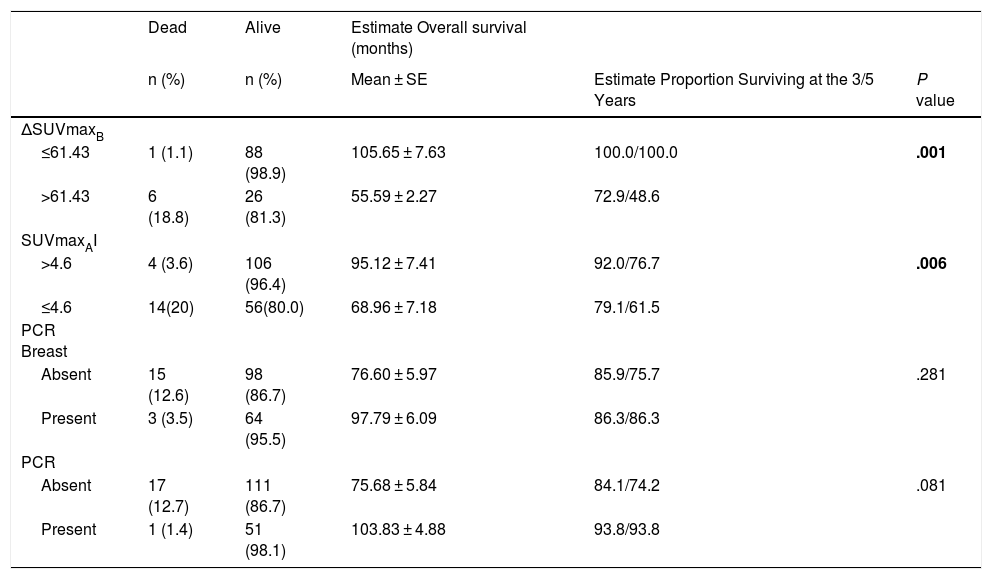
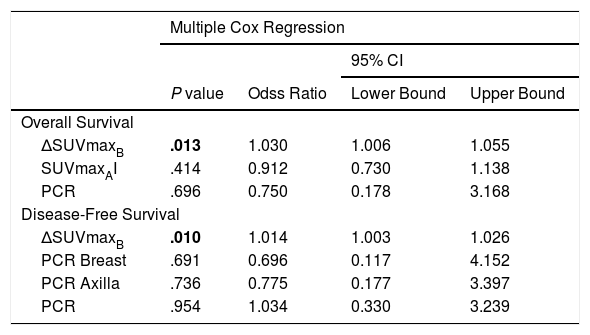
ResultsΔSUVmaxB, pCRB, pCRA, and pCR parameters were found to be associated with relapse (P < .001, P = .033, P = .016, and P = .013, respectively). ΔSUVmaxB and SUVmaxAI were associated with mortality (P = .001 and P = .006, respectively). Multiple Cox regression analyses revealed that ΔSUVmaxB value was an independent prognostic factor for relapse and mortality (P = .013 and P = .010, respectively).
ConclusionThe results showed that ΔSUVmaxB was an independent prognostic factor for relapse and mortality in patients with axillary lymph node–positive breast cancer who received NAC.
En este estudio, se tuvo como objetivo determinar el papel pronóstico del valor de captación máximo estandarizado (SUVmáx) basal obtenido por PET/TC antes del tratamiento, y el cambio en el SUVmáx (ΔSUVmáx [%]) en pacientes con cáncer de mama con ganglios linfáticos axilares positivos que habían recibido quimioterapia neoadyuvante (NAC).
MétodosSe evaluaron en el estudio 180 pacientes con SUVmáx basal y 121 pacientes con medición de SUVmáx después del tratamiento. Se midieron el valor de SUVmáx inicial de la mama (SUVmáxBI) y axila (SUVmáxAI), y el cambio en el SUVmáx de la mama (ΔSUVmáxB) y axila (ΔSUVmáxA). El valor de corte óptimo de SUVmáx y ΔSUVmáx se determinó mediante el análisis de la curva ROC. La supervivencia libre de enfermedad (SLE) y la supervivencia global (SG) se calcularon mediante curvas de Kaplan-Meier.
ResultadosSe encontró que los parámetros ΔSUVmáxB, pCRB, pCRA y pCR se asociaron con la recaída (P < .001, P = .033, P = .016 y P = .013, respectivamente). ΔSUVmáxB y SUVmáxAI se asociaron con la mortalidad (P = ,001 y P = ,006, respectivamente). El análisis de regresión de Cox múltiple reveló que el valor de ΔSUVmáxB era un factor pronóstico independiente para la recaída y la mortalidad (P = ,013 y P = ,010, respectivamente).
ConclusiónLos resultados muestran que ΔSUVmáxB es un factor pronóstico independiente de recaída y mortalidad en pacientes con cáncer de mama con ganglios linfáticos axilares positivos que recibieron NAC.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora