This study has aimed to analyze the evolution of patients diagnosed with differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) with a negative 131I-Na whole body scan (WBS), high levels of serum thyroglobulin (Tg) and negative 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET-FDG) study.
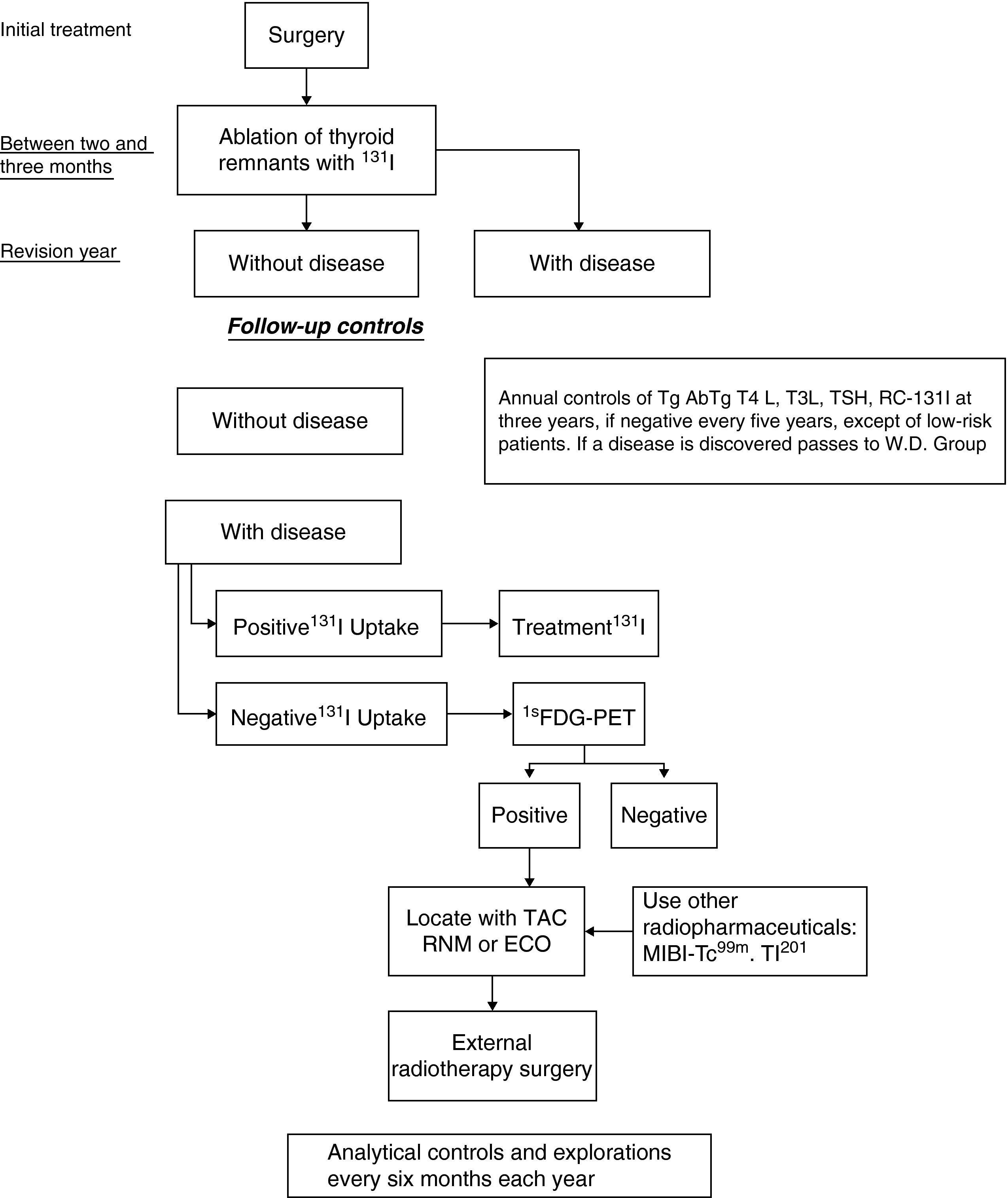
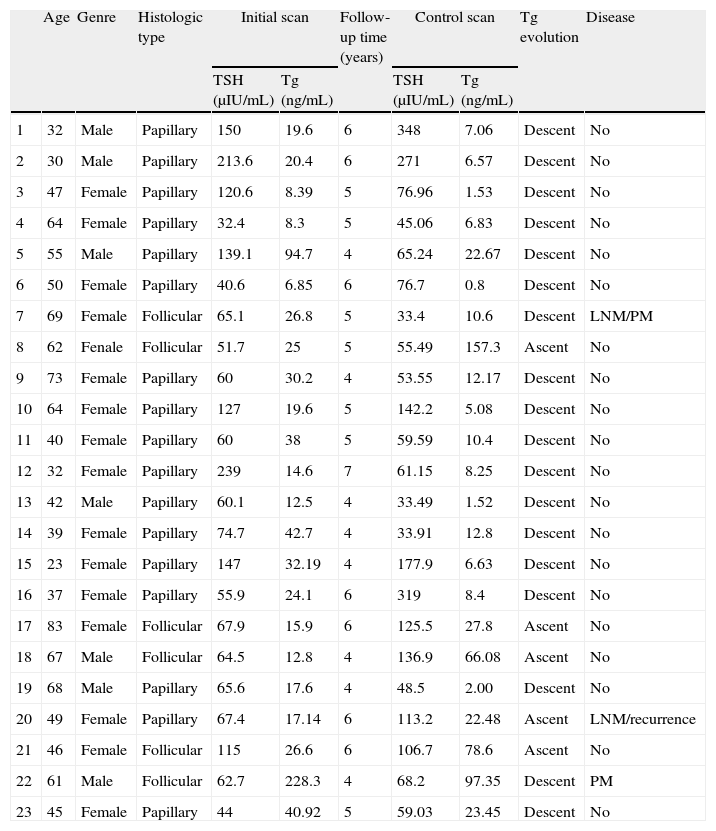
Material and methodsTwenty-three patients diagnosed and treated for DTC were studied retrospectively. Patients were aged between 23 and 83 and had shown, between January 2001 and December 2002, negative WBS, Tg values in a range of suspected recurrence or metastasis (Tg>2ng/mL with thyroid hormone withdrawal) and a negative PET-FDG study. The patients were monitored clinically, radiologically and analytically for a minimum period of 4 years. After this, a new evaluation was made of their state of disease with a control WBS, also observing the evolution of Tg. All WBS were performed with a 185MBq diagnostic dose of 131I-Na.
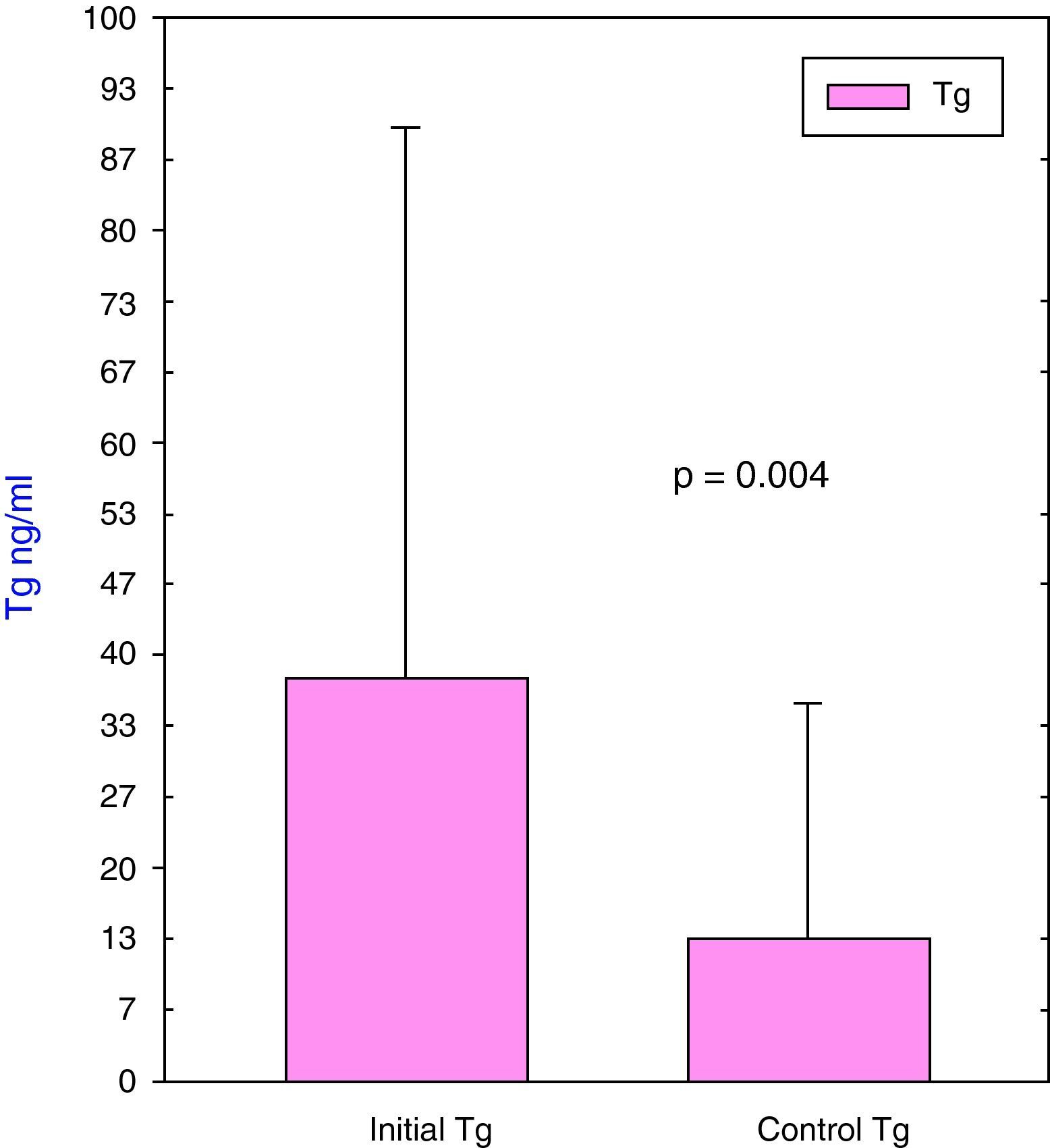
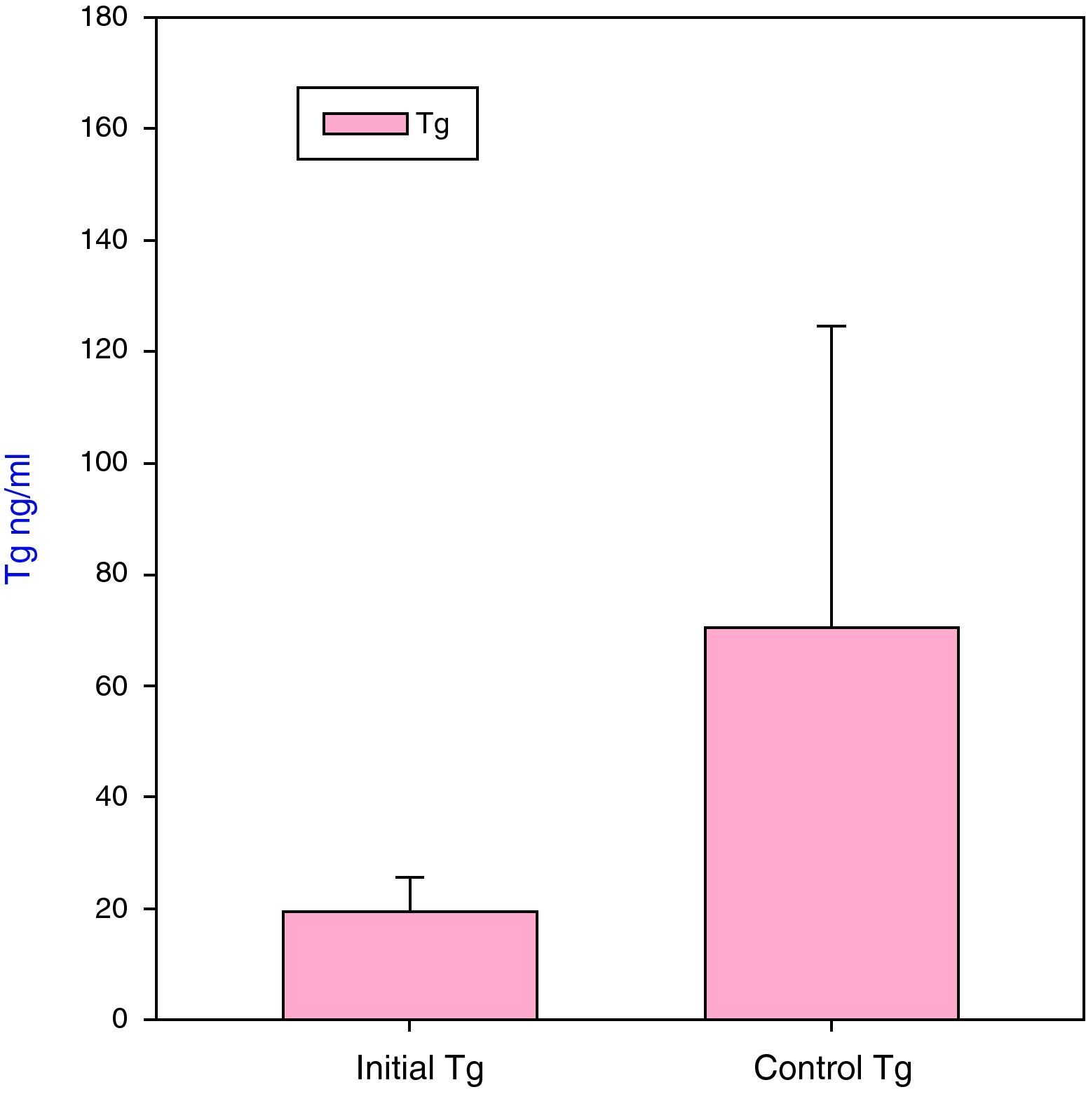
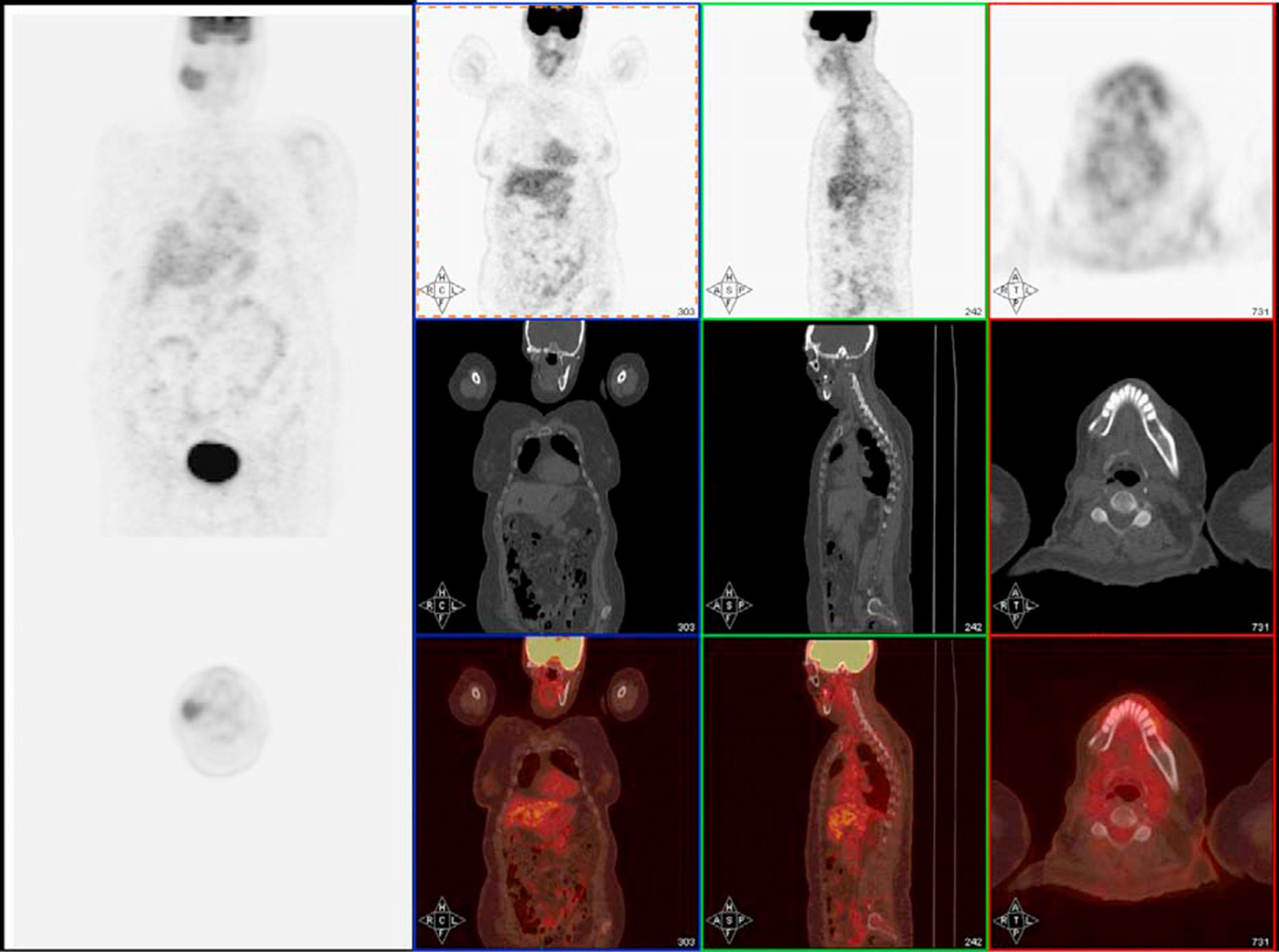
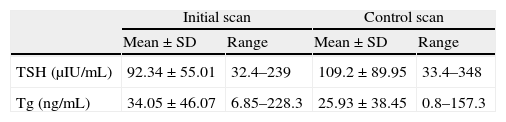
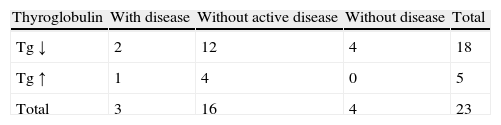
ResultsIn 18/23 patients, Tg decreased and in 5 it increased. Four patients (17%) were free of active disease (negative WBS Tg<2ng/mL). A total of 16 patients (70%) were free of disease according to the WBS but had elevated Tg. Three patients (13%) had disease and high levels of Tg, two of them with positive WBS and the third with positive 99mTc-MIBI scan and CT.
ConclusionsMost patients with a negative WBS, high Tg serum levels and negative PET-FDG had good evolution, with descending Tg levels, normal levels even being reached in a significant percentage of them.
Pretendemos analizar la evolución de los pacientes diagnosticados de carcinoma diferenciado de tiroides (CDT) con un rastreo de cuerpo completo con 131I-Na (RCC) negativo, una tiroglobulina sérica (Tg) elevada y una tomografía por emisión de positrones con 18F-fluordeoxiglucosa (PET-FDG) negativa.
Material y métodosSe estudiaron retrospectivamente a 23 pacientes diagnosticados y tratados de CDT, con edades comprendidas entre los 23 y 83 años, que entre enero de 2001 y diciembre de 2002 presentaron, un RCC negativo con valores de Tg en un rango de sospecha de recurrencia o metástasis (Tg>2ngr/mL con supresión de tratamiento hormonal) y una PET-FDG negativa. Tras un seguimiento clínico, radiológico y analítico de estos pacientes durante un periodo mínimo de 4 años, se vuelve a evaluar el estado de enfermedad con un RCC de control, observando a su vez la evolución de la Tg. Todos los RCC se realizaron con dosis diagnósticas de 185MBq de 131I-Na.
ResultadosEn 18 de los 23 pacientes la Tg descendió y en 5 ascendió. Cuatro pacientes (17%) estaban libres de enfermedad (RCC negativo y Tg<2ngr/mL). Dieciséis pacientes (70%) estaban libres de enfermedad según el RCC pero con cifras elevadas de Tg. En 3 pacientes (13%) se observó enfermedad y cifras elevadas de Tg, 2 con RCC positivo y el tercero con 99mTc-MIBI y TC positivos.
ConclusionesLa mayoría de los pacientes con RCC negativo, Tg elevada y PET-FDG negativa muestran una buena evolución, descendiendo los niveles de Tg e incluso alcanzando valores de normalidad en un porcentaje significativo de ellos.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora