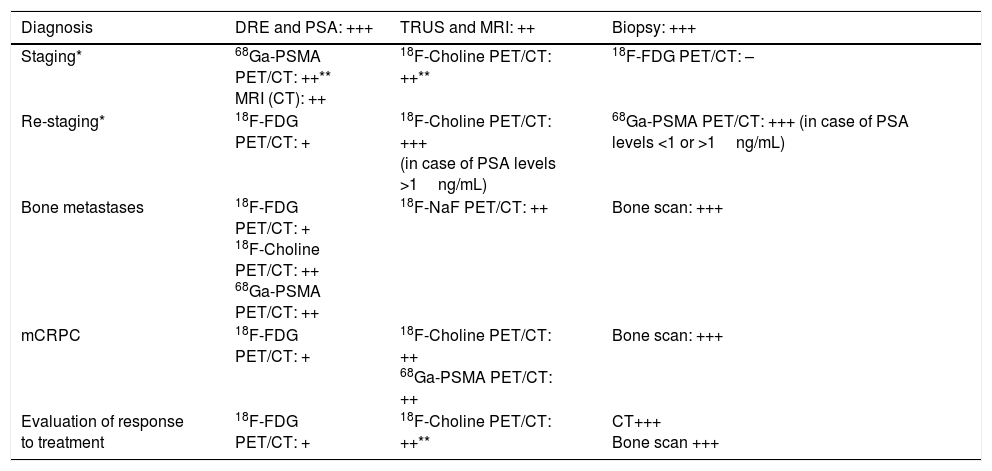
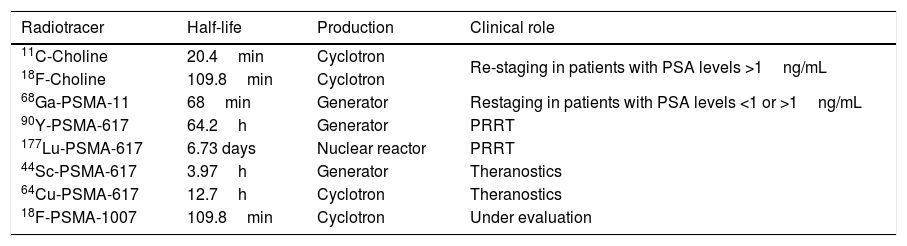
Prostate Cancer (PCa) represents the most common malignant tumor in men but according to the European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines, a mass screening for PCa diagnosis should not be performed due to over-diagnosis and over-treatment related problems. An early clinical diagnosis is possible, mainly based on digital rectal examination and Prostatic Specific Agent (PSA) testing. However, the only mandatory test to define the presence of PCa is ultrasound guided-biopsy, obtained on multiple samples, which has also a high prognostic value. In this context, diagnostic imaging plays an important role as confirmed by EAU that in a 2016 update of their guidelines on PCa stated the importance of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) with 11C- or 18F-choline combined with computed tomography (CT) to identify local relapse, lymph node involvement and metastatic spread at all stages. Consequently, in 2017, the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) together with the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) published new guidelines for 68Ga-Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) PET/CT to help physicians in the recommendation, execution and interpretation of PET/CT scans in patients with PCa. Thus, the aim of this “evidence paper” is to define the current diagnostic algorithm in PCa in order to increase the general level of confidence in approaching such a crucial topic.
El Cáncer de Próstata (CaP) representa el tumor maligno más frecuente en los varones pero, según las directrices de la European Association of Urology (EAU) no deben realizarse cribados masivos para el diagnóstico de CaP debido a problemas relacionados con el sobre-diagnóstico y sobre-tratamiento. El diagnóstico clínico precoz es posible, principalmente basado en el tacto rectal y la determinación del Antígeno Prostático Específico (PSA). Sin embargo, el único test que puede determinar la presencia de un CaP es la biopsia guiada por ecografía, obteniendo múltiples muestras, la cual tiene un elevado valor pronóstico. En este contexto, la imagen diagnóstica juega un importante papel tal como lo confirmó la EAU, que en una actualización de 2016 de su guía clínica sobre CaP estableció la importancia de la Tomografía por Emisión de positrones (PET) con 11C- o 18F-colina combinada con la Tomografía Computarizada (TC) para individualizar la recidiva local, la afectación de ganglios linfáticos y la diseminación metastásica en todos los estadios. En consecuencia, en 2017, la European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) junto con la Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) compartieron nuevas directrices para la PET/TC con 68Ga-Antígeno de Membrana Prostático Específico (PSMA) para ayudar a los médicos en la recomendación, realización e interpretación de los estudios PET/TC en pacientes con CaP. De esta manera, el objetivo de este “artículo de evidencia” es definir el algoritmo diagnóstico actual en el CaP para incrementar el nivel de confianza global en el enfoque de un tema tan crucial.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora