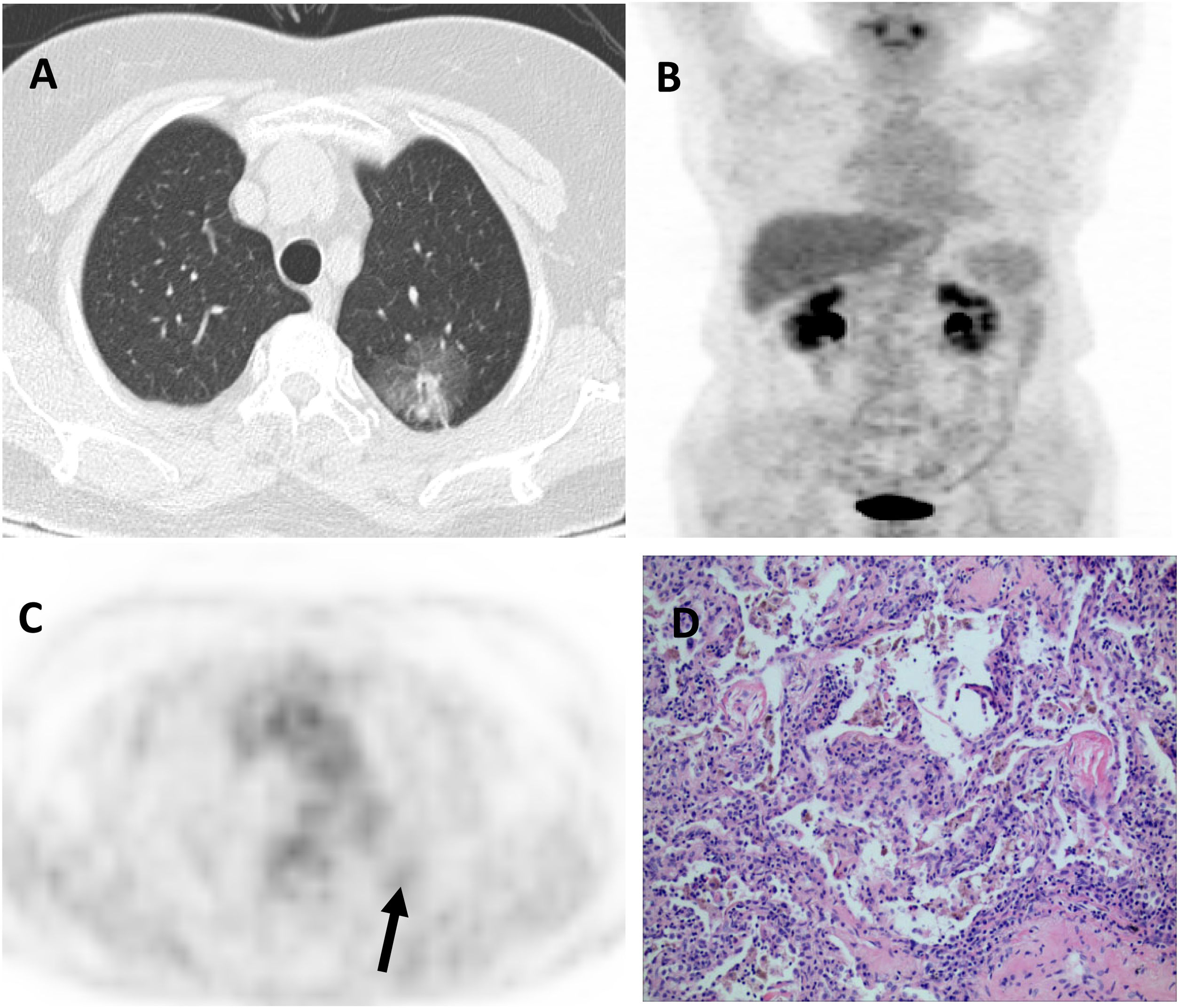
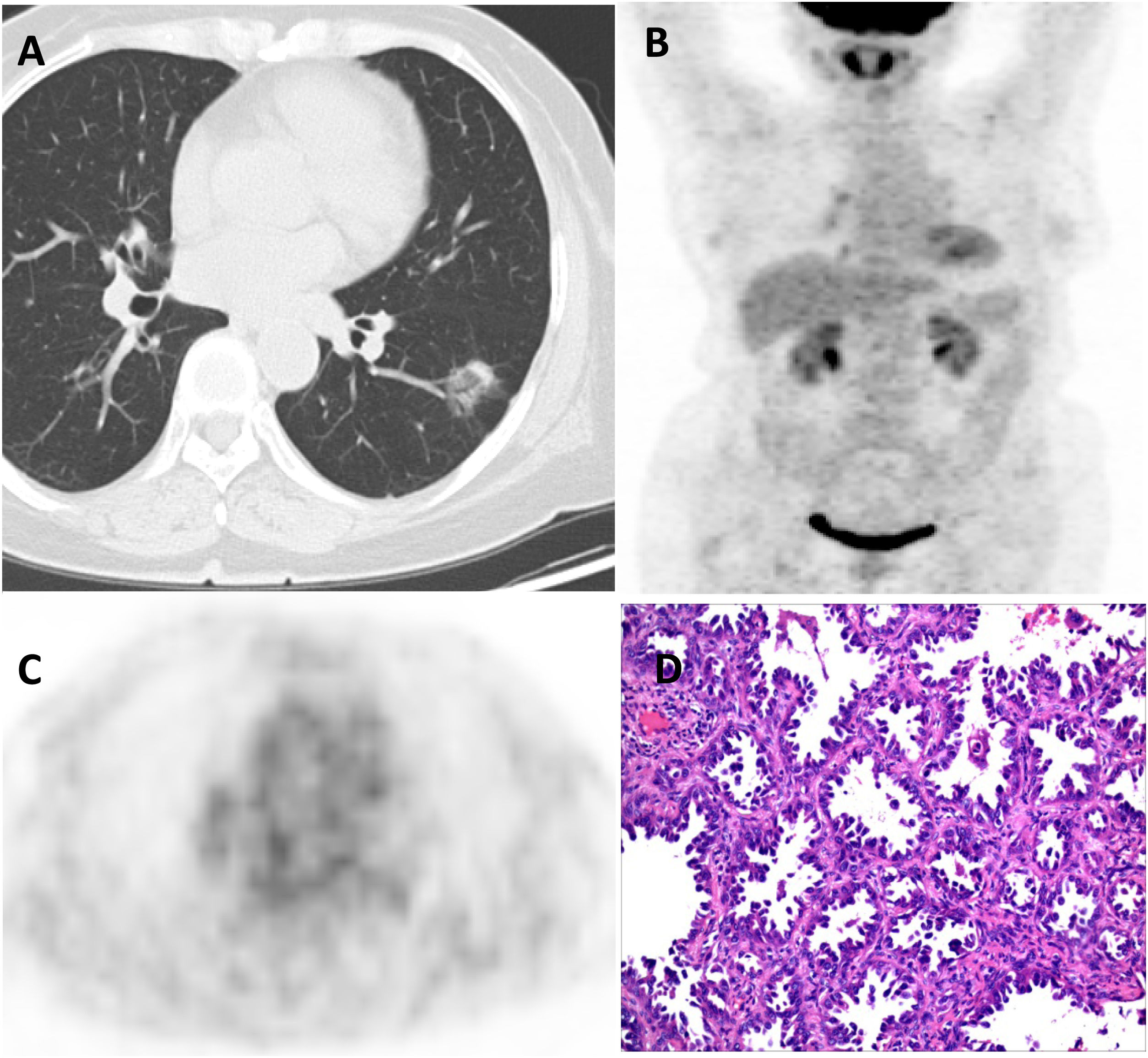
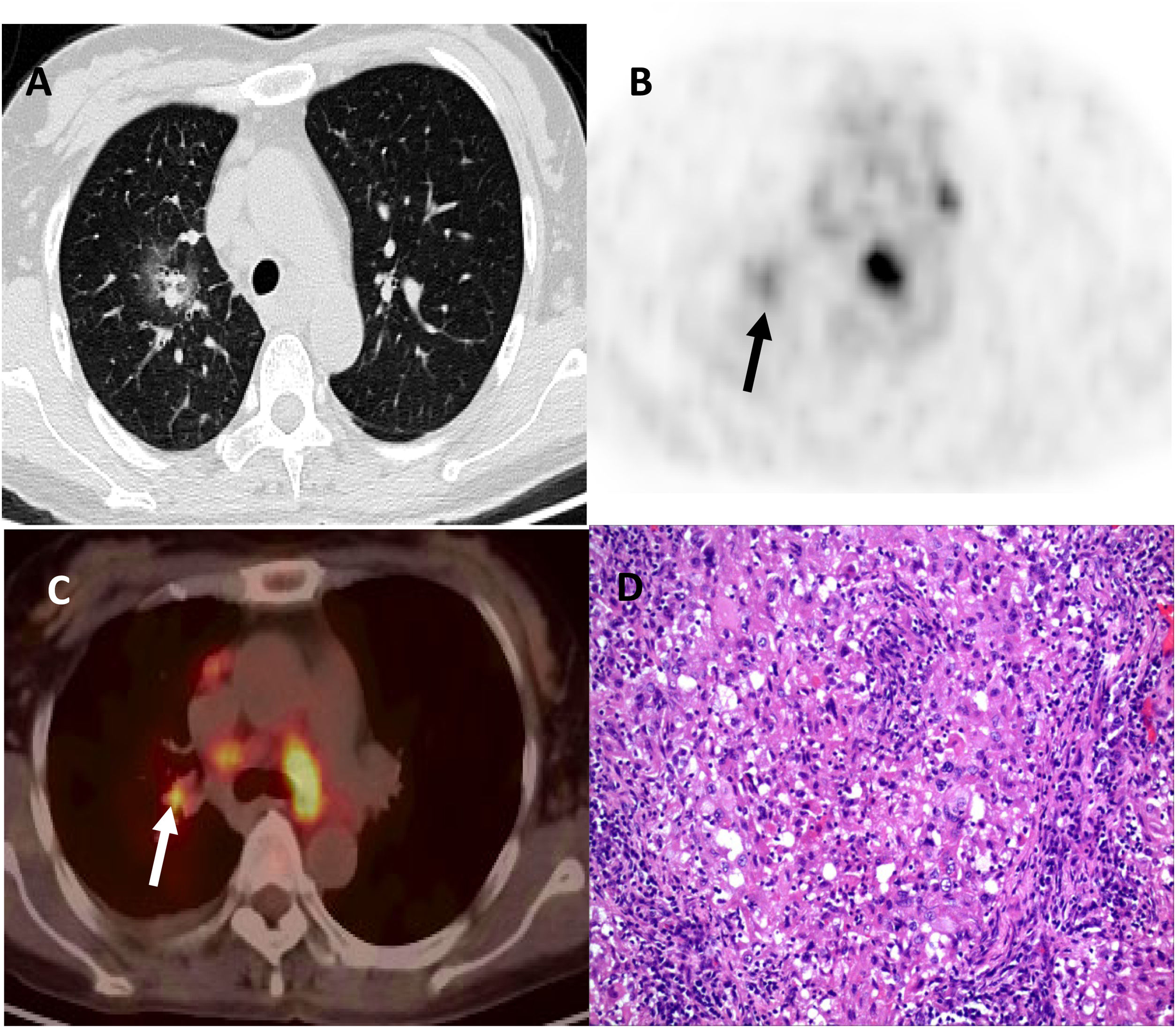
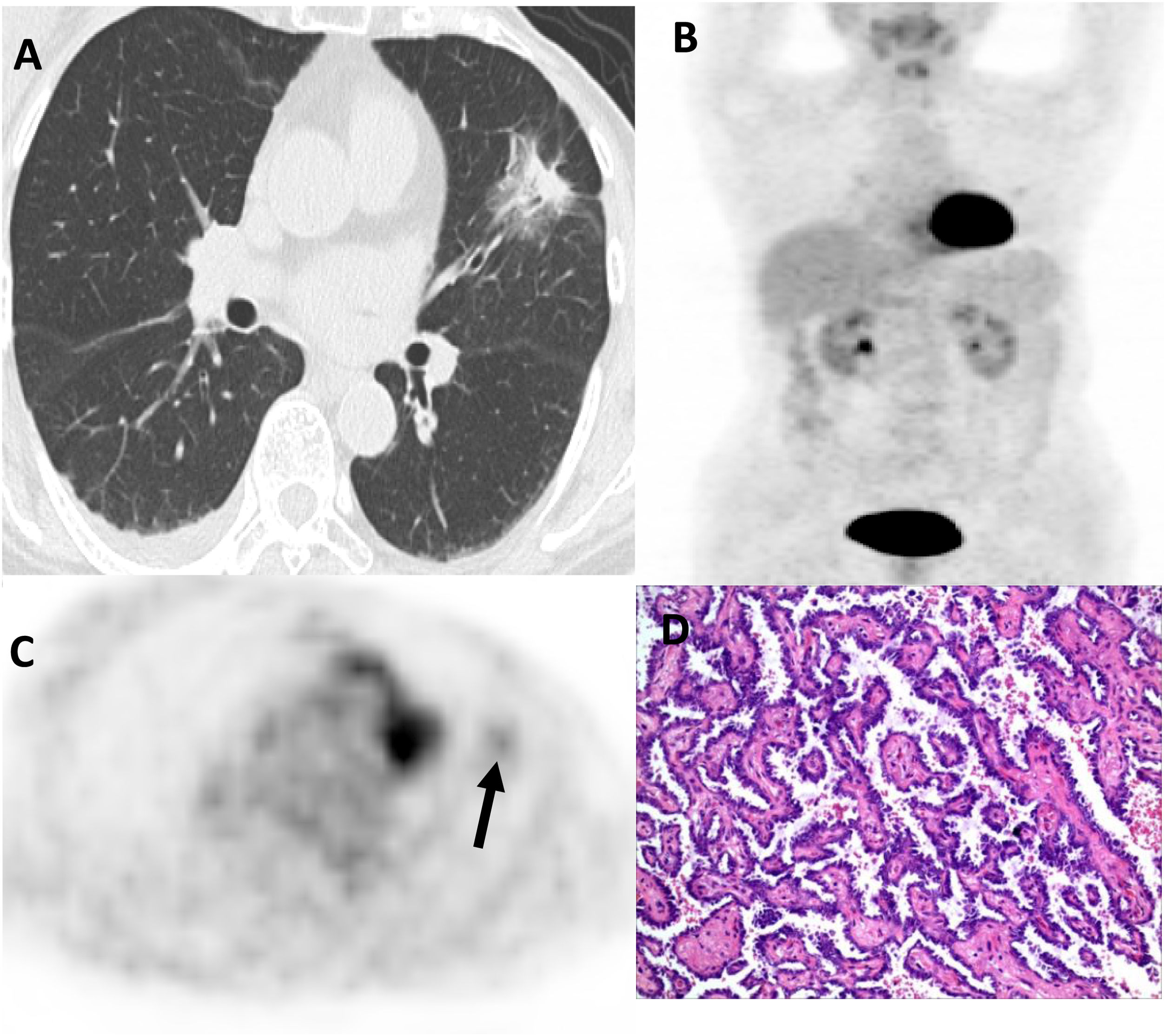
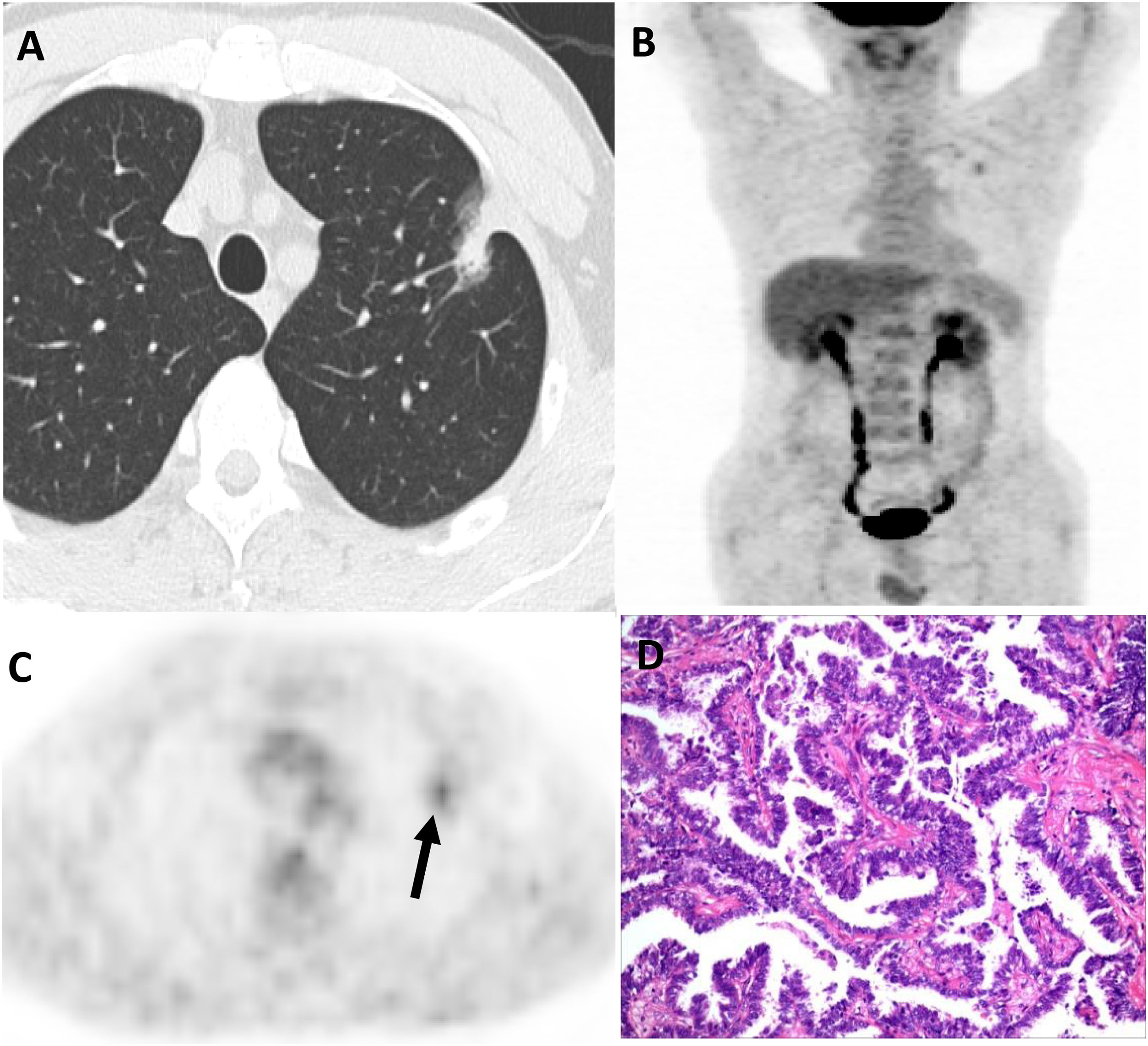
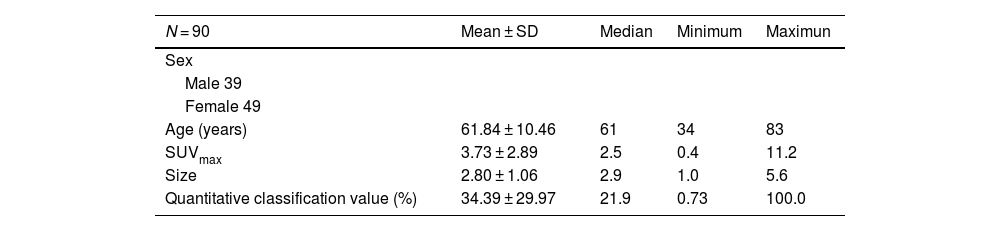
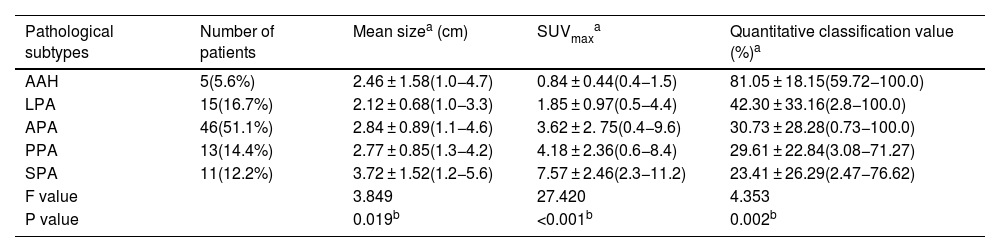
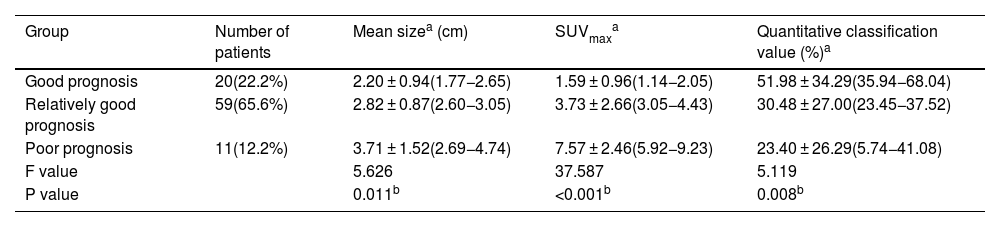
The aim of this study is to analyze the correlation between [18F]-FDG PET/CT (positron emission tomography/computed tomography) findings and pathological subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma with ground-glass opacity (GGO).
Materials and methods88 patients were included in this study, which underwent [18F]-FDG PET/CT and were finally diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma. A total of 90 GGO lesions were analyzed. The size and SUVmax of all lesions were measured, the proportion of solid components of GGO in lesions was calculated, and quantitative classification was performed. The above GGO lesions were divided into three groups based on the 2011 IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma pathological classification, namely good prognosis group, relatively good prognosis group and poor prognosis group. Chi-square test, independent sample t test, and analysis of variance were used for statistical analysis.
ResultsThere was a negative correlation between the SUVmax and quantitative classification value (r = −0.638, P < 0.001). Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH), acinar predominant adenocarcinoma (APA), lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma (LPA), papillary predominant adenocarcinoma (PPA), and solid predominant adenocarcinoma (SPA) had significant differences in GGO lesion size, SUVmax, and quantitative classification value (F = 3.849, P = 0.019; F = 27.420, P < 0.001; F = 4.353, P = 0.002). There were significant differences in GGO lesion size, SUVmax, and quantitative classification value among the good prognosis group, relatively good prognosis group, and poor prognosis group (F = 5.626, P = 0.011; F = 37.587, P < 0.001; F = 5.119, P = 0.008).
ConclusionGGO lesion size, SUVmax, and quantitative classification value are correlated with different pathological subtypes and can be used toevaluate the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma with GGO.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)