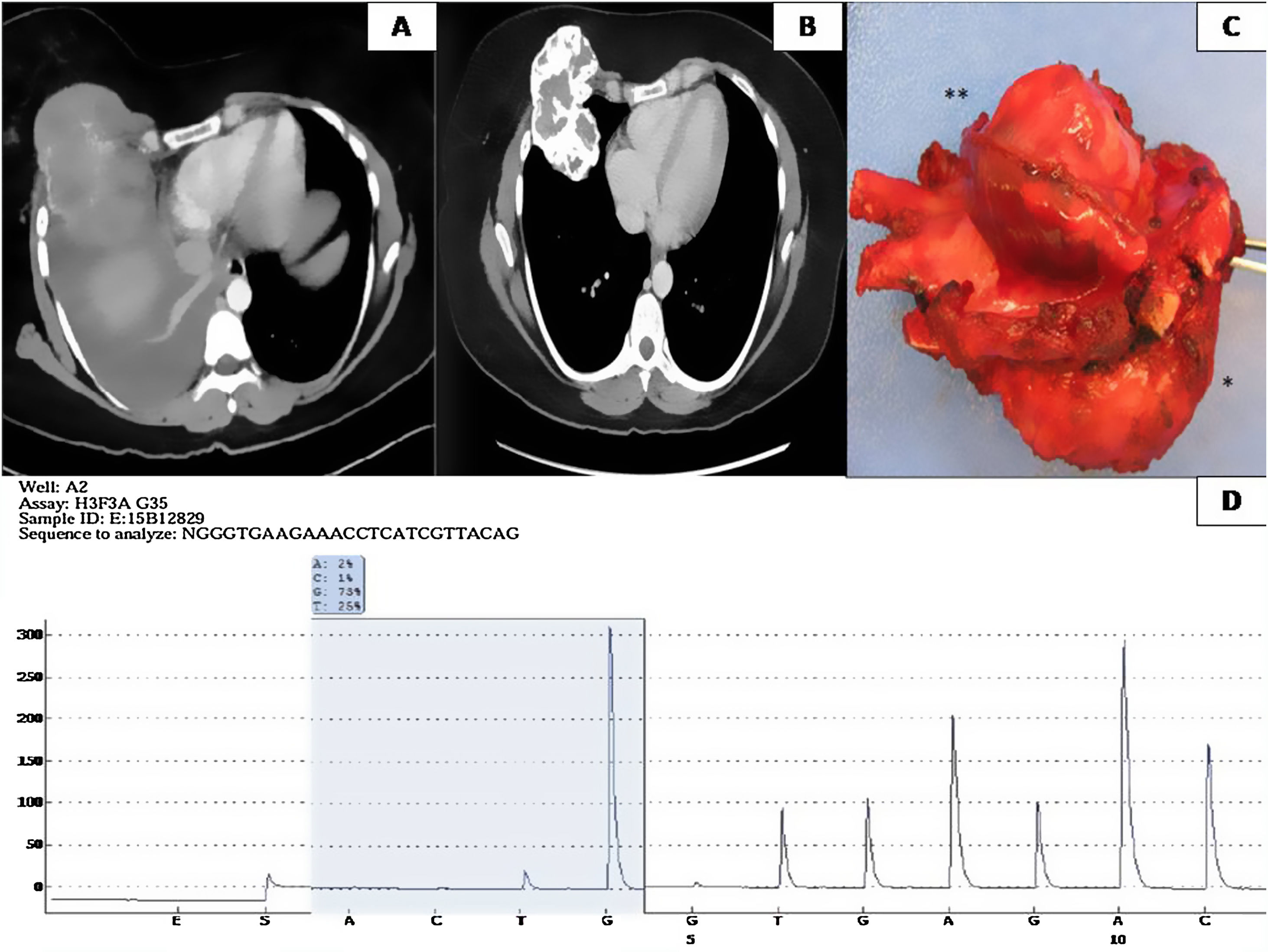
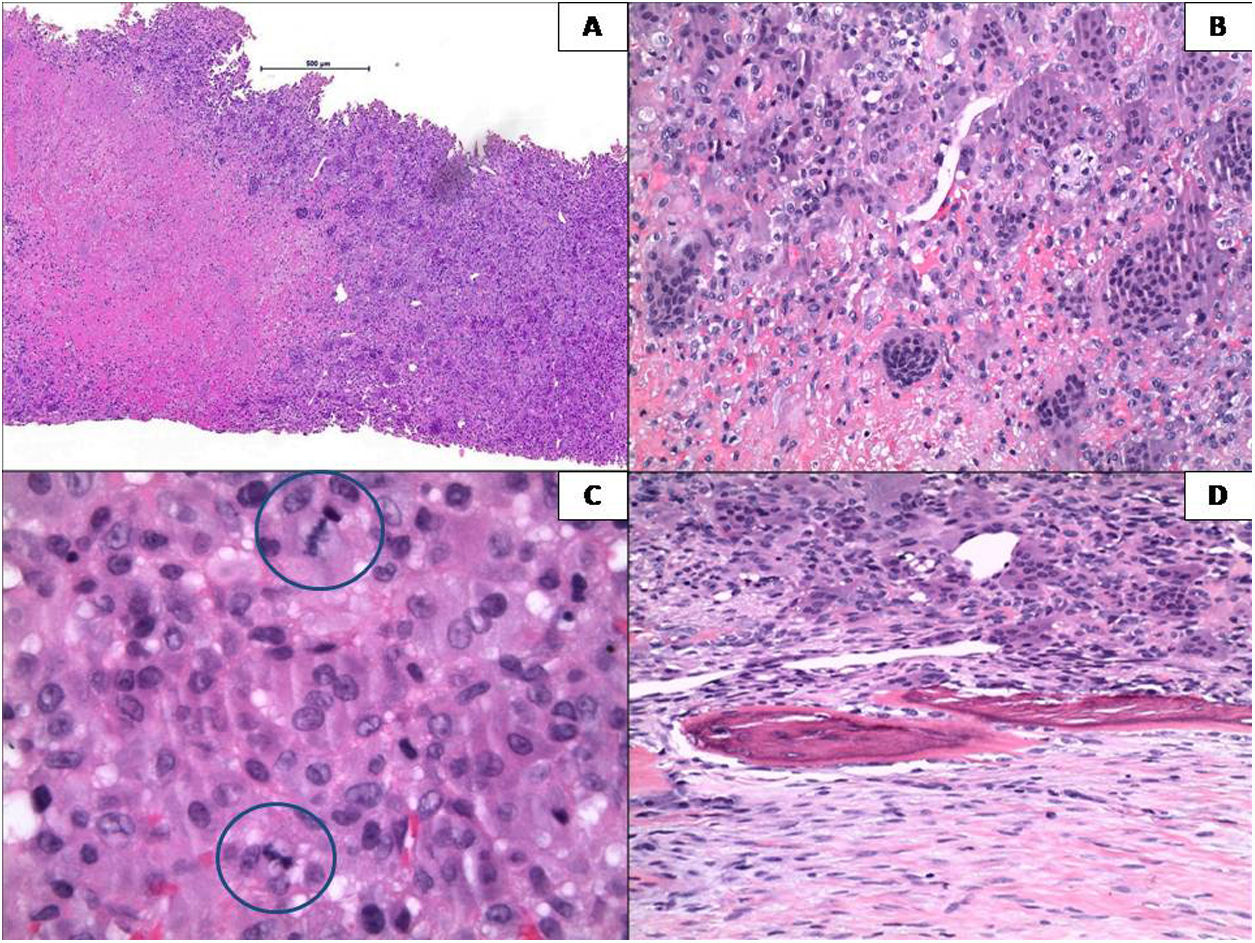
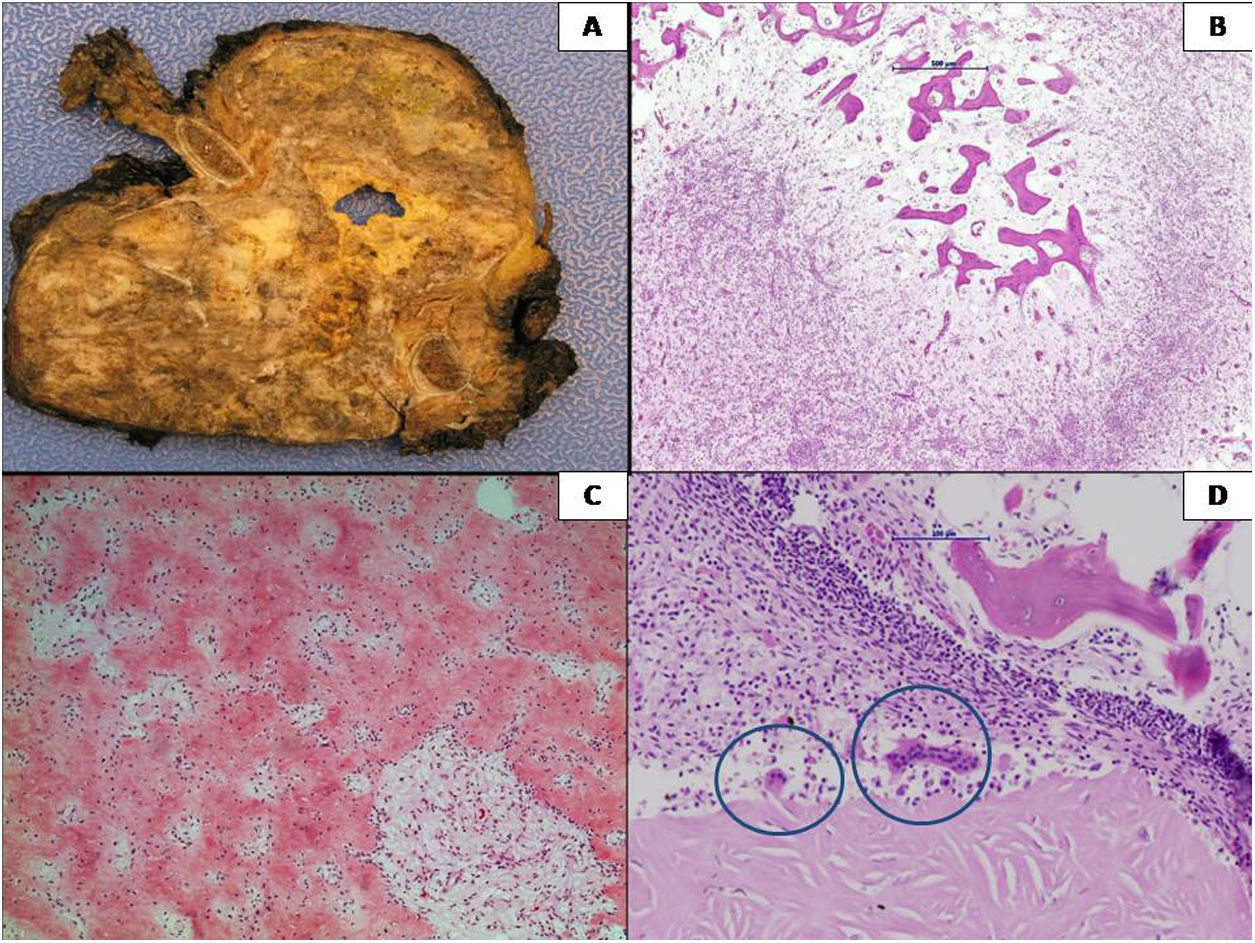
El tumor de células gigantes óseo (TCGO) representa el 4-5% de los tumores óseos primarios, se localiza en la epífisis de huesos largos, cuerpos vertebrales y huesos planos, y es más frecuente en el sexo femenino entre los 20 y 45 años. Presentamos el caso de una mujer de 31 años con dolor torácico de un mes de evolución. En la exploración física se palpó un nódulo en mama derecha y semiología de derrame pleural ipsilateral. El estudio mediante TAC torácica evidenció una masa infiltrante. La lesión fue biopsiada, permitiendo el diagnóstico de TCGO. Debido a la localización y a la morfología, se planteó un amplio diagnóstico diferencial. Adicionalmente, se detectó la mutación del gen de la histona H3F3A, reforzando el diagnóstico. Recibió tratamiento neoadyuvante con denosumab, haciendo posible la posterior resección quirúrgica de la lesión. En la pieza quirúrgica se observaron cambios histológicos, fuente de pitfalls diagnósticos.
Giant cell tumour of bone (GCTOB) accounts for 4-5% of all primary bone tumours and occurs most frequently in females between 20 and 45 years old. It is found in the epiphyses of the long bones, vertebral bodies and flat bones.
We report the case of a 31-year-old woman who presented with a one month history of thoracic pain. On examination, a mass was found in the right breast with signs of an ipsilateral pleural effusion. A thoracic CAT scan revealed an infiltrating mass which was subsequently biopsied and a GCTOB was diagnosed. Due to the localization and the morphology, a wide range of differential diagnoses were considered. Genetic studies detected a mutation of the gene H3F3A, supporting the original diagnosis. The patient underwent treatment with denosumab followed by surgical resection of the mass. The histopathology of the tumour revealed various histological changes which were a source of diagnostic pitfalls.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora