Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization rates in healthy patients are unclear. Previously published studies suggest that the fungus could play a role in the physiopathology and progression of chronic respiratory diseases.
AimsThe goal of this study was to determine the prevalence of colonization by this fungus in the lower respiratory tract of immunocompetent patients who are not at risk of dysbiosis.
MethodsThe presence of P. jirovecii was confirmed in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples from adults who underwent bronchoscopy for non-infectious reasons, had no immunosuppressive factors, and had not been on antibiotic treatment for at least one month. The results were compared with those obtained in the study on the presence of Pneumocystis in environmental dust samples obtained by swabbing surfaces in the participating subjects’ domestic settings. Real-time PCR was the technique used for detecting the fungus in both types of samples.
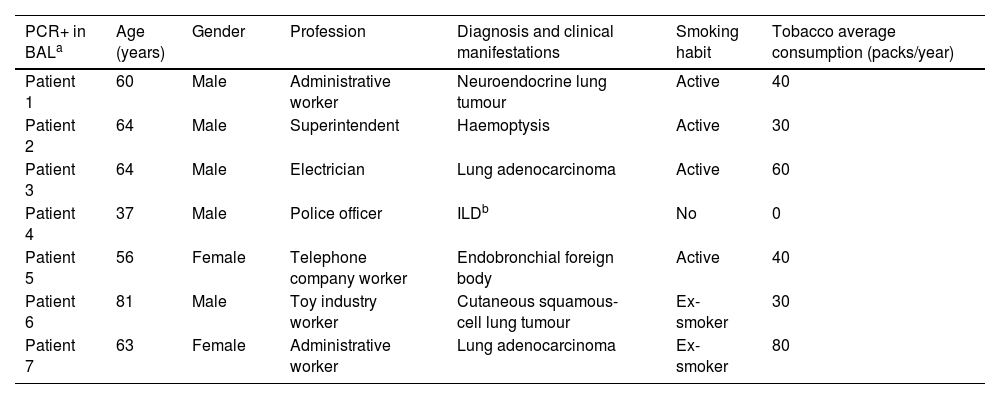
ResultsA total of 97 BAL samples and 49 domestic environment samples were studied. The medical reasons for needing a bronchoscopy were, mainly, the examination of both pulmonary neoplasm in 55 patients (57%) and diffuse interstitial lung disease in 21 patients (22%). The overall prevalence of P. jirovecii in our population was 7.22% in BAL samples and 0% in domestic samples.
ConclusionsThe presence of P. jirovecii in the lower respiratory tract is relevantly linked with the patient's immune status, not with an underlying pathology. Prevalence is low in immunocompetent individuals who do not have any infectious pathology and are not having antimicrobial treatments. Our results do not enable us to figure out which the environmental niche of P. jirovecii is.
Las tasas de colonización de Pneumocystis jirovecii en los pacientes sanos no están claras. Estudios previos sugieren que este hongo podría desempeñar un papel en la fisiopatología y en la progresión de enfermedades respiratorias crónicas.
ObjetivosEl objetivo de este estudio fue determinar la prevalencia de colonización por Pneumocystis en el tracto respiratorio inferior de los pacientes inmunocompetentes y sin riesgo de disbiosis.
MétodosLa presencia de P. jirovecii fue confirmada en muestras de lavado broncoalveolar (LBA) de adultos que se sometieron a una broncoscopia por causa no infecciosa, sin factores de inmunodepresión y que no hubiesen recibido tratamiento antibiótico al menos el mes previo. Los resultados se compararon con aquellos sobre la presencia de Pneumocystis en muestras de polvo de ambiente y superficies del entorno doméstico de los sujetos participantes. Para la detección en ambos tipos de muestras se utilizó PCR en tiempo real.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 97 muestras de LBA y 49 muestras del entorno doméstico. Las indicaciones para la broncoscopia fueron principalmente estudio de neoplasia pulmonar en 55 pacientes (57%) y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa en 21 pacientes (22%). La prevalencia total de P. jirovecii en nuestra población fue del 7,22% en las muestras de LBA y del 0% en las muestras domésticas.
ConclusionesLa presencia de P. jirovecii en el tracto respiratorio inferior está principalmente relacionada con el estado inmunológico del paciente, en lugar de con una enfermedad subyacente. La prevalencia en individuos inmunocompetentes, sin enfermedad infecciosa y sin tratamiento antimicrobiano reciente, es baja. Nuestros resultados no permiten dilucidar cuál es el nicho ambiental de P. jirovecii.