The helminth fauna of 8 introduced and 1 native species (Chirostoma jordani) of freshwater fishes from Xochimilco Lake in southern México City, Mexico, is studied for the first time. Five species of fishes from the families Goodeidae, Atherinopsidae and Poeciliidae were positive to helminth infections. Their helminth fauna consists of 5 species of parasites, including 1 adult tapeworm (Schyzocotyle acheilognathi), 2 trematode metacercariae (Posthodiplostomum minimum and Tylodelphys aztecae), and 2 larval stages of nematodes (Contracaecum sp. and Eustrongylides sp.). Schyzocotyle acheilognathi is recorded for the first time in the poeciliid Pseudoxiphophorus jonesii. The metacercariae of P. minimum and T. aztecae are the species that reached the highest prevalence, mean intensity and mean abundance values among the analyzed fish. The goodeid G. atripinnis exhibited the richest helminth fauna, since this species was parasitized by 5 helminth species. We hypothesize that the low helminth species richness of the Xochimilco Lake ichthyofauna, compared to that found in other water bodies in Central Mexico, might be the result of the biotic and abiotic conditions of the lake which are influenced by the pollution levels in the area. An alternative explanation would be that 8 of the 9 species of fishes analyzed are introduced species into Xochimilco Lake, and have not been in the system long enough to allow other helminth species potentially available to become established.
El presente trabajo representa el primer estudio sobre los helmintos de 8 especies de peces introducidas y una nativa (Chirostoma jordani) en el lago de Xochimilco, localizado al sur de la Ciudad de México, México. Cinco de las 9 especies estudiadas, representantes de Goodeidae, Atherinopsidae y Poeciliidae, se encontraron infectadas por helmintos. La fauna helmintológica de estos peces está compuesta por 5 especies de parásitos: un cestodo en estado adulto (Schyzocotyle acheilognathi), 2 larvas de tremátodos (Posthodiplostomum minimum y Tylodelphys aztecae) y 2 de nemátodos (Contracaecum sp. y Eustrongylides sp.). Se registra por primera vez S. acheilognathi en el poecílido Pseudoxiphophorus jonesii. Las metacercarias de P. minimum y T. aztecae son las especies que presentaron los valores más altos de prevalencia, abundancia e intensidad promedio en los peces estudiados. Por su parte, el goodeido Goodea atripinnis exhibió la mayor riqueza dado que se encontró parasitado por las 5 especies de helmintos. Se considera que la baja riqueza de especies de helmintos en peces del lago de Xochimilco, en comparación con otros cuerpos de agua del centro de México, podría atribuirse a las condiciones abióticas y bióticas existentes en la localidad, las cuales son influidas por los niveles de contaminación en la zona. Una hipótesis alternativa al punto referido anteriormente es el hecho de que 8 de las 9 especies de peces analizadas fueron introducidas al lago de Xochimilco, por lo que su tiempo de exposición a las especies de helmintos disponibles no ha sido suficiente.
Freshwater fishes are the vertebrate group most intensively studied for helminth parasites in Mexico. According to Pérez-Ponce de Leo¿n, Garci¿a-Prieto, and Mendoza-Garfias (2011), almost 51% of the freshwater fish species have been analyzed, and almost 300 helminth species have been recorded. Even though the inventory is nearing completion (see discussion in Pérez-Ponce de León & Choudhury, 2010), the helminth parasite diversity of freshwater fishes in many areas of the country has not been documented. This does not necessarily mean that new species will be described at the same rate, but the distribution ranges of the known species will be documented more accurately by conducting survey work in unexplored areas. Interestingly, even though Xochimilco Lake lies within México City, their freshwater fish helminth fauna had not been studied. Actually, helminthological studies of vertebrates in this area are very scarce. Only 6 species of amphibians and reptiles, and 1 species of mammal have been studied. From these hosts 29 helminth species were reported (see García-Prieto, Falcón-Ordaz, & Guzmán-Cornejo, 2012; Paredes-León, García-Prieto, Guzmán-Cornejo, León-Règagnon, & Pérez-Ortíz, 2008). The aim of this note is to report the endohelminth parasite fauna of some freshwater fishes in Xochimilco Lake, and to provide the parameters of the infections produced by each helminth species.
Xochimilco Lake is located in the southeast part of México City and consists of an interconnected system of 7 lakes and 9 canals distributed within a Natural Protected Area known as “Ejidos de Xochimilco y San Gregorio Atlapulco” (Tovar-Garza, 2014). Samples were obtained between February and August 2012 in 4 localities: canal A: 19°16'58.115''N, 99°6'8.160''W; canal B: 19°16'34.090''N, 99°5'49.466''W; “pista de canotaje, Virgilio Uribe”: 19°16'2''N, 99°6'16.920''W, and “Área Turística #27”: 19°15'36.974''N, 99°5'5.797''W. In total, 277 individual fish belonging to 9 species were collected with seine and casting nets: 1 native species belonging to Atherinopsidae: Chirostoma jordani Woolman, 1894 (“charal”, n=30) and 8 introduced species of the families Goodeidae: Goodea atripinnis Jordan, 1880 (“tiro”, n=98); Poeciliidae: Gambusia sp. (“guayacón”, n=5), Pseudoxiphophorus jonesii Günther, 1874 (“guatopote”, n=12), Poecilia mexicana Steindachner, 1863 (“topote del Atlántico”, n=7), Poecilopsis gracilis Heckel, 1848 (“guatopote jarocho”, n=49), and Xiphophorus hellerii Heckel, 1848 (“espada”, n=47); Cichlidae: Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus 1758 (“tilapia”, n=15), and Cyprinidae: Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus 1758 (“carpa común”, n=14) (see Bojórquez & Arana, 2014).
Fish were euthanized by spinal severance (pithing) following AVMA (2013) and immediately dissected. All internal organs were separated in Petri dishes with 0.65% saline. Helminths were collected, counted in situ and fixed in 4% (steaming) formalin and preserved in vials with 70% alcohol. Platyhelminthes were stained with Mayer's paracarmine and Delafield's hematoxylin, and mounted on permanent slides with Canada balsam. Nematodes were cleared with lactophenol in semipermanent slides. Taxonomic identification was achieved by using specialized literature and keys to species identification (Anderson, Chabaud, & Willmott, 2009; Gibson, Jones, & Bray, 2002; Scholz, 1997; Yamaguti, 1971). Specimens were deposited in the CNHE with the accession numbers: 9317-9325 (P. minimum), 9326-9332 (T. aztecae), 9333-9336 (S. acheilognathi), 9338-9339 (Contracaecum sp.), 9337 (Eustrongylides sp.). Infection parameters, i.e., prevalence, mean intensity and mean abundance were calculated following Bush, Lafferty, Lotz, and Shostak (1997).
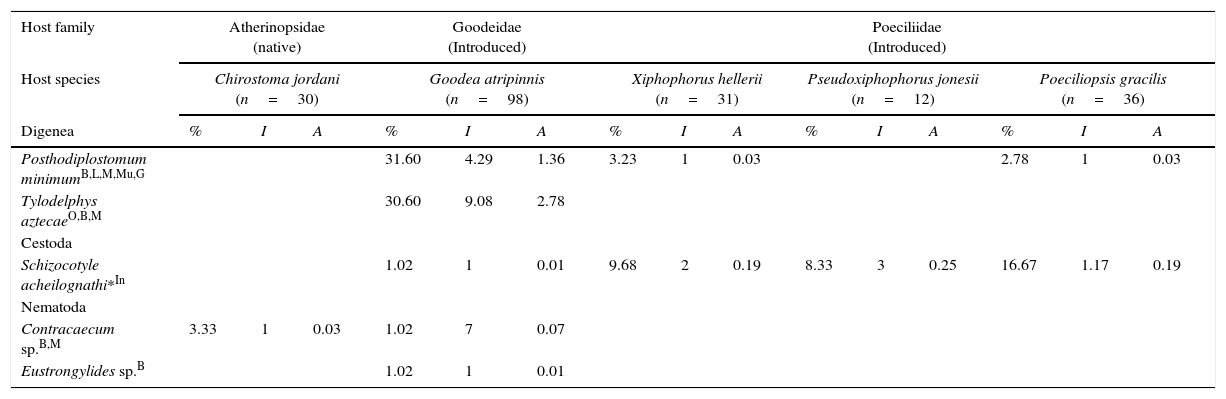
Four host species were uninfected: O. niloticus, C. carpio, Gambusia sp., and P. mexicana; the remaining 5 species were parasitized at least by 1 helminth species, i.e., 1 species of Goodeidae (G. atripinnis), 1 of Atherinopsidae (C. jordani) and 3 of Poeciliidae (X. hellerii, P. jonessii, and P. gracilis) (Table 1). The helminth fauna consist of 5 taxa, including the adult tapeworm Schyzocotyle acheilognathi (Yamaguti, 1934), 2 larval trematodes [Posthodiplostomum minimum (MacCallum, 1921) Dubois, 1936, Tylodelphys aztecae García-Varela, Sereno-Uribe, Pinacho-Pinacho, Hernández- Cruz and Pérez-Ponce de León, 2016] and 2 larval stages of nematodes (Contracaecum sp. and Eustrongylides sp.). The highest endohelminth species richness was found in G. atripinnis, since this goodeid was parasitized by all helminth taxa that we record in this study; in contrast, the atherinopsid C. jordani and the poeciliid P. jonesii each harbored a single helminth taxon, Contracaecum sp. and S. acheilognathi, respectively. Posthoplostomum minimum and S. acheilognathi were the most common taxa, since they were found in 3 and 4 of the 9 species of freshwater fish studied in this survey, respectively (Table 1). Four taxa (P. minimum, T. aztecae, Contracaecum sp. and Eustrongylides sp.) are allogenic species, i.e., they complete their life cycles when fish-eating birds feed upon freshwater fish. The metacercariae of P. minimum and T. aztecae reached the highest prevalence, mean intensity and mean abundance levels (Table 1).
Endohelminths of 5 species of freshwater fish in Xochimilco Lake, Mexico.
| Host family | Atherinopsidae (native) | Goodeidae (Introduced) | Poeciliidae (Introduced) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host species | Chirostoma jordani (n=30) | Goodea atripinnis (n=98) | Xiphophorus hellerii (n=31) | Pseudoxiphophorus jonesii (n=12) | Poeciliopsis gracilis (n=36) | ||||||||||
| Digenea | % | I | A | % | I | A | % | I | A | % | I | A | % | I | A |
| Posthodiplostomum minimumB,L,M,Mu,G | 31.60 | 4.29 | 1.36 | 3.23 | 1 | 0.03 | 2.78 | 1 | 0.03 | ||||||
| Tylodelphys aztecaeO,B,M | 30.60 | 9.08 | 2.78 | ||||||||||||
| Cestoda | |||||||||||||||
| Schizocotyle acheilognathi*In | 1.02 | 1 | 0.01 | 9.68 | 2 | 0.19 | 8.33 | 3 | 0.25 | 16.67 | 1.17 | 0.19 | |||
| Nematoda | |||||||||||||||
| Contracaecum sp.B,M | 3.33 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.02 | 7 | 0.07 | |||||||||
| Eustrongylides sp.B | 1.02 | 1 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
n, sample size; %, prevalence; I, mean intensity; A, mean abundance; B, body cavity; L, liver; M, mesentery; Mu, muscle; G, gonads; O, operculum; In, intestine; *, adult.
Xochimilco Lake represents a new locality record for the 5 helminth species found. The cestode S. acheilognathi is recorded for the first time as a parasite of P. jonesii and was the most widely distributed helminth species among the fishes of the lake. This result is consistent with the generalist condition of the tapeworm, which is the adult worm with the highest number of freshwater fish infected in Mexico (Rojas-Sánchez & García-Prieto, 2008).
Our study reports 5 endohelminth species of freshwater fishes from Xochimilco Lake which reveals a depauperate helminth community. The low richness values found in fishes from Xochimilco Lake contrast with the endohelminth fauna of the same fish species in other water bodies of Mexico. For instance, the atherinopsid C. jordani is infected by 10 species of endohelminth parasites in Cuitzeo Lake, Michoacán (Lira-Guerrero, García-Prieto, & Pérez-Ponce de León, 2008), while in Xochimilco Lake it was infected by only 1 species; in the same way, the “tiro” G. atripinnis and the “topote del Atlántico” P. gracilis, which are parasitized by 5 and 2 helminth taxa in this study, respectively, contrast with the 8 and 5 species that have been recorded for the same species of hosts in Pátzcuaro Lake, Michoacán (Pérez-Ponce de León, García-Prieto, León-Règagnon, & Choudhury, 2000) and Metztitlán Lake, Hidalgo (Monks, Zárate-Ramírez, & Pulido-Flores, 2005). A possible explanation to the different endohelminth species richness found among lakes can be the biotic and abiotic conditions of Xochimilco Lake compared with those found in Michoacán and Hidalgo lakes. Particularly in Xochimilco Lake, there is a severe anthropogenic influence, including high levels of contamination (Narchi, 2013; Vega-Rojas, 2010). Pollution is the result of the urbanization of the surrounding area of the canals and lakes, since Xochimilco actually lies within the city and some part of the sewage of the city is poured into the lake (Aguayo-Ríos, 2008). Khan and Thulin (1991) pointed out that chronic exposure to pollutants over a time causes biochemical, physiological and behavioral host changes all of which can influence infection levels. These authors also considered that pollutants can affect the free living forms of some species of helminths or intermediate host survival. For these reasons, fish parasites have been proposed as bio-indicators of the environmental health of aquatic ecosystems (see Pérez-Ponce de León, 2014 and references therein).
An alternative hypothesis to explain the low helminth species richness is the fact 8 of the 9 fish species analyzed are introduced species in Xochimilco Lake; Torchin, Lafferty, Dobson, McKenzie, and Kuris (2003) analyzed the differences in parasite infection levels between native and introduced fish species concluding that richness and prevalence found in native populations are greater than that found in exotic populations. Results obtained in our study seem to contradict that suggested pattern; Chirostoma jordani, the only native species included in our work, hosted only 1 helminth species, whereas G. atripinnis (an introduced species) recorded the highest species richness. However, the difference in parasite species richness among both fish species could be attributed to the sample size of G. atripinnis, which is more than 3 times greater than that of C. jordani; the analysis of a large number of hosts of the introduced species, allowed to detect accidental helminth species with very low values of prevalence and mean intensity (Table 1). More rigorous comparative studies are necessary to establish accurately the factors that determine the low richness values found in fishes from Xochimilco Lake.
A common characteristic between the endohelminths of fish in Xochimilco and other water bodies of Central Mexico is the predominance of allogenic species which complete their life cycles in fish-eating birds (Hoffman, 1999; Olsen, 1986; Yamaguti, 1975; Yorke & Maplestone, 1962) thus, fish play an important role for the transmission of these helminth species to definitive host higher up in the food chain. The presence of allogenic species is the result of the eutrophication process observed in all these aquatic ecosystems, which favors the vegetation growth that provide suitable conditions for the establishment of bird populations, maintaining the life cycles of the allogenic species in the system. A similar conclusion was previously reached by Espinosa-Huerta, García-Prieto, and Pérez-Ponce de León (1996) when comparing the helminth parasite communities of the atherinopsid C. attenuatum in 2 lakes with different eutrophication levels (Pátzcuaro and Zirahuén). The presence of permanent populations of fish-eating birds, as well as the abundance of intermediate host populations (snails) in these areas, allows species as P. minimum and T. aztecae to reach high prevalence and mean abundance values as seen in this and in other studies (e.g., Pérez-Ponce de León et al., 2000; Martínez-Aquino, Mendoza-Palmero, Aguilar-Aguilar, & Pérez-Ponce de León, 2014). Likewise, snail abundance along with some biological traits of the trematodes as the intramollusc asexual reproduction (increasing the infective potential of these species) and their low host specificity levels (which allows incorporating a greater number of species of fish as intermediate hosts to access the definitive host), contribute to explain the dominance of these helminths in the region.
This paper provides a background to allow biologist to continue to analyze the host–parasite interactions between helminths and fish in the locality. This information would be very useful in the future since the parasitological data can be used to monitor the ecosystem health (Pérez-Ponce de León, 2014). Thus, parasites can provide an independent source of information about the environmental conditions of the lake, and the implications for the conservation of the aquatic fauna.
We thank Luis Zambrano, Armando Tovar Garza and all the students of the Laboratorio de Restauración Ecológica, Instituto de Biología, UNAM, México City, and the fisherman Roberto Altamirano for their help during fieldwork. We also acknowledge Héctor Espinosa, Christian Lámbarri and Pavél Gutiérrez for the fish identification and for incorporating the specimens into the Colección Nacional de Peces, Instituto de Biología, UNAM, México City. This study was partially funded by the program PAPIIT-UNAMIN204514 to GPPL.
Peer Review under the responsibility of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.