Female urinary incontinence is a common problem in middle-aged women. Up to 50% of the adult female population have stress urinary incontinence, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in these women is around 50%. The aim of this study is to evaluate sexual function before and after a urinary incontinence surgical procedure using tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) or transobturator tape (TOT).
Material and methodsA prospective study was conducted on 22 sexually active women who underwent TVT or TOT procedures for stress urinary incontinence by assessing the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) before, and 3 and 6 months after surgery.
ResultsThe study included 22 women with a mean age of 48.3±6.46 years, who underwent TVT or TOT for stress urinary incontinence. The median abdominal leak point pressure (ALPP) was 85.5±17.2cm H2O, with a median pelvic organ prolapse quantification (POPQ) of 0.28±0.45. Female sexual function assessed with the FSFI improved in all the aspects of the questionnaire. The mean total FSFI score before surgery was 21.57±3.53, at 3 months after surgery it was 26.05±3 (P=0.0001), and at 6 months post-op it was 27.28±5.03 (P=0.001). Coital incontinence improved in 90% of the participants, and 95% responded that they were satisfied with the results of the procedure.
ConclusionSexual function in women who underwent TVT and TOT procedures improved considerably up to 6 months after surgery. Coital urinary incontinence improved in most of the women. Despite the evidence being variable as regards the outcomes in terms of sexual function after TVT and TOT, it is considered that these procedures substantially improve sexual function in women with stress urinary incontinence.
La incontinencia urinaria femenina es un problema frecuente. La incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo es responsable del 50% de los casos y afecta considerablemente la calidad de vida y la función sexual de las mujeres. La prevalencia de disfunción sexual en mujeres con incontinencia urinaria asciende hasta el 50%. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la función sexual femenina antes y después de la cirugía antiincontinencia con cintas vaginales libres de tensión.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo multicéntrico que mediante el cuestionario Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) evalúa la función sexual en 22 mujeres antes de la cirugía con cinta vaginal libre de tensión transvaginales (TVT) y transobturadoras (TOT) y hace seguimiento a los 3 y a los 6 meses después.
ResultadosUn total de 22 mujeres fueron tratadas mediante cirugía antiincontinencia con cintas vaginales libres de tensión. Su edad media de era de 48,3±6,46 años; el Abdominal Leak Point Pressure (ALPP) medio 85,5±17,2cm H2O y el POPq medio de 0,28±0,45. Encontramos que la función sexual femenina evaluada con el FSFI mejoró en todos los dominios, el puntaje total del FSFI prequirúrgico fue 21,57±3,53, mientras que a los 3 meses de la cirugía fue 26,05±3 con una p=0,0001 y a los 6 meses de la cirugía fue de 27,28±5,03 con una p=0,001. En cuanto al escape de orina durante el coito, mejoró en el 90% de las pacientes, y el 95% refirieron sentirse satisfechas con el procedimiento.
ConclusionesLa función sexual en mujeres llevadas a cirugía antiincontinencia con cintas vaginales libres de tensión mejora notablemente con respecto a la evaluación prequirúrgica. La pérdida de orina durante el coito se resuelve en la mayoría de los casos. A pesar de que la evidencia sea variable, consideramos que la cirugía antiincontinencia puede mejorar considerablemente la función sexual en mujeres con incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo.
Female urinary incontinence is a frequent problem and affects many women worldwide. Stress urinary incontinence is responsible for 50% of all cases and is an important parameter of deterioration in the quality of life of many women, including the area of sexual function.1 The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women with urinary incontinence ranges from 19 to 50%.2 This must be understood as a multicausal and multidimensional problem that has psychological, biological, and interpersonal components. It is widely accepted that urinary incontinence has an adverse effect on the sexual function of women. This is explained by different mechanisms: the chronic irritative process of urine on the vaginal mucosa predisposes to different skin problems that generate pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia); fear of urine leakage during intercourse, which has a prevalence of 10–56%, and causes the postponement of the sexual act due to shame or discomfort with the partner; alteration in desire and sexual interest with loss of the arousal phase and significant decrease in vaginal lubrication, which causes discomfort and pain during coitus, and, finally, loss of self-esteem or psychological stress, which leads to perpetuating the cycle. The last two points are also frequent complaints of women with sexual dysfunction in the absence of urinary incontinence.3–5
Taking into account that approximately 4–10% of these women will undergo an anti-incontinence procedure at some point in their life1 and that the prevalence of sexual dysfunction is approximately 50% in women with some degree of incontinence,2 the increasing use of anti-incontinence techniques, such as tension-free transvaginal (TVT) or transobturator (TOT) tapes, should aim to improve the quality of life. Considering that female sexual dysfunction is caused by urinary incontinence, these techniques—in theory—should have a positive effect in the sexual area too. However, the evidence to date is controversial, as some studies report that sexual function following anti-incontinence surgery has deteriorated,6–8 while others evidence an obvious improvement in sexual function after the surgical procedure.9,10 Up to date in Colombia there is no evidence regarding what happens to the female sexual function after performing this type of procedures.
The aim of this article is to determine whether female sexual function is positively or negatively affected by anti-incontinence surgery with tension-free vaginal tapes in women with stress urinary incontinence.
Methods and materialsThe idea of this study was born as part of our clinical practice, since it is common in outpatient urology consultation that women, when the pathophysiology of stress urinary incontinence and how it might negatively affect sexual function is explained to them, show great interest in the postoperative outcomes and expected results in the sexual area. Without any evidence in our country regarding the sexual function of women who underwent anti-incontinence surgery with tension-free tapes, it is difficult to make objective recommendations in our population.
The study population consisted of 22 women diagnosed with stress urinary incontinence based on clinical history and urodynamic testing, who were considered, during the outpatient urology consultation, candidates for anti-incontinence surgery with TVT or TOT. All patients underwent a preoperative evaluation that included physical examination, gynecological examination with assessment of pelvic organ prolapse (POP-Q). Age, parity, body mass index, and clinical history were recorded, and they all underwent urodynamic study. This is a multicenter study that began recruiting patients in February 2012 and was concluded in December 2015. The study was conducted at the Hospital Universitario San Ignacio and the Clínica Colsubsidio in the city of Bogotá and at the Clínica Diagnósticos Especializados S.A. (DESA) in the city of Cali. The study was previously approved by the respective Ethics and Research Committees of the different health centers. Surgical procedures were performed by professors of the Urology and Gynecology Unit of each of the departments with the surgical technique that has been standardized for several years, without any modification.
Patients were divided into two groups according to pre-established criteria for using the transobturator or transvaginal technique. Patients were invited to participate in the study after a clear explanation of its characteristics, risks, and benefits, through an agreement to participate. The inclusion criteria of the study were reviewed: candidates for anti-incontinence surgery with TOT or TVT; urodynamics that evidenced stress urinary incontinence with Abdominal Leak Point Pressure (ALPP) greater than 60cm H2O according to the McGuire classification; negative urine culture; presence of defects in the anterior, apical, and posterior compartments according to the POP-Q classification up to grade ii–iii, and sexually active women. Women with evidence of intrinsic sphincter deficiency (defined as ALPP less than 60cm H2O with little or no urethral mobility) were excluded, as well as patients with a high probability of loss to follow-up or with low engagement (located in rural areas), patients presenting with pregnancy, coagulopathies, or mental deficiencies that prevented understanding the conditions and objectives of the program, and those who declared that they did not want to participate in the study.
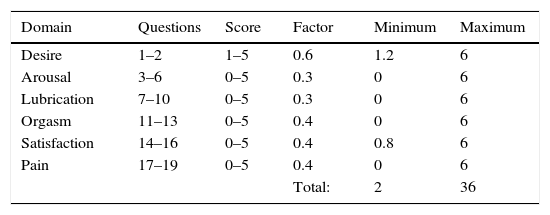
Patients were summoned on the day of the surgery according to the schedule of activities. Demographic data were recorded and a follow-up sheet was created for each patient. All patients were given the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) questionnaire validated in English and Spanish. This questionnaire consists of 19 questions that evaluate six domains: desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain during sexual intercourse. Each question has 5 or 6 answer options, with a score ranging from 0 to 5. The sum of the scores of each domain is multiplied by a factor and the final score is the arithmetic sum of the domains: the higher the score, the better the sexual function. The total score ranges from 2 to 36 (Table 1). This questionnaire had to be completed before the procedure. Postoperative control was done at 8 days and patients were recommended to resume sexual activity at least 3 weeks after the procedure. Control was carried out at 3 and 6 months after the surgery with the FSFI questionnaire and with a questionnaire designed by the group of researchers that included 7 questions assessing urinary incontinence, urine leakage during intercourse, the quality of life in the sexual area, and satisfaction with the surgical procedure.
For data analysis, nonparametric statistics were used by applying the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, which is used to compare the median of two related samples and to determine the degree of difference between them. We used the IBM-SPSS software (version 20).
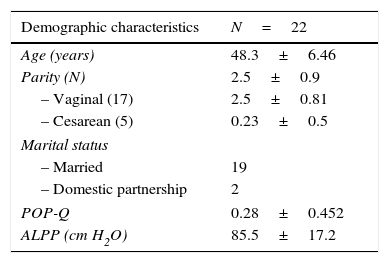
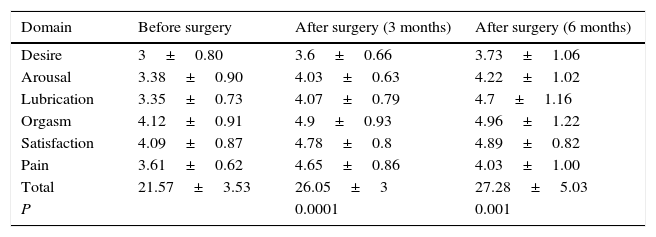
ResultsA total of 22 sexually active women with stress urinary incontinence were treated with tension-free vaginal tape: 20 with the TOT technique and 2 with the TVT technique. All 22 patients completed both the FSFI questionnaire and the questionnaire designed by the group of researchers. The demographic variables of the population are described in Table 2. Among the variables, it is worth highlighting age, which was 48.3±6.46 years—which is within the age range of other studies that have evaluated female sexual function before and after implanting tension-free tapes, and ALPP, which was 85.5±17.2cm H2O. Patients with intrinsic sphincter deficiency, as well as sexually inactive women were excluded. POP-Q was 0.28±0.45, which means that in this cohort there were no women with POP less than 1cm above the level of the hymen (grade i).FSFI showed an improvement in female sexual function in all domains when comparing preoperative and postoperative scores at 3 and 6 months after surgery. The total score of preoperative FSFI was 21.57±3.53, while at 3 months after surgery it was 26.05±3, and at 6 months after surgery 27.28±5.03, which shows a difference of almost 7 points of improvement in the FSFI score when comparing sexual function before surgery and at 6 months after the procedure. The results were statistically significant, with P=0.0001 when comparing results before surgery and at 3 months after procedure, and P=0.001 when comparing scores before surgery and at 6 months after surgery. When evaluating patients individually, 20 of them (90%) reported improvement in the overall assessment of female sexual function, while only 2 (10%) showed deterioration in the total FSFI score. One of these patients reported that her main problem was not connected to urine leakage, but it was related to vaginal lubrication, which significantly deteriorated the quality of sexual intercourse and the female sexual function score in FSFI (Table 3).The questionnaire developed by the group of researchers evaluated urinary continence, urine leakage during sexual intercourse, and overall satisfaction with surgery. We found that, despite surgery, 2 patients persisted with involuntary loss of urine at 3 and 6 months after the procedure; one patient achieved continence at 3 months, but at 6 months after surgery she presented again with stress incontinence; the other patient persisted with incontinence at 3 months after surgery, but at the 6-month follow-up she no longer had involuntary leakage of urine. This represents a total of 4 patients, corresponding to 20% of the participants. With regard to urine leakage during sexual intercourse, 100% of patients suffered from it before surgery and only 2 patients (10%) persisted with leakage after the procedure. Regarding overall satisfaction with surgery, 21 patients (95%) were satisfied with the procedure and only 5% reported feeling unsatisfied with surgery.
Demographic and clinical variables.
| Demographic characteristics | N=22 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 48.3±6.46 |
| Parity (N) | 2.5±0.9 |
| – Vaginal (17) | 2.5±0.81 |
| – Cesarean (5) | 0.23±0.5 |
| Marital status | |
| – Married | 19 |
| – Domestic partnership | 2 |
| POP-Q | 0.28±0.452 |
| ALPP (cm H2O) | 85.5±17.2 |
Data are presented as standard deviation (±) or as number of patients.
Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) before and after surgery (n=22).
| Domain | Before surgery | After surgery (3 months) | After surgery (6 months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desire | 3±0.80 | 3.6±0.66 | 3.73±1.06 |
| Arousal | 3.38±0.90 | 4.03±0.63 | 4.22±1.02 |
| Lubrication | 3.35±0.73 | 4.07±0.79 | 4.7±1.16 |
| Orgasm | 4.12±0.91 | 4.9±0.93 | 4.96±1.22 |
| Satisfaction | 4.09±0.87 | 4.78±0.8 | 4.89±0.82 |
| Pain | 3.61±0.62 | 4.65±0.86 | 4.03±1.00 |
| Total | 21.57±3.53 | 26.05±3 | 27.28±5.03 |
| P | 0.0001 | 0.001 |
Data are presented as standard deviation (±) or as number of patients.
A systematic review and a meta-analysis described that urinary leakage during coitus is significantly reduced after anti-incontinence surgery, concluding that in these patients the probability of improving their sexual function increases 2–3 times, while half of the women do not show any change in their sexuality. There is no difference in the improvement in terms of sexual function when comparing TVT vs. TOT; they establish, however, that the quality of the studies is not very good due to the heterogeneity of the populations, the use of unvalidated questionnaires, and the separation of the outcomes of interest from the functional results of the surgery. For these reasons, they recommend that, in advising women with sexual dysfunction who will undergo anti-incontinence surgery, it should be made clear that urine leakage during intercourse usually improves, whereas sexual function in general may remain the same, or there is a limited possibility that it will improve or worsen.3 When comparing the results of this systematic review and the meta-analysis with our study, we found that, in terms of urinary incontinence, the results are comparable, but in terms of sexual function, we find that it improves significantly after anti-incontinence surgery with TVT or TOT.
There are several studies that have evaluated sexual function before and after anti-incontinence surgery with tension-free vaginal tapes.11 Among these, Neumann et al. found a significant improvement in sexual function, assessed with the FSFI, which is the same questionnaire we used in our study. They reported that the sexual function improved in 53.3% of patients, it had no changes after surgery in 38%, and it deteriorated in 6.7%.12 The study by Glavind et al., in which 51 patients were evaluated before and after TVT surgery using the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Urinary Incontinence Sexual Questionnaire-12 (PISQ-12), showed a significant improvement in the resolution of involuntary urinary leakage during intercourse: 18 patients had this condition before the procedure, while only 2 persisted with coital urinary leakage after the surgery. The overall PISQ-12 score increased from 33.7 to 36.7 (3 points of difference) after surgery, which shows improvement in all the domains of the questionnaire. In this study, 78% of the women scored higher in the postoperative period, 10% had the same score, and 12% had a lower score.13 These results are comparable to ours, where sexual function and urinary leakage during intercourse have improved considerably after surgery.
On the other hand, there are studies that have described a significant deterioration in sexual function after surgery with tension-free vaginal tapes. Among these, a prospective study evaluated 55 women with stress urinary incontinence who were treated with anti-incontinence surgery using the TOT technique, with a follow-up at 6 months after procedure. FSFI was used to evaluate female sexual function, which is the same questionnaire we used in our study. They found that the FSFI score increased in 31 patients (56.4%), it remained the same in 9 patients (16.4%), and deteriorated in 15 patients (27.3%). Before surgery, 12 patients (21.8%) presented with urinary leakage during sexual intercourse, while in the postoperative period only one (8.3%) persisted with this condition, which evidences a resolution rate of 91.7% for coital urinary leakage.14 In their study, Lau et al. evaluated 56 women who underwent TVT-O procedure for stress urinary incontinence. Using the PISQ-12, the Urogenital Distress Inventory (UDI-6), and the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ-7), they reported that 27 of 56 women (48%) stated that her sexual function deteriorated after surgery, 20 (37%) declared that it improved, and 9 (15%) that it remained the same. Three patients had recurrence of stress urinary incontinence after surgery. There was a substantial improvement in the UDI-6 and IIQ-7 scores and they recommend that during pre-operative counseling women should not be promised that their sexual function will improve.2
ConclusionsAnti-incontinence surgery with TOT and TVT improves urinary symptomatology and involuntary leakage of urine, while also significantly improving female sexual function and preventing urinary leakage during intercourse, which is very common in these patients. In our study we observed that in all domains of the FSFI (desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain), the score obtained at 3 and 6 months after procedure was considerably higher. Arousal went from 3.38±0.9 before surgery to 4.22±1.02 at 6 months; desire before surgery had a score of 3.0±0.8 vs. 3.73±1.06 at 6 months; lubrication increased from 3.35±0.73 before surgery to 4.7±1.16 at 6 months; the ability to achieve orgasm was initially reported at 4.12±0.91 and at 4.96±1.22 at 6 months after surgery; initial satisfaction was 4.09±0.87, and it increased to 4.89±0.82 at 6 months; and, finally, pain went from 21.57±3.53 to 27.28±5.03 at 6 months. In the latter domain, it should be clarified that higher scores mean less pain during sexual intercourse. Regarding satisfaction with surgery, most patients were satisfied with the procedure and only one patient was unsatisfied, but due to reasons unconnected to the surgery.
We believe that during preoperative counseling it can be explained to patients that anti-incontinence surgery with tension-free vaginal tapes for stress urinary incontinence improves involuntary urine leakage, coital urinary leakage, and female sexual function in all the domains at 3 and 6 months after the procedure. We recommend, however, conducting further research with a larger sample and adding validated questionnaires to assess urinary incontinence before and after surgery.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.