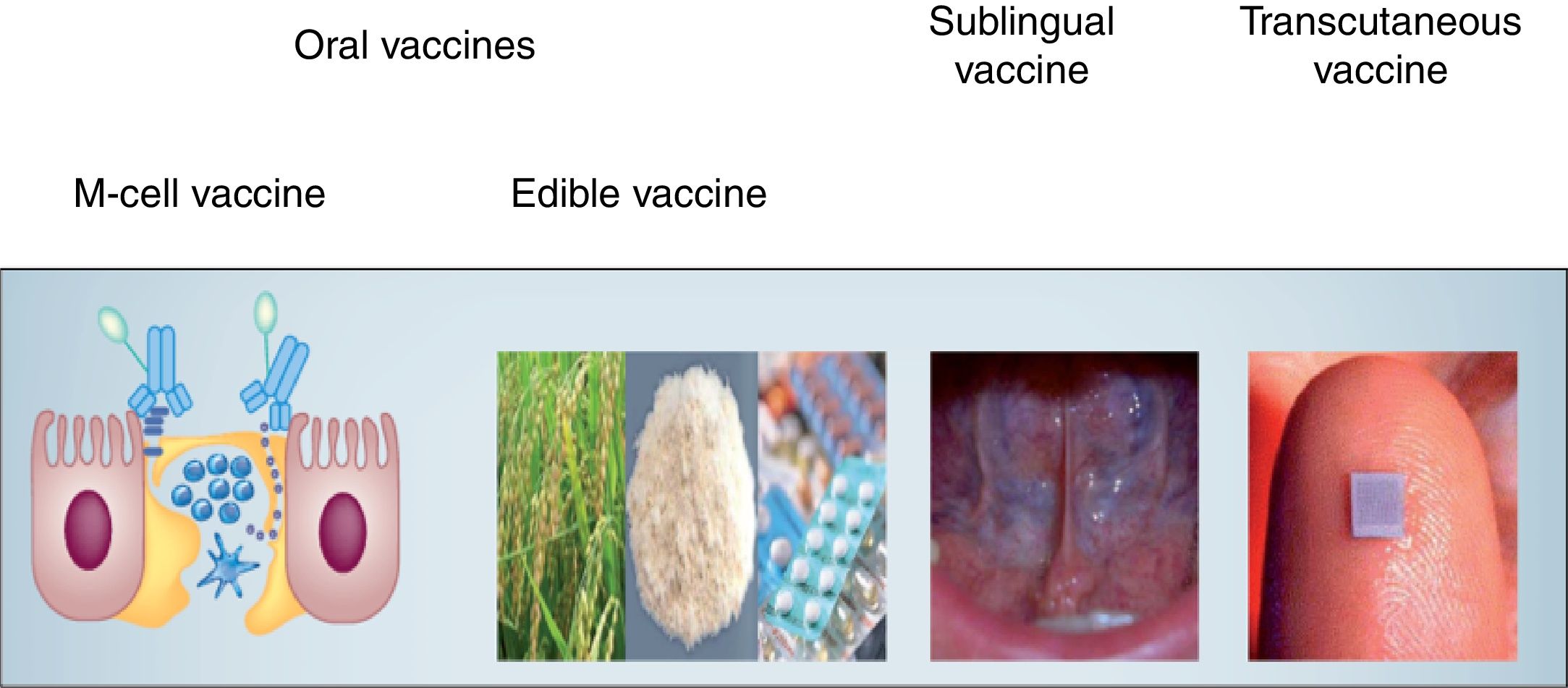
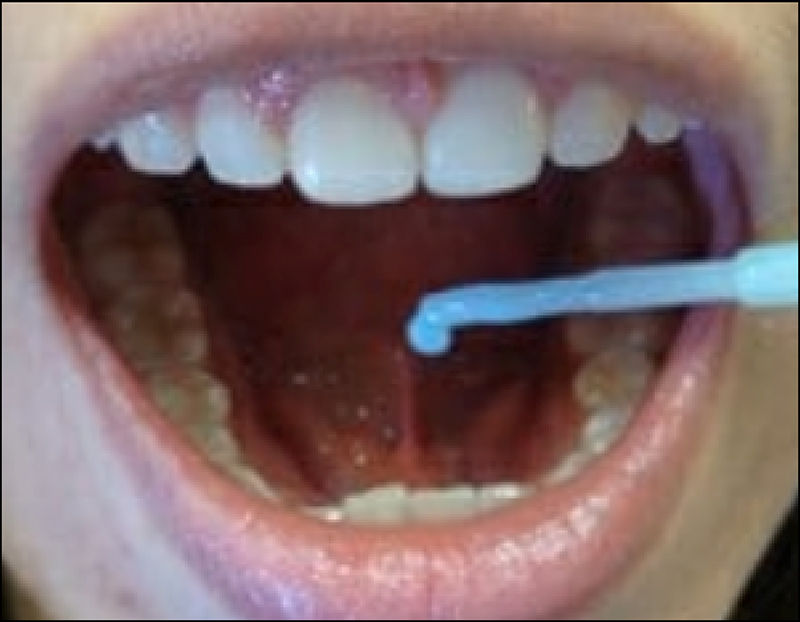
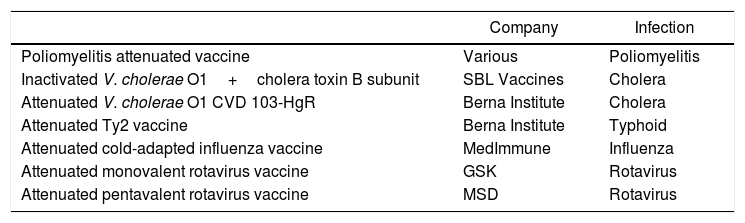
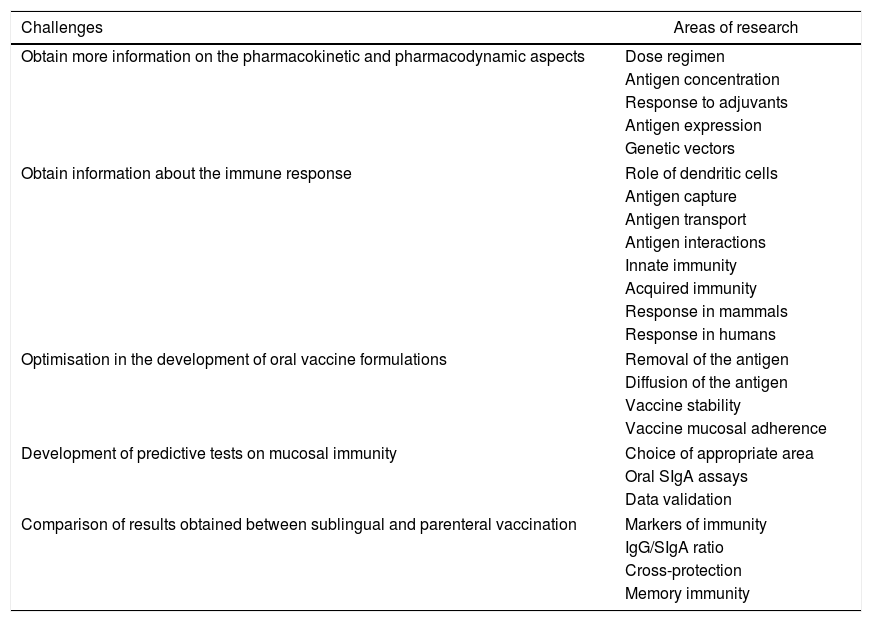
From the studies on the innate and adaptive immune response of the oral mucosa, experiments have been initiated on the use of the sublingual route in the administration, absorption and immunization of a vaccine against the human influenza virus. Unlike intranasal administration, the sublingual route is effective and safe and does not redirect the antigen or adjuvant to the central nervous system. The first studies conducted with soluble proteins from the influenza A virus associated with an adjuvant showed that they induced a broad and intense immune response in all mucous membranes and extramucosal tissues, including the production of secretory (IgA-s) and non-secretory (IgG) antibodies, systemic immunity and response in specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (Th1 and Th2). Different studies have shown that the sublingual immune response is equally effective if other antigenic presentations are used (M2 protein, recombinant vectors or attenuated virus). The ease of administration by this route, either in its liquid presentation or in tablets, would facilitate the acceptability and adhesion of the population, especially children, to the vaccination of the entire population against influenza.
A partir de los estudios sobre la respuesta inmunitaria innata y adaptativa de la mucosa oral se han iniciado experimentos sobre la utilización de la ruta sublingual en la administración, absorción e inmunización de una vacuna frente al virus humano de la gripe. A diferencia de la administración intranasal, la ruta sublingual es eficaz y segura, y no redirecciona el antígeno o el adyuvante al sistema nervioso central. Los primeros estudios realizados con proteínas solubles procedentes del virus gripal A asociadas a un adyuvante demostraron que inducían una amplia e intensa respuesta inmunitaria en todas las mucosas y tejidos extramucosales, incluyendo la producción de anticuerpos secretores (IgA-s) y no secretores (IgG), inmunidad sistémica y respuesta en linfocitos T citotóxicos específicos (Th1 y Th2). Los diferentes estudios han comprobado que la respuesta inmunitaria sublingual es igual de eficaz si se utilizan otras presentaciones antigénicas (proteína M2, vectores recombinantes o virus atenuado). La facilidad de administración por esta ruta, ya sea en su presentación líquida como en tabletas, facilitaría la aceptabilidad y la adhesión de la población, especialmente la infantil, a la vacunación de toda la población frente a la gripe.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora