El objetivo de este análisis es conocer las características del proceso asistencial y detectar posibles problemas del funcionamiento del Código Ictus (CI) en sus 2 primeros años de implementación a partir de la incidencia poblacional de ictus en un sector territorial del Plan Director de Enfermedades Cerebrovasculares.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio prospectivo de cohorte constituida por personas con un primer episodio de ictus, entre 15-89 años de edad. Se realizó un análisis de los indicadores clínicos de resultados según los requerimientos del CI territorial, y de supervivencia por curvas de Kaplan-Meier y bivariante entre pacientes fallecidos y supervivientes.
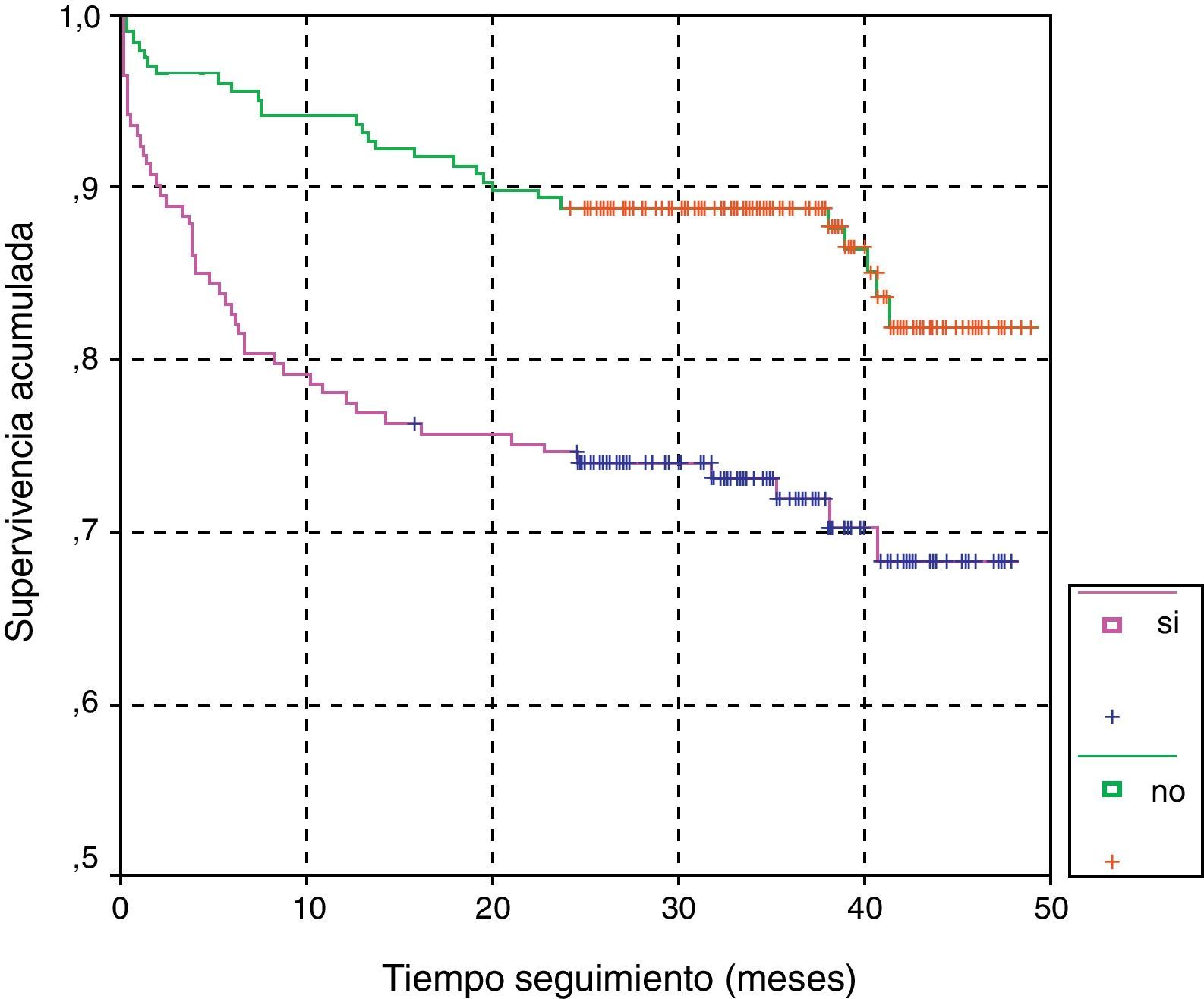
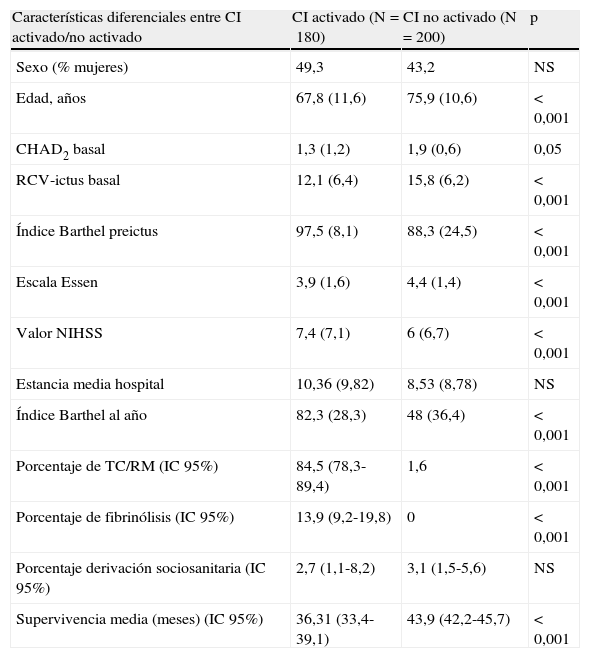
ResultadosSe incluyeron 380 pacientes ≤80 años, activándose el CI en el 54,3% (IC 95%: 49,0-59,3), intrahospitalariamente en el 77% de casos. El 80% de la ventana terapéutica se consume hasta la llegada al hospital. En el 13,9% (IC 95%: 9,2-19,8) se trató con fibrinólisis. La mortalidad inmediata fue del 9,9% (IC 95%: 7,5-12,5).
ConclusionesLa implantación del CI es un sistema que mejoró la atención precoz del ictus en todo el territorio, pero su activación en el ámbito de atención primaria fue baja.
We aimed to know the characteristics of the urgent stroke assistance system, the Stroke Code (SC) model, 2 years after its implementation through testing the specific impact on several result indicators on individuals with a first stroke.
Patients and methodProspective study of a cohort who suffered a first stroke episode, 15 to 89-year-old. Several clinical indicators were selected to evaluate results according to the SC and an analysis survival for Kaplan-Meier's curves was made as well as a bivariate analysis between dead and surviving patients. Data were collected by a community based registry.
ResultsA total of 380 patients ≤80-year-aged were enrolled and the SC was activated in 54.3% (CI95%: 49,0-59.3), 77% at the hospital. An 80% of the therapeutic window was wasted before arrival to hospital. In 13.9% (CI95%: 9,2-19,8) thrombolysis was used. The immediate mortality was 9.9% (CI95%: 7.5-12.5).
ConclusionsThe implantation of the SC is a system that improved the welfare chain of stroke in the whole territory, but its activation in the area of primary care was low.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora