Polyautoimmunity is a frequent phenomenon in clinical practice, and is defined as the presence of more than one autoimmune disease in the same patient.1 It may be characterised as “overt,” when there is clinical coexistence, or “latent,” when autoantibodies unrelated to the index disease are detected but clinical criteria are not met.2 The effect of polyautoimmunity on the clinical course of the index disease is currently not well defined and should be further studied.1,2
We present the case of a 63-year-old white woman with history of subacute thyroiditis and lumbar disc herniation, who attended the emergency department due to a 72-h history of numbness of the abdomen and anterior aspect of both thighs. She reported constipation over the previous week, with no other symptoms.
The general physical examination was normal, with the patient being afebrile and haemodynamically stable. Neurological examination revealed an inframamillary sensory level with tactile and vibratory hypoaesthesia affecting the distal region of the upper limbs and globally in the lower limbs, with preserved thermoalgesia. At the motor level, we observed symmetrical exaggerated patellar reflex with increased reflexogenic zone and absence of clonus, together with a bilaterally indifferent plantar reflex. Muscle tone was normal and strength was preserved globally in all 4 limbs. Biceps and triceps reflexes were also normal. Regarding coordination, she presented dysmetria on the finger-to-nose test and pronounced wide-based gait that prevented walking. Romberg sign was positive.
Normal results were obtained in the emergency blood analysis, chest radiography, and electrocardiogram.
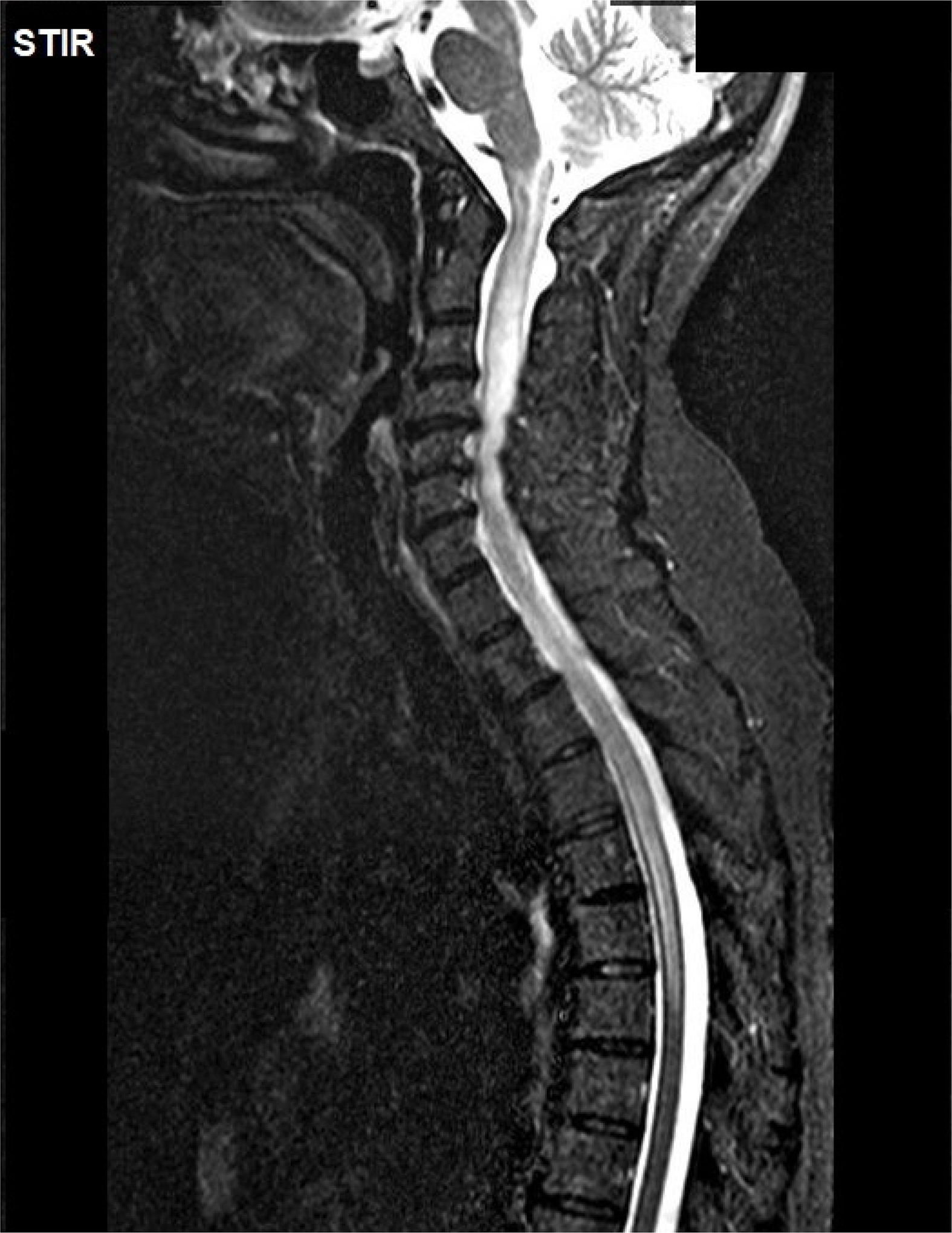
Suspecting myelopathy, we admittted the patient to the neurology department and requested an emergency brain and spinal MRI study (Fig. 1). We performed a lumbar puncture and complete blood analysis (Table 1). After infectious aetiology had been ruled out, the patient was treated with intravenous methylprednisolone (1 g/day) for 5 days. Due to the lack of response, we started plasmapheresis (5 sessions), observing a partial improvement of sensory symptoms and gait (the patient could walk a few steps with bimanual support).
Laboratory analysis. A. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). B. Serum.
| A. CSF | RESULTS |
|---|---|
| CYTOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY | - CSF glucose 60 mg/dL (blood glucose 106 mg/dL), protein 105 mg/dL.- 0 red blood cells/μL, 63 white blood cells/μL (16% mononuclear and 84% polymorphonuclear). - No neoplastic cells. |
| MICROBIOLOGY | - Negative Gram stain and culture results.- Negative meningitis/encephalitis panel. |
| AUTOANTIBODIES (Abs) | - Negative onconeuronal Abs (Hu, Yo, Ri, CRMP5, Amphiphysin, Titin, SOX1, Zic4, GAD65).- Negative neuronal cell-surface Abs (NMDAR, VGKC, DPPX, GABAbR, AMPAR). |
| IMMUNOLOGY | - IgG index 0.70, Kappa index 0.49, positive oligoclonal bands (“mirror-pattern” or type 4). |
| B. SERUM | RESULTS |
|---|---|
| SEROLOGY | - HIV-1/2 Abs, Syphilis Total and RPR assay, Borrelia burgdorferi-IgG: negative.- Hepatitis: HBsAg-negative, HBcAc-negative, HBsAc 60 U/L, negative anti-HCV. |
| AUTOANTIBODIES (Abs) | - Positive anti-aquaporin 4 (AQP4)-IgG, negative anti-MOG Abs.- Negative onconeuronal and neuronal cell-surface Abs.- Anti-nuclear Abs (ANA) 1/640, anti-dsDNA Abs * 60 IU/mL (normal range: 0 - 35).- Negative ENA panel (anti-Sm, anti-RNP, anti-Ro (SS/A), anti-La (SS/B), anti-Scl-70, anti-Jo-1).- Anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) Abs * 123.4 IU/mL (normal range: 0 - 35). |
Laboratory analysis confirmed diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD). We requested that the preventive medicine department assess vaccination needs, and the biological product advisory committee approved onset of treatment with subcutaneous tocilizumab.
Given the presence of immunological criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the rheumatology department ruled out associated symptoms of SLE. After ruling out active disease with an analytical study of the complement system and renal function, we discharged the patient for outpatient follow-up by the neurology and rheumatology clinics.
NMOSD is an infrequent autoimmune neurological disorder with an annual incidence in the white population of less than 1 case per million population,3 with 80% of patients presenting detectable levels of aquaporin-4 autoantibodies (AQP4-IgG).4 Furthermore, half of patients initially present longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM),5 which typically manifests as complete deficit below the lesional level, although sensory symptoms predominated in our patient.
Studies in the literature report that NMOSD with positive results for AQP4-IgG is accompanied by overt polyautoimmunity in 20%–30% of cases (with Sjögren syndrome and autoimmune thyroid disease being the most frequently associated comorbidities) and latent polyautoimmunity in 40%–70% (mainly antinuclear [ANA] and anti-Ro/SSA antibodies).6–8
Our patient presented history of subacute thyroiditis with positive results for anti–thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies as overt polyautoimmunity. Some authors have recently suggested that patients with NMOSD associated with anti-TPO antibodies present poorer prognosis of the neurological condition, as they are predisposed to present recurrent episodes of LETM; however, the pathophysiological mechanism remains unknown.9
In addition, she exhibited high titres of ANA and positive anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies, indicating latent polyautoimmunity, as she did not meet the clinical criteria for SLE established by the existing diagnostic guidelines (despite the fact that the presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies has close to 100% specificity for SLE).10 Some case series report that SLE usually manifests before NMOSD in 75% of patients with polyautoimmunity,8 although this course was reversed in our case.
In conclusion, it is important to be aware of these autoimmune comorbidities, as early diagnosis and treatment may improve the quality of life of patients with NMOSD.
Data confidentialityThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Informed consentIt has not been obtained because no identifying data is included.
Ethical standardsThe authors declare that no experiments with humans or animals have been performed. No data that identify patients are disclosed.
FundingThis study has received no specific funding from any public, private, or non-profit organisation.