Radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) represents the gold standard treatment for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC); however, attempts have been made to treat upper urinary tract CIS (UT-CIS) conservatively. The aim of this study was to compare the outcome of patients with primary UT-CIS treated in our center by means of RNU vs. bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) instillations.
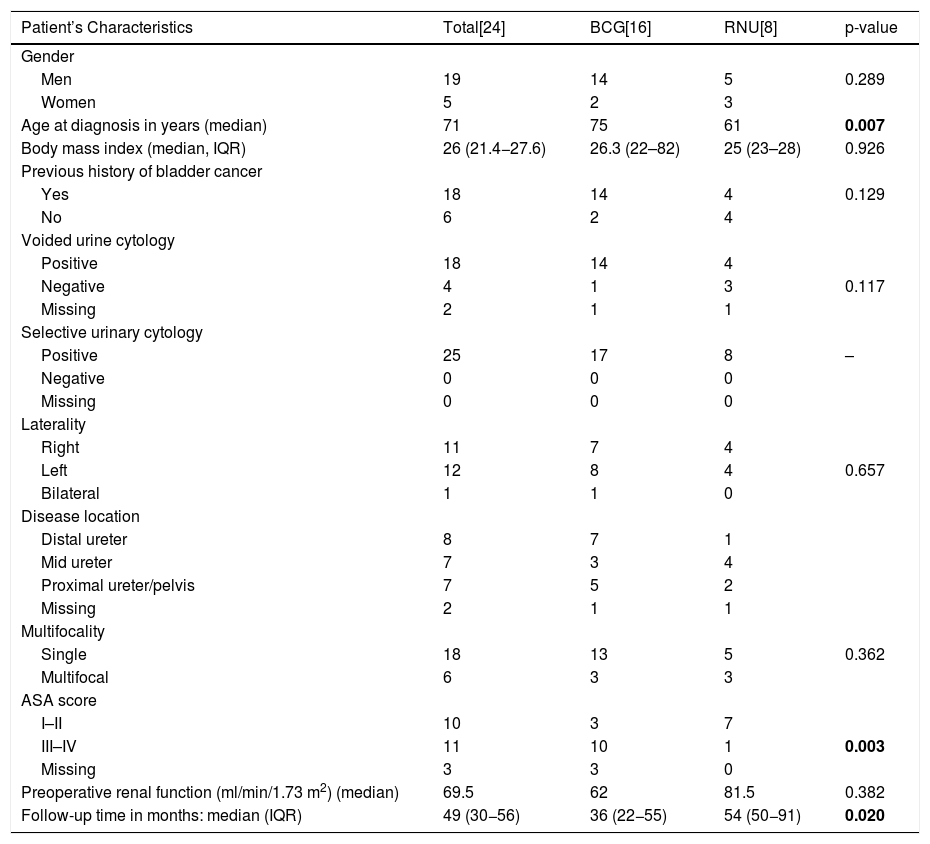
MethodsThis retrospective study included patients with diagnosis of primary UT-CIS between 1990 and 2018. All patients had histological confirmation of UT-CIS in the absence of other concomitant UTUC. Histological confirmation was obtained by ureteroscopy with multiple biopsies. Patients were treated with BCG instillations, RNU or distal ureterectomy. Clinicopathological features and outcomes were compared between RNU and BCG groups.
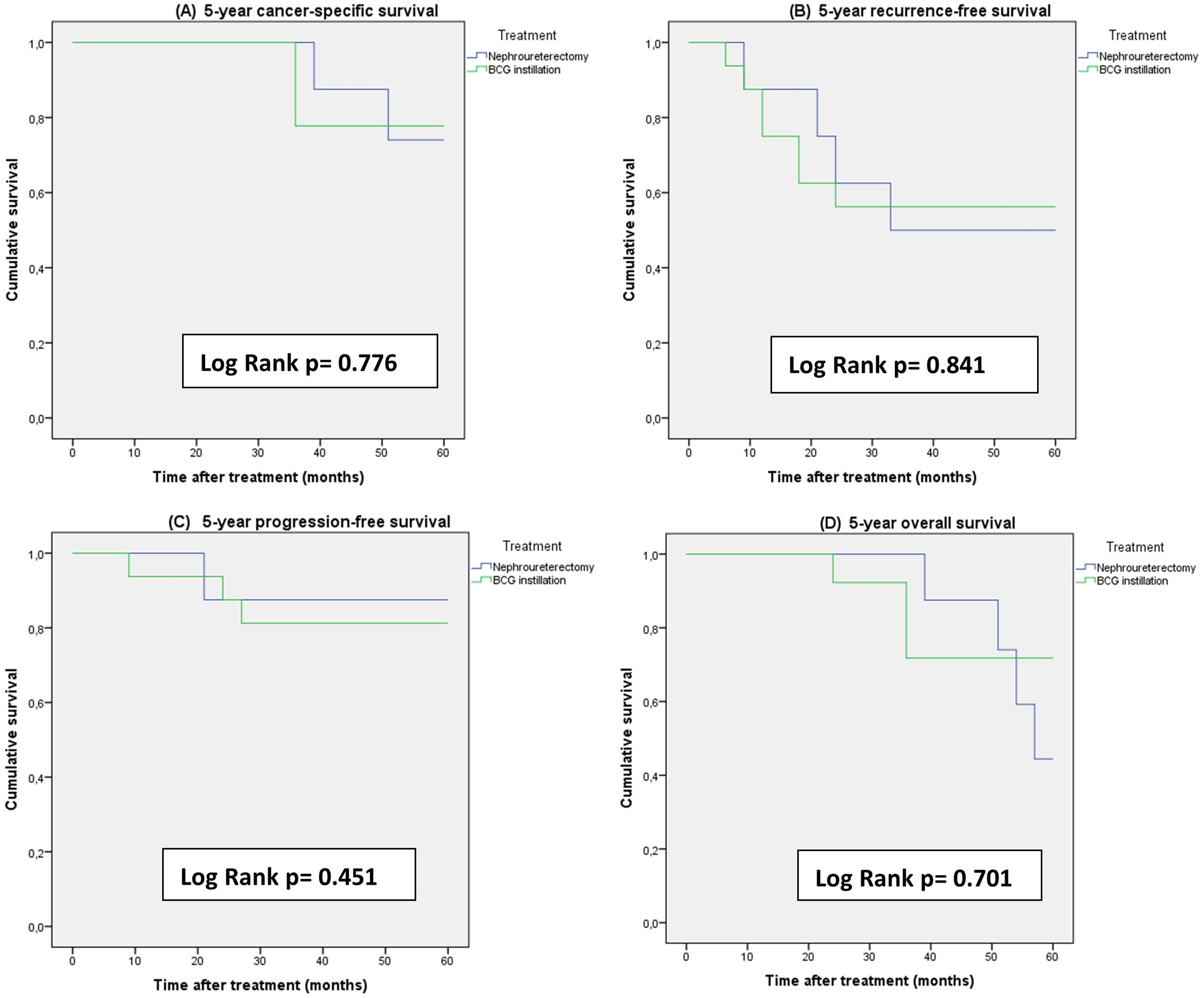
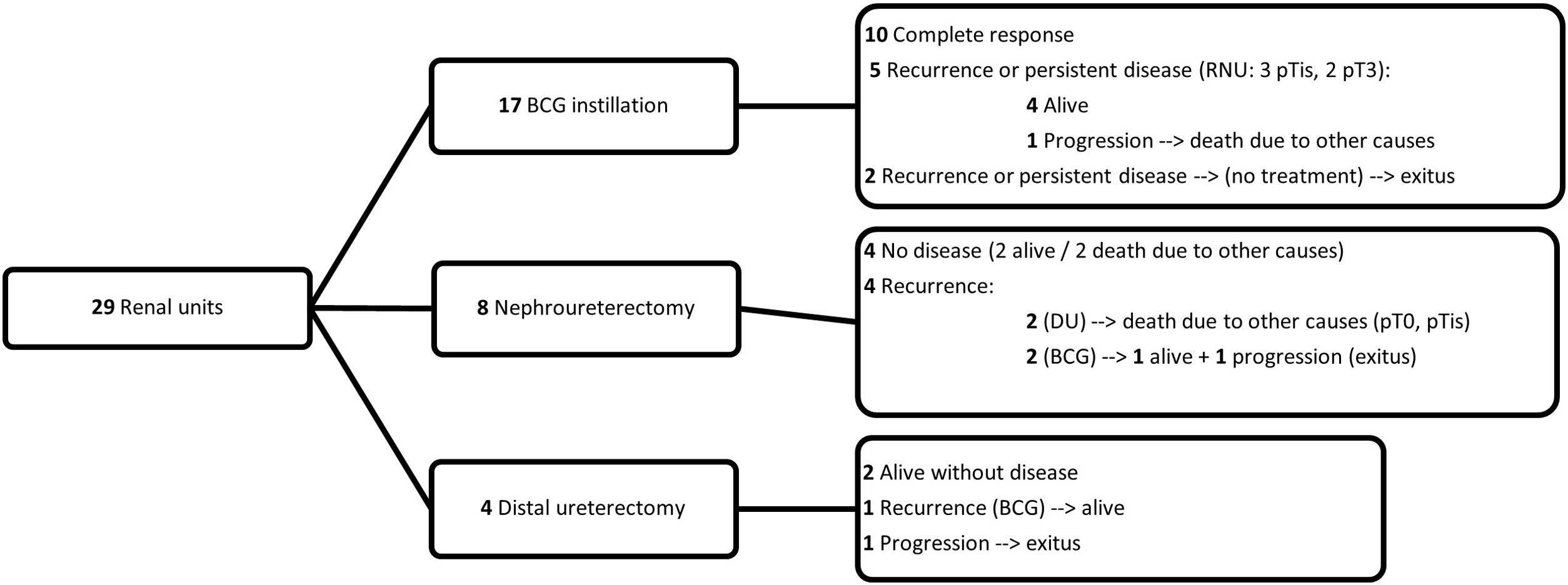
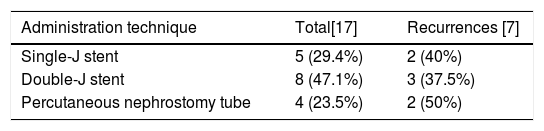
ResultsA total of 28 patients and 29 renal units (RUs) were included. Sixteen (57.1%) patients (17 RUs) received BCG. BCG was administered via nephrostomy tube in 4 patients, with a single-J ureteral stent in 5, and using a Double-J stent in 7. Complete response and persistence or recurrence were detected in ten (58.8%) and seven (41.2%) RUs treated with BCG, respectively. Eight (27.6%) RUs underwent RNU, and 4 (13.8%) Rus distal ureterectomy. No differences were found in recurrence-free survival (p=0.841) and cancer-specific survival (p=0.77) between the RNU and BCG groups.
ConclusionsAlthough RNU remains the gold standard treatment for UT-CIS, our results confirm that BCG instillations are also effective. Histological confirmation of UT-CIS is mandatory before any treatment.
La nefroureterectomía radical (NFU) es el tratamiento estándar del carcinoma de tramo urinario superior (TUS). No obstante, desde 1985 se ha introducido el tratamiento conservador en el manejo del carcinoma in situ en TUS (cisTUS). El objetivo de este estudio fue comparar la evolución oncológica de los pacientes con cisTUS tratados en nuestro centro con NFU vs instilaciones de bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG).
MétodosSe trata de un estudio retrospectivo de pacientes con diagnóstico de cisTUS primario entre 1990−2018. Todos los pacientes presentaban diagnóstico histológico de cisTUS con ausencia de otro carcinoma de TUS concomitante. La confirmación histológica se obtuvo mediante ureteroscopia con múltiples biopsias. Los pacientes fueron tratados mediante NFU, ureterectomía distal o instilaciones de BCG. Los datos clinicopatológicos y la evolución oncológica fue comparada entre los grupos NFU y BCG.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 28 pacientes, 29 unidades renales (UR). Dieciséis (57,1%) pacientes (17 UR) recibieron BCG. Las instilaciones fueron administradas por nefrostomía en 4 pacientes, uni-J en 5 y doble J en 7. La respuesta completa y la persistencia o recurrencia fueron detectados en diez (58,8%) y siete (41,2) UR tratadas con BCG. Ocho UR (27,6%) fueron tratadas con NFU, con una recurrencia contralateral detectada en 4 casos (50%). Finalmente, 4 UR con cisTUS (13,8%) fueron tratados con ureterectomía distal. No se detectaron diferencias en supervivencia libre de recurrencia (p=0,841) y supervivencia cáncer específica (p=0,77) entre los grupos de NFU y BCG.
ConclusionesAunque la nefroureterectomía radical representa el tratamiento estándar para el CIS de tramo urinario superior, nuestros resultados confirman que las instilaciones con BCG también son efectivas. La confirmación histológica de cisTUS debería realizarse previamente a la decisión terapéutica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora