To analyze the predictive utility of penile color Doppler ultrasonography after the injection of vasoactive agents for recovering erectile function after radical prostatectomy.
Material and methodsA retrospective study was conducted on patients with erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy who were treated with intracavernous injections of prostaglandins E1 between January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2012. The study included patients with no history of erectile dysfunction prior to the surgery and who did not respond to medical treatment. Color Doppler was performed on all patients after the intracavernous injection. A peak systolic velocity ≥30cm/s and an end diastolic velocity ≤5cm/s were considered normal hemodynamic values. We assessed the result of the treatment during the follow-up using the International Index of Erectile Function-5.
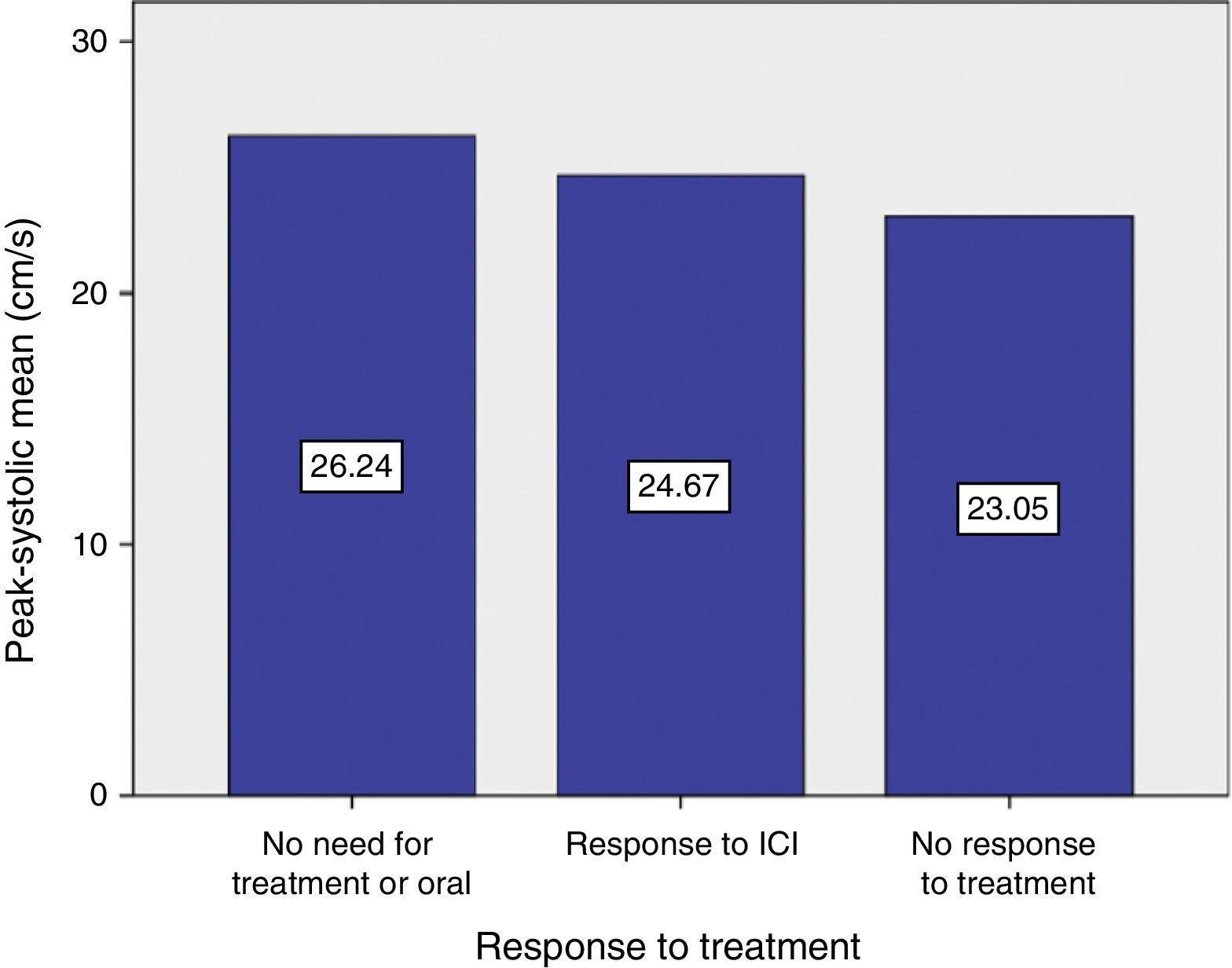
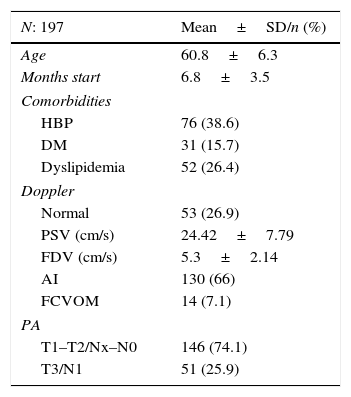
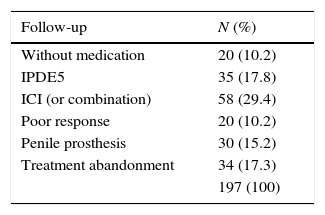
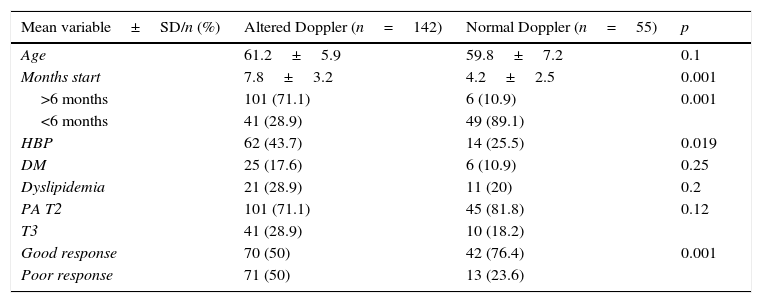
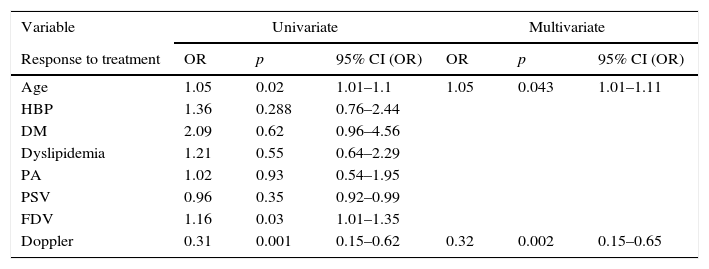
ResultsWe included 197 patients. The mean age was 60.8 (±6.3). The pathological diagnosis for all patients was adenocarcinoma, 74.1% of which were confined to the organ (T1–T2/Nx–N0). Treatment with injections after the surgery was started after a mean duration of 6.8 months (+3.5). The Doppler ultrasonography results were normal for 53 patients (26.9%). During the follow-up, 113 patients (57.4%) maintained functional erections; 55 of these patients (28%) did not require injections. Normal Doppler ultrasonography results were associated with a favorable response to treatment (p<.01).
ConclusionsThe prostaglandin E1 test will help provide a diagnosis in erectile dysfunction for patients who have undergone prostatectomies. The test helps provide information on the vascular condition of the penis and useful prognostic information for the follow-up of these patients.
Analizar la utilidad predictiva de la ecografía doppler color peneana tras la inyección de vasoactivos en la recuperación de la función eréctil tras prostatectomía radical.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo en pacientes con disfunción eréctil tras prostatectomía radical tratados con inyecciones intracavernosas de prostaglandinas E1 entre el 1 de enero de 2006 y el 31 de diciembre de 2012. Se incluyeron enfermos sin antecedente de disfunción eréctil previa a la cirugía, no respondedores a tratamiento médico. En todos se realizó eco doppler color tras la inyección intracavernosa. Una velocidad picosistólica ≥30cm/seg y una velocidad diastólica final ≤5cm/seg fueron considerados valores hemodinámicos normales. Se evaluó el resultado del tratamiento durante el seguimiento mediante el uso de IIEF-5.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 197 pacientes. La edad media fue de 60,8 (±6,3DE). El diagnóstico anatomopatológico en todos ellos fue de adenocarcinoma, siendo el 74,1% organoconfinados (T1-T2/Nx-N0). El tratamiento con inyecciones tras la cirugía se inició una vez transcurridos 6,8 meses de media (±3,5 DE). La ecografía doppler fue normal en 53 pacientes (26,9%). Durante el seguimiento, 113 pacientes (57,4%) mantenían erecciones funcionales, estando 55 de ellos (28%) sin necesidad de inyecciones. La presencia de una ecografía doppler normal se asoció a una respuesta favorable al tratamiento (p<0,01).
ConclusionesEl test de prostaglandina E1 nos va a permitir una orientación diagnóstica en la disfunción eréctil de los pacientes prostatectomizados. Permite obtener información sobre el estado vascular del pene y aporta información pronóstica de utilidad en el seguimiento de estos pacientes.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora