La displasia urotelial y el carcinoma in situ (CIS) están relacionados con la recurrencia y la progresión del carcinoma urotelial. Diferenciar el CIS y la displasia de la atipia reactiva suele ser difícil sobre la base de las características histológicas. La integración de los hallazgos histológicos con la inmunohistoquímica se utiliza en la práctica habitual para realizar el diagnóstico del CIS y, para ello, se utilizan los marcadores inmunohistoquímicos CK20, CD44, Ki67 y p53 como complemento al estudio histológico.
En este trabajo, nos propusimos evaluar CK20, CD44, Ki67 y p53 como marcadores inmunohistoquímicos en pacientes con CIS, mediante una revisión sistemática y un metaanálisis.
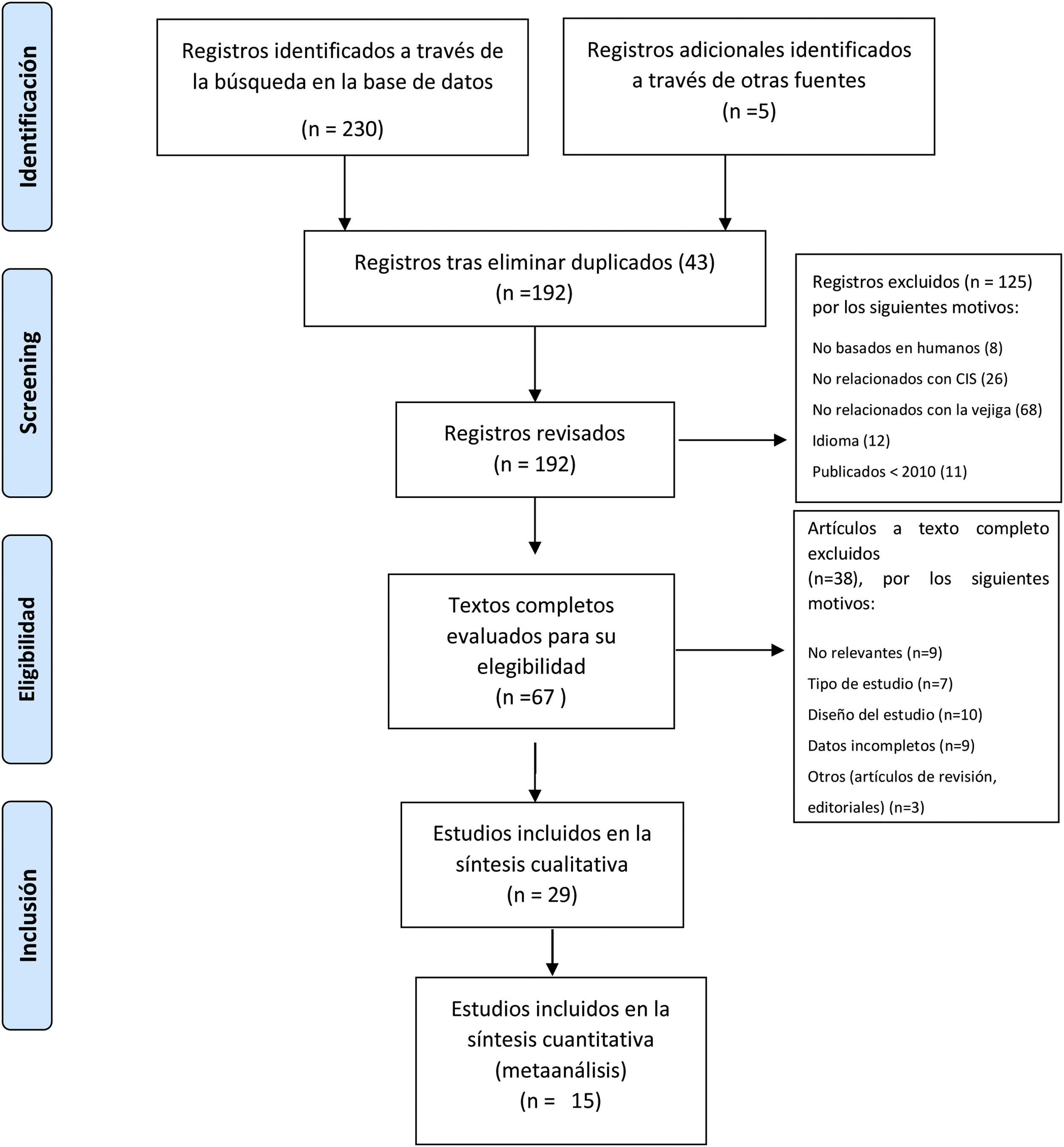
Materiales y métodosSe realizó una revisión sistemática con búsqueda en bases de datos electrónicas de estudios en inglés publicados desde enero de 2010 hasta abril de 2021. Se consideraron elegibles los estudios que evaluaban la expresión de CK20, CD44, Ki67 y p53 en el CIS.
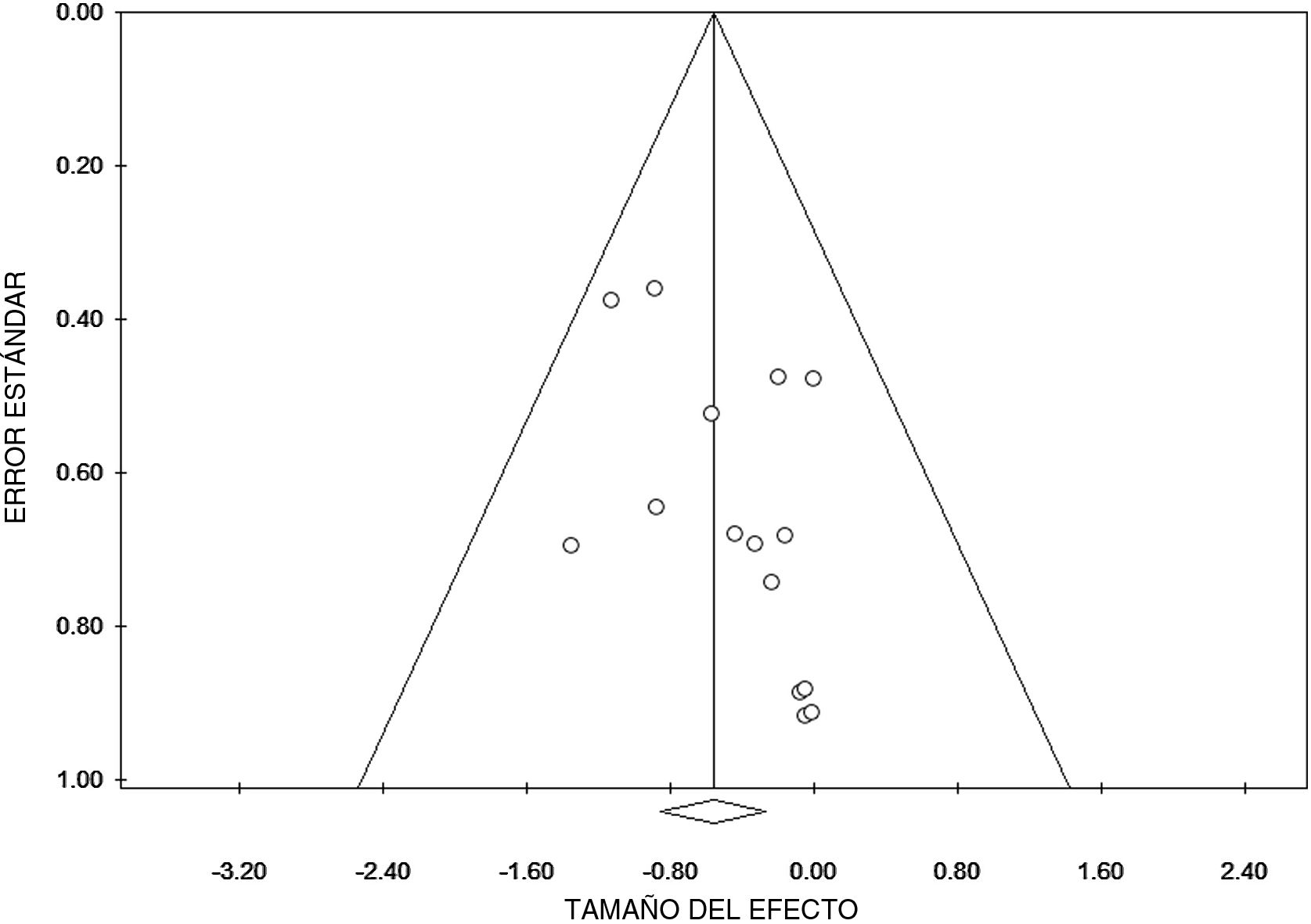
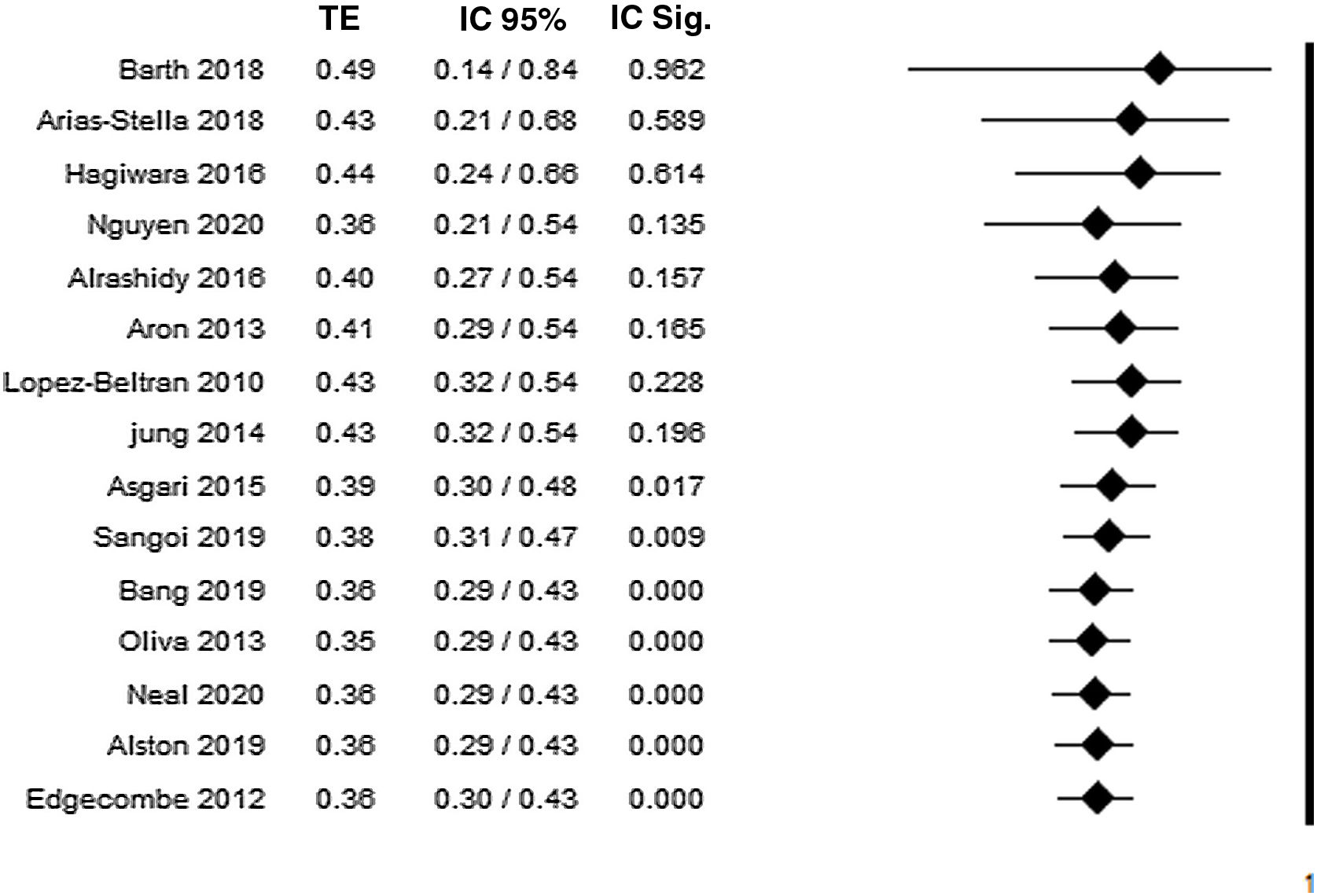
ResultadosEn total, 15 referencias fueron aptas para la revisión cuantitativa. La tasa global de expresión de CK20, CD44, Ki67 y p53 en el CIS fue del 43%, 31%, 44% y 38%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesNuestro estudio apoya el consenso de la Sociedad Internacional de Patología Urológica de 2014 sobre la evaluación histológica como método de referencia para diagnosticar el CIS urotelial, y sugiere que una correlación muy estrecha entre los datos morfológicos, inmunohistoquímicos y clínicos es esencial para proporcionar el mejor manejo de los pacientes con carcinoma vesical.
Urothelial dysplasia and carcinoma in situ (CIS) are related to recurrence and progression of urothelial carcinoma. Differentiating CIS and dysplasia from reactive atypia is often difficult based only on histological features. The integration of histological findings with immunohistochemistry is used in routine practice to make a diagnosis of CIS and, for this purpose, the immunohistochemical markers CK20, CD44, Ki67 and p53 are used to supplement histology.
In this work, we aimed to assess CK20, CD44, Ki67 and p53 as immunohistochemical markers in patients with CIS through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Materials and methodsA systematic review was performed by searching electronic databases for English-language studies published from January 2010 to April 2021. Studies were considered eligible if they evaluated the CK20, CD44, Ki67 and p53 expression in CIS.
ResultsIn total, 15 references were suitable for quantitative review. The overall rate of CK20, CD44, Ki67 and p53 expression in CIS was 43%, 31%, 44%, 38%, respectively.
ConclusionsOur study supports the 2014 International Society of Urologic Pathology consensus that histological assessment remains the gold standard to diagnose urothelial CIS and suggests that a very close correlation between morphological, immunohistochemical and clinical data is essential to provide the best management for patients with bladder carcinoma.