The aim of this study is to develop a new experimental model of inducing interstitial cystitis (IC) through vesical instillation of a polymeric solution containing the NO donor S-nitrousglutathione (GSNO) and to compare it to the experimental interstitial cystitis induced by vesical instillation of protamine and potassium chloride.
Materials and methodsFor that purpose 40 female Wistar rats were used, divided into four groups: (1) saline solution+GSNO; (2) saline solution+polymeric solution (without GNSO); (3) protamine sulphate+KCl; (4) protamine sulphate+GSNO. The rats received one application (5 animals) or 3 applications (5 animals) of the corresponding substance through intravesical instillation, and after 6days (5 animals) or 9days (5 animals) they were euthanized and their bladders were removed for macroscopic evaluation and histological study.
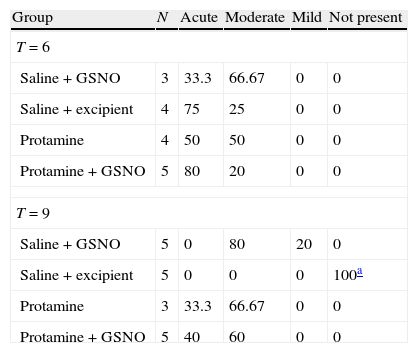
ResultsIn the macroscopic evaluation we observed edema and hyperemia of the mucosa in 2 (22%) of the animals in group 1, in 0 (0%) of the animals in group 2, in 10 (100%) of the animals in group 3, and in 5 (50%) of the animals in group 4. In the protamine+KCl group and in saline+GSNO similar effects were observed on the bladder wall. The animals in group 2 (saline+polymeric) showed vascular congestion, significantly smaller than the rest after 9days instillations (p=0.0035). Significant increased fibrosis was observed after instillations in groups 3 and 4, after 6days (p=0.3781) and 9days (p=0.0459), respectively, when compared to control (group 2). All groups presented neutrophilic infiltrate of variable intensity 6days after instillations (p=0.7277). After 9days, there was a regression of the infiltrate, with no evidence of accentuated neutrophilic reaction in all the groups (p=0.2301).
ConclusionThe inflammatory response to bladder instillation of an aqueous solution of S-nitrousglutathione was very similar to that induced by bladder instillation of protamine and KCl. Instillation of an aqueous solution of GSNO can be considered a new model for experimental induction of interstitial cystitis.
La principal finalidad de este estudio es el desarrollo de un nuevo modelo experimental para la inducción de cistitis intersticial (CI) mediante la instilación vesical de una solución polimérica que contiene el S-nitrosoglutatión donante de óxido nítrico (GSNO), y su comparación con la cistitis intersticial experimental inducida por instilación vesical de protamina y cloruro potásico.
Material y métodosPara la consecución de nuestro objetivo utilizamos 40 hembras de rata Wistar divididas en cuatro grupos: (a) solución salina+GSNO; (b) solución salina+solución polimérica (sin GNSO); (c) sulfato de protamina+KCl; y (d) sulfato de protamina+GSNO. Se realizó bien una aplicación a las ratas (5 animales), bien 3 aplicaciones (5 animales) de la sustancia correspondiente mediante instilación vesical, y al cabo de 6 días (5 animales) o 9 días (5 animales) se les practicó la eutanasia y se les extrajeron las vejigas para su evaluación macroscópica y estudio histológico.
ResultadosEn términos de evaluación macroscópica observamos edema e hiperemia de la mucosa en dos (22%) de los animales del grupo 1, en 0 (0%) de los del grupo 2, en 10 (100%) de los del 3 y en 5 (50%) de los animales del grupo 4. En el grupo de protamina+KCl y en solución salina+GSNO se observaron efectos similares en la pared vesical. Los animales del grupo 2 (solución salina+polimérica) mostraban congestión vascular, bastante menos significativa que en el resto después de 9 días de instilaciones (p=0.0035). Se observó un aumento de la fibrosis tras las instilaciones en los grupos 3 y 4 a los 6 días (p=0.3781) y a los 9 días (p=0.0459) respectivamente, en comparación con los controles (grupo 2). En todos los grupos aparecía un infiltrado de neutrófilos con intensidad variable a los 6 días de las instilaciones (p=0.7277). Al cabo de 9 días se producía una regresión del infiltrado, y sin evidencias de reacción neutrofílica marcada en todos los grupos (p=0.2301).
ConclusiónLa respuesta inflamatoria a la instilación vesical de una solución acuosa de S-nitrosoglutatión fue muy parecida a la inducida por la instilación vesical de protamina y KCl. La instilación de una solución acuosa de GSNO puede considerarse un nuevo modelo para la inducción experimental de cistitis intersticial.