To evaluate the clinical and urodynamic differences associated with the presence or absence of detrusor overactivity (DO) in women with overactive bladder (OAB) referred to Functional Urology and Urodynamic Units in Spain.
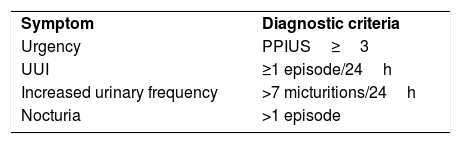
Material and methodsObservational, cross-sectional, multicenter and prospective study conducted in Spain in women with clinical diagnosis of OAB, who had been referred to urodynamic study (UDS) of which centralized reading was performed. Patients completed the 3-day bladder diary (DM3d) with the PPIUS scale (Patient Perception of Intensity of Urgency Scale), the B-SAQ (Bladder control Self-Assessment Questionnaire) and the OABq-SF (Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form). The questionnaires and UDS variables of women with OAB, with or without DO, were compared using the Mann-Whitney test (continuous variables) and the chi-square test (χ2) (categorical variables).
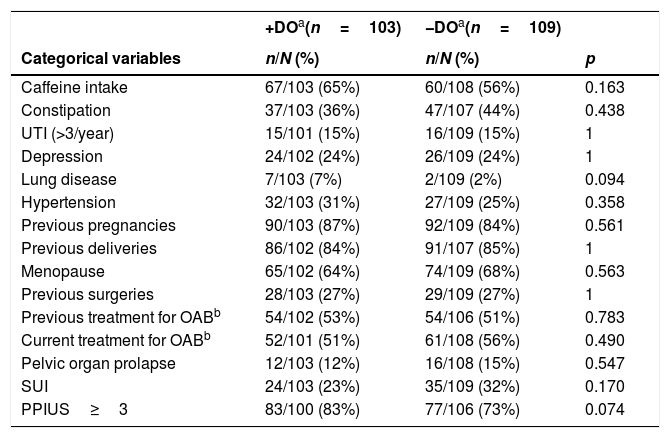
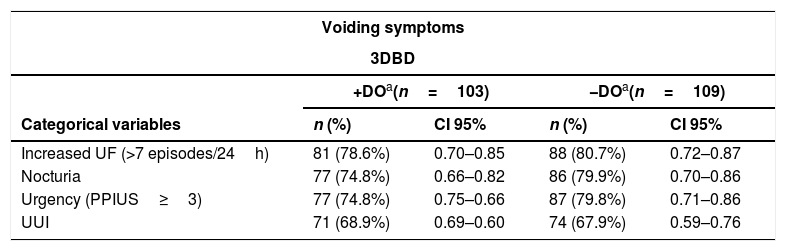
ResultsA total of 247 women with OAB were evaluated, and 103 of them had DO. According to the presence or absence of DO, significant differences were observed in the number of episodes of urge urinary incontinence (UUI), urinary frequency, nocturia, mean micturition volume and number of pads (p<0.05 for all comparisons). A higher percentage of patients with OAB and DO presented reduced bladder capacity, urgency, urge urinary incontinence (UUI) and lower volume for first voiding desire, strong desire to void and maximum cystomanometric capacity in UDS compared with patients without DO (p<0.05 for all comparisons). The only significant differences between both groups were regarding the B-SAQ symptoms scale (p=0.011).
ConclusionsThe presence of DO in women with OAB is related to a more severe alteration of the bladder storage phase.
Evaluar las diferencias clínicas y urodinámicas en mujeres con vejiga hiperactiva (VH) asociadas con la presencia o ausencia de hiperactividad del detrusor (HD). derivadas alas unidades de Urología Funcional y Urodinámica en España.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, transversal, multicéntrico y prospectivo realizado en España en mujeres con diagnóstico clínico de VH derivadas para estudio urodinámico (EUD) del cual se realizó lectura centralizada. Las pacientes completaron el diario miccional de 3días (DM3d) con la Patient Perception of Intensity of Urgency Scale (PPIUS), el Cuestionario de Autoevaluación del Control de la Vejiga (CACV) y la Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form (OABq-SF). Se compararon los cuestionarios y las variables del EUD de mujeres con VH con y sin HD empleándose el test de Mann-Whitney (variables continuas) y el test de χ2 (variables categóricas).
ResultadosSe evaluaron 247 mujeres con VH, de ellas 103 presentaron HD. Según la presencia o no de HD se observaron diferencias significativas en el número de episodios de incontinencia urinaria de urgencia (IUU), frecuencia miccional, nicturia, volumen miccional medio y número de absorbentes (p<0,05 para todas las comparaciones). En pacientes con VH y HD un mayor porcentaje presenta capacidad vesical reducida, urgencia, IUU y volúmenes menores para el primer deseo miccional, fuerte deseo miccional y capacidad cistomanométrica máxima en EUD vs pacientes sin HD (p<0,05 para todas las comparaciones). En los cuestionarios solo hubo diferencias en la subescala de síntomas del CACV entre ambos grupos (p=0,011).
ConclusionesLa presencia de HD en mujeres con VH se relaciona con una alteración más severa de la fase de llenado vesical.