To analyze the evolution of kidney function after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy (PN) and radical nephrectomy (RN) and to identify predictive factors for renal function impairment.
Materials and methodRetrospective study of patients with two kidneys, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and single renal tumor cT1, treated in our center between 2005 and 2018.
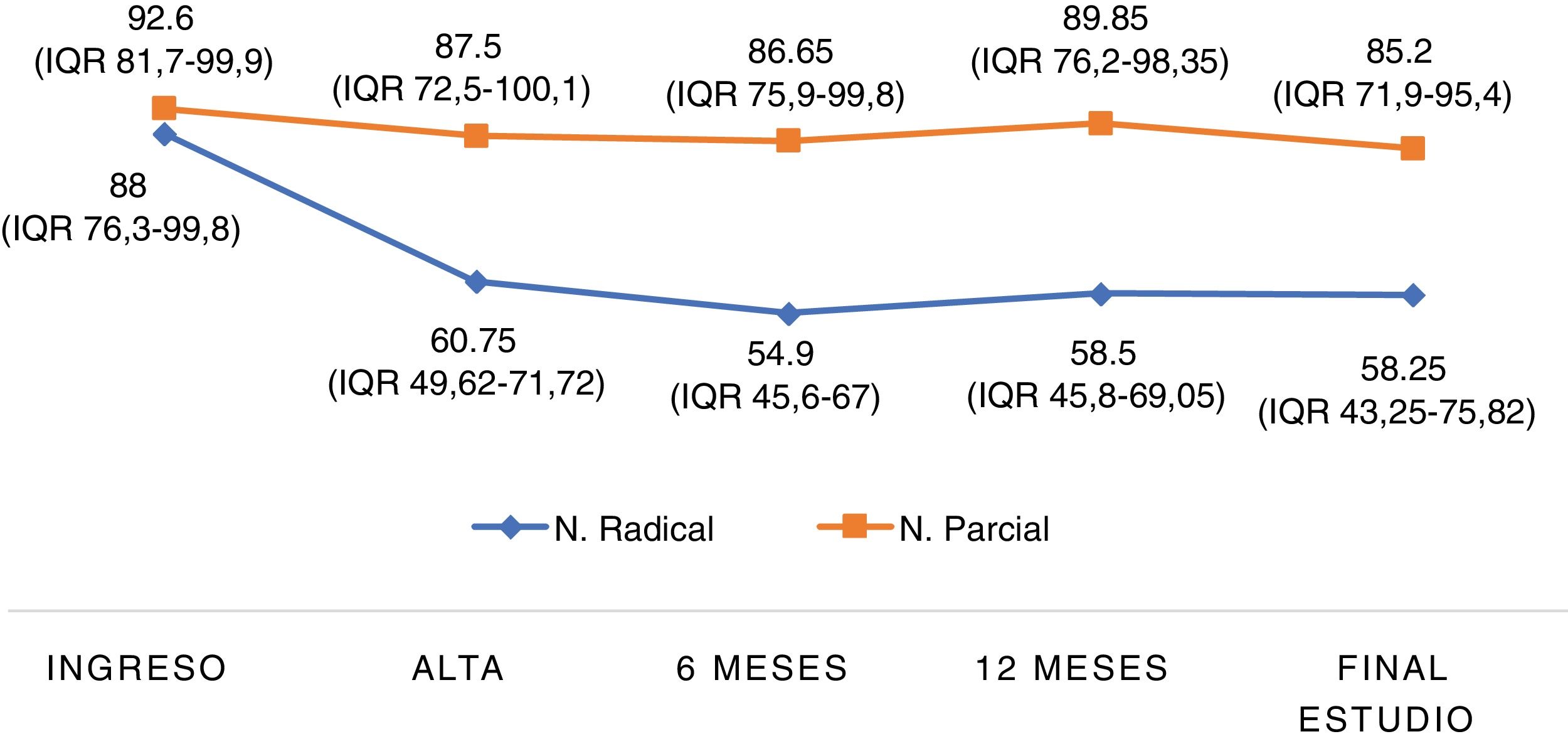
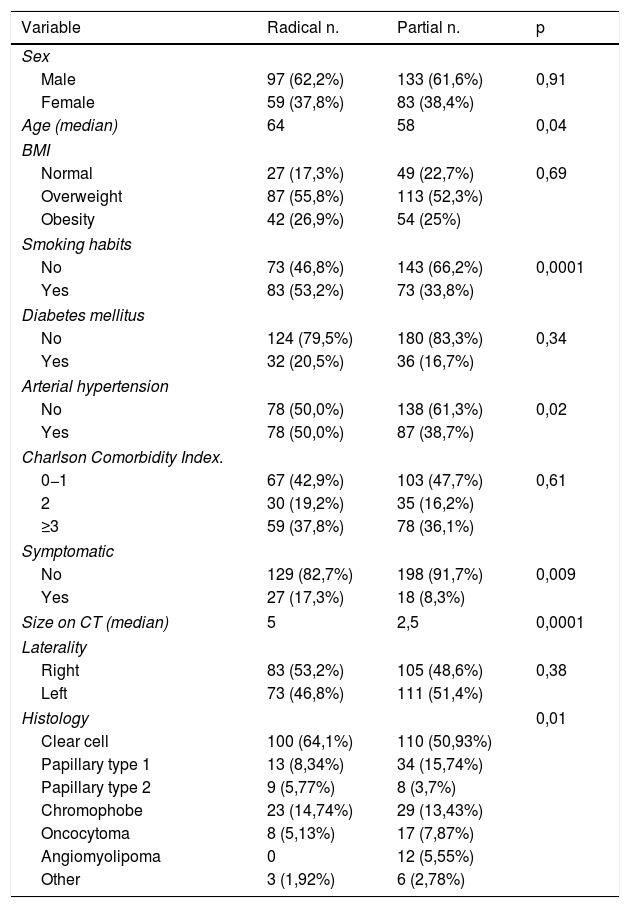
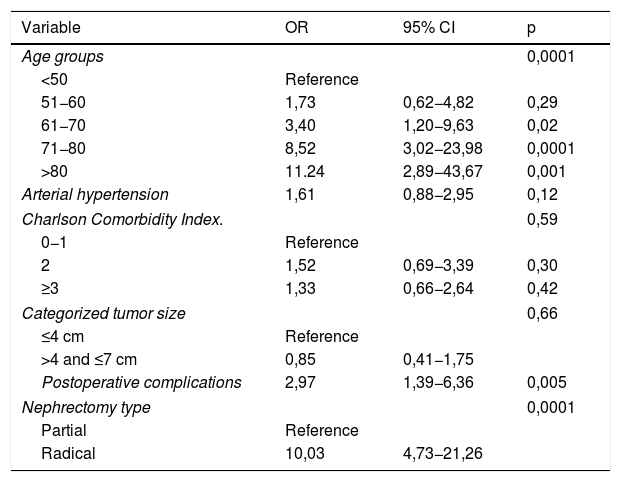
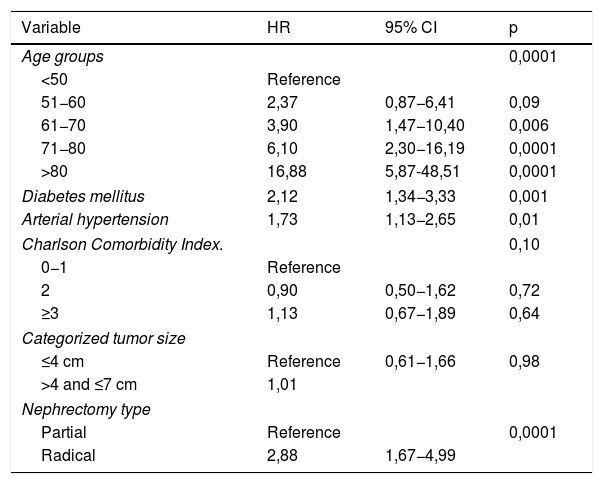
ResultsA total of 372 patients met the inclusion criteria for the study; 156 (41.9%) were treated with RN and 216 (58.1%) with PN. There was a difference of 26.75 mL/min/1.73 m2 in GFR between RN and PN at discharge. Age >60 years, postoperative complications (OR 2.97, p = 0.005) and RN (OR 10.03, p = 0.0001) were predictors of GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at discharge. Only RN (OR 7.69, p = 0.0001) behaved as an independent prognostic factor for GFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 at discharge. The median follow-up of the series was 57 (IQR 28–100) months. At the end of the follow-up period, nine (6%) patients treated with RN developed severe chronic kidney disease (CKD) and three (2%) developed end stage renal disease (ESRD). Age >70 years, diabetes mellitus (DM) (HR 2.12, p = 0.001), arterial hypertension (AHT) (HR 1.73, p = 0.01) and RN (HR 2.88, p = 0.0001) behaved as independent predictors of GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The independent predictors for GFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 were age >70 years, DM (HR 1.99 CI 95% 1.04–3.83, p = 0.04) and RN (HR 5.88 CI 95% 2.57–13.45, p = 0.0001).
ConclusionsRN is a short- and long-term risk factor for CKD although with a low probability of severe CKD or ESRD in patients with preoperative GFR >60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Age, DM and AHT contribute to worsening renal function during follow-up.
Analizar la evolución de la función renal tras nefrectomía parcial (NP) y radical (NR) laparoscópica e identificar factores predictores de deterioro de función renal.
Material y métodoEstudio retrospectivo de pacientes birrenos con filtrado glomerular (FG) > 60 mL/min/1,73 m2 y tumor renal único cT1 tratados en nuestro centro entre los años 2005 y 2018.
Resultados372 pacientes cumplieron los criterios de inclusión para el estudio. 156 (41,9%) fueron tratados mediante NR y 216 (58,1%) mediante NP. Al alta hubo una diferencia de 26,75 mL/min/1,73 m2 de FG entre NR y NP. La edad > 60 años, las complicaciones postoperatorias (OR 2,97, p = 0,005) y NR (OR 10,03, p = 0,0001) fueron factores predictores de FG < 60 mL/min/1,73 m2 al alta. Únicamente la NR (OR 7,69, p = 0,0001) se comportó como factor pronóstico independiente de FG < 45 mL/min/1,73 m2 al alta. La mediana de seguimiento de la serie fue de 57 (IQR 28 a 100) meses. Al final del seguimiento, nueve (6%) pacientes tratados con NR desarrollaron enfermedad renal crónica (ERC) grave y tres (2%) insuficiencia renal terminal (IRT). Edad > 70 años, diabetes mellitus (DM) (HR 2,12, p = 0,001), hipertensión arterial (HTA) (HR 1,73, p = 0,01) y NR (HR 2,88, p = 0,0001) se comportaron como factores predictores independientes de FG < 60 mL/min/1,73 m2. Para un FG < 45 mL/min/1,73 m2 fueron edad > 70 años, DM (HR 1,99 IC 95% 1,04 a 3,83, p = 0,04) y NR (HR 5,88 IC 95% 2,57 a 13,45, p = 0,0001).
ConclusionesLa NR es un factor de riesgo a corto y largo plazo de ERC, aunque con baja probabilidad de ERC grave o IRT en pacientes con FG > 60 mL/min/1,73 m2 preoperatoria. Edad, DM e HTA contribuyen al empeoramiento de la función renal durante el seguimiento.