To know the incidence of vesicourethral anastomotic stricture in patients with prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. Our secondary aim was to verify if postoperative radiotherapy increases the risk of presenting anastomotic stricture.
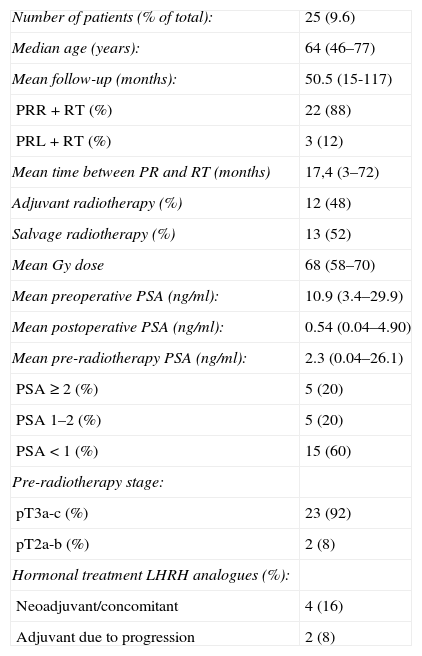
Materials and methodsWe retrospectively checked the clinical records of patients that had undergone radical prostatectomy as their primary treatment between January 2000 and December 2008, with a minimum clinical follow-up of 12 months. Of the total patients, 258 met the foregoing requirements. Among them, 25 (9.6%) received postoperative radiotherapy, 12 (48%) received adjuvant radiotherapy and 13 (52%) received salvage radiotherapy. The mean age of the patients that received radiotherapy was 64 (46–77) years. The mean pre-radiotherapy PSA was 2.3 (0.04–26.1)ng/ml. The mean time between surgery and radiotherapy was 17.4 (3–72) months. The mean dosage administered was 68 (58–70)Gy. The mean follow-up was 50.5 (15–177) months.
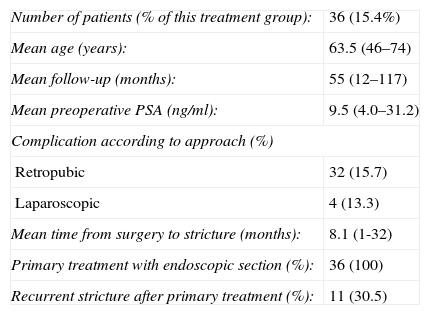
ResultsOf 25 prostatectomized patients that received radiotherapy, four (16%) developed vesicourethral anastomotic stricture. The mean time from the completion of the radiotherapy until the appearance of the stricture was 4 months (1–22). On the other hand, 36 (15.4%) of the prostatectomized patients that did not receive postoperative radiotherapy presented the same complication. Comparatively, we did not note significant differences between both groups (p=0.599).
ConclusionsIn our retrospective review, postoperative radiotherapy did not significantly increase the incidence of vesicourethral anastomotic stricture.
conocer la incidencia de la estenosis de la anastomosis vesicouretral en pacientes con cáncer de próstata tratados con prostatectomía radical. El objetivo secundario fue analizar si la radioterapia postoperatoria incrementa el riesgo de presentar una estenosis de la anastomosis.
Material y métodosse revisaron retrospectivamente las historias de los pacientes sometidos a prostatectomía radical como tratamiento primario entre enero 2000 y diciembre del 2008, con un seguimiento clínico mínimo de 12 meses. Del total de pacientes 258 cumplían los requisitos anteriores. De ellos 25 (9,6%) recibieron radioterapia postoperatoria, 12 (48%) de forma adyuvante y 13 (52%) de rescate. La edad media de los pacientes irradiados fue 64 (46-77) años. La mediana del PSA pre-radioterapia fue 2,3 (0,04-26,1) ng / ml. El tiempo medio entre la cirugía y la radioterapia fue 17,4 (3-72) meses. La dosis media administrada fue 68 (58-70) Gy. El seguimiento medio fue 50,5 (15-117) meses.
Resultadosde 25 pacientes prostatectomizados que recibieron radioterapia 4 (16%) desarrollaron estenosis de la anastomosis vesicouretral. El tiempo medio desde la finalización de la radioterapia hasta la aparición de la estenosis fue de 4 meses (1-22). Por otro lado, 36 (15,4%) pacientes prostatectomizados que no recibieron radioterapia postoperatoria presentaron esta misma complicación. Comparativamente no se apreciaron diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos (p=0,599).
Conclusionesen nuestra revisión retrospectiva, la radioterapia postoperatoria no incrementó de forma significativa la incidencia de estenosis de la anastomosis vesicouretral.