Although Gramineae pollens are the main reason for seasonal allergy in many parts of Europe, the influence of regional flora on sensitisation and symptoms has always been a topic of interest. The aim of this study was to document the sensitisation to pollens and to evaluate their clinical importance in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis living in Ankara/central Anatolia.
MethodsThe study included those subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis living in Ankara. Skin prick testing with a panel of common aeroallergens as well as grass, individual tree and weed pollens predominant in the region was performed. The patients were followed by symptom-medication scores during the same season in which regional pollens were also counted.
ResultsThe final eligible study consisted of 54 subjects (F/M: 26/28; mean age: 29.4 years). Trees were the most common pollen source consisting of 95 % of the total amount, followed by grasses (3 %) and weeds (2 %). Sensitisation to Gramineae, to at least one weed; and to tree pollens were 100 %, 85.2 % and 94.4 %, respectively. The most common positive skin tests among tree pollens were to Oleaceae (59.2 %), Aesculus (57.4 %); and Tilia (42.5 %) despite low pollen counts. Chenopodiaceae (88 %) and Plantago (63 %) were the most sensitised weed pollens, with high pollen counts. All patients had significant symptoms during May and June.
ConclusionAlthough Gramineae pollens seem to be major allergens for seasonal allergic rhinitis in Ankara, the particular role of tree pollens and weed pollens cannot be discarded on symptom development in sensitised patients.
The prevalence of pollen allergy is presently estimated to be up 40 %. Exposure to allergens represents a key factor among the environmental determinants1. Although particular different plant species exist in varying regions, previous trials showed Gramineae pollens to be the major cause of seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) in our country affecting 1.3 %-6.4 % of the population in accordance with other European countries2–10. On the other hand, regional pollen load has also been reported to have major impact on the clinical presentation of seasonal respiratory allergies. As an example of this, subjects living in regions with overabundance of tree pollens reported having a high incidence of positive reactions to tree pollens as an important cause of SAR, although generally it is believed that tree pollens are not as allergic as Gramineae pollens8.
Ankara is situated in central Anatolia at an altitude of 870m above sea level with dominant steppe vegetation and is 70km from natural Pinus forests. In the early years of the Republic of Turkey, there was an increase in plantation in Ankara owing to its arid properties. As a result of this development process of the city, today many species particularly of trees such as Populus, Platanus, Acer, Cupressaceae/Taxaceaea, Fraxinus as well as others with varying allergenic properties are seen in the city creating a high tree pollen load for allergic patients.
Many studies performed in Ankara region agreed that tree pollens comprised the majority of the pollen load whereas grass and weed pollens contributed less than 10 % of total yearly pollen counts9–11. These studies also pointed out the dominant individual pollens to which people were exposed in the region. Our recent trial showed a high sensitisation to a mixture of tree pollen in subjects with SAR living in the region3. However, the sensitivity rates to individualised pollens dominant in the region are not known and indeed whether this pollen load contributes significant symptoms in sensitised people living in our district.
In this study, we aimed to document the sensitisation rates to certain pollens dominant in the region which are selected according to the results of previous aeropalinologic trials performed in Ankara region and to evaluate the clinical importance of these sensitisations in patients with SAR living in Ankara. To do this, we followed subjects with isolated pollen allergy and living in Ankara city for at least three years and correlated the results with regional pollen counts.
METHODSPatientsThe study was conducted in our tertiary care clinic located in Ankara between January and December 2004. The eligible study subjects were the patients who admitted to our outpatient clinic with symptoms of SAR. The subjects in whom pollen (Gramineae and/or tree and/or weed) allergy was demonstrated in skin prick tests (SPTs) and diagnosed as allergic rhinitis according to ARIA guidelines13 and living in Ankara for at least 3years consisted the final study group. The rationale for selecting the subjects living at least three years in Ankara was that clinical presentation to certain pollen might require up to 3years of exposure. Subjects with concomitant allergy to perennial allergens such as house dust mites, cat, dog and cockroach in SPTs and those receiving allergen specific immunotherapy or not willing to participate to the study were not included. A verbal informed consent was obtained from each subject prior to study.
Study protocolAfter enrolment to the study, demographic and disease characteristics were recorded (age; sex; family history of atopy; duration and severity of rhinitis; distribution of symptoms according to months; presence of asthma). Following this step, all subjects were asked to fill in a symptom-medication score on a daily basis and to return it at the end of year. During the same period, atmospheric pollen counts were assessed.
Skin prick testsSPTs were performed using a common panel including Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Dermatophagoides farinae, grass, tree, and weed pollens (Table I), cat, dog, alternaría, cladosporium and cockroach allergen extracts (Allergopharma/Germany). Pollens for this study were selected according to the results of previous aeropalinologic trials conducted in Ankara and ten years cumulative pollen counts prepared by Ankara University Science Faculty (Fig. 1)9–11. Positive and negative controls were histamine (10mg/ml) and phenolated glycerol saline, respectively. Skin testing was performed by puncture method and a mean wheal diameter of 3mm or greater than with the control solution was considered positive.
Pollens used in skin prick test panel
| Gramineae |
| Mixture of Dactylis glomerata, Lolium perenne, Phleum pratense |
| Trees |
|
| Weeds |
|
Airborne pollen grains were counted in Ankara atmosphere from January to December 2004. The Burkard (Burkard manufacturing, Rickmansworth, Herts, UK) seven-day recording volumetric spore trap was used for sampling. The trap was installed on the roof of the Science Faculty building of Ankara University, which is 15m high. The orifice was 80cm above roof level. The pollen was sucked at an airflow rate of 10 litres per minute onto tapes which were coated with a thin film of vaseline-paraffin wax in toluene. The tape was then mounted in glycerine jelly. The twelve transverse stripes were counted on each slide, at a magnification of ×400. Counts were made at two-hour intervals and total daily counts were converted to number of pollen grains per cubic metre of air. Pollens were counted daily by the Palynological Laboratory in the Department of Biology of Ankara University.
CLINICAL EVALUATIONSymptom-medication scoresA symptom-medication score method was used to determine whether symptoms were associated with pollen counts. The subjects were asked to record their symptom and medication scores in the presence of symptoms and/or medication use. Symptoms for rhinitis and asthma were scored as follows:
"0": no symptoms,
"1": mild symptoms not disturbing daily activities of the subjects and not requiring medication
"2": moderate symptoms moderately disturbing daily activities and requiring medication
"3": severe symptoms which disturb patient's daily activities and require intensive medication for palliation.
Medication scores were filled for each drug consumed for the previous 24 hours. One point was given for each drug consumption except that of nasal steroids scored as 2 points and total medication score was scored as sum of points for each drug. Total monthly symptom and medication scores were used in the analysis of the data. The patients were instructed to use medications in accordance with the international guidelines13.
Severity of rhinitisSeverity of rhinitis was determined according to ARIA guidelines13. Intermittent AR is defined as experiencing symptoms for < 4days/week or < 4 consecutive weeks. Persistent AR is defined as symptoms occurring > 4days/week and > 4 consecutive weeks. In addition, a severity scale of mild to moderate-severe according to effects of symptoms on sleep and daily activities was used.
Statistical analysisNominal values were expressed as n (%) with inter-group differences determined by Chi-square test. Continuous variables were given as mean ± SEM. Symptom and medication scores were given as a mean of total sum in a month (total sum/number of days in that month). As the symptom and medication scores showed non-homogeneous distribution, within-group comparisons were made by Wilcoxon signed-ranks test. All directional p values were two-tailed and significance was assigned to values lower than 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed by Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, v. 11.0 for Windows, Chicago, IL, USA).
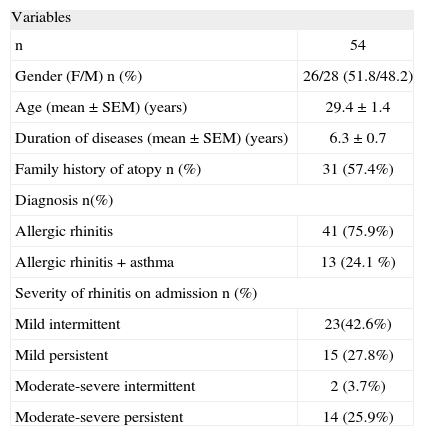
RESULTSStudy groupThe final study group consisted of 54 subjects (F/M: 26/28; mean age: 29.4years) with SAR. Demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table II. The majority had allergic rhinitis alone (41; 75.9 %) and had mild intermittent rhinitis on admission (23; 42.6%).
Characteristics of study population
| Variables | |
| n | 54 |
| Gender (F/M) n (%) | 26/28 (51.8/48.2) |
| Age (mean ± SEM) (years) | 29.4 ± 1.4 |
| Duration of diseases (mean ± SEM) (years) | 6.3 ± 0.7 |
| Family history of atopy n (%) | 31 (57.4%) |
| Diagnosis n(%) | |
| Allergic rhinitis | 41 (75.9%) |
| Allergic rhinitis + asthma | 13 (24.1 %) |
| Severity of rhinitis on admission n (%) | |
| Mild intermittent | 23(42.6%) |
| Mild persistent | 15 (27.8%) |
| Moderate-severe intermittent | 2 (3.7%) |
| Moderate-severe persistent | 14 (25.9%) |
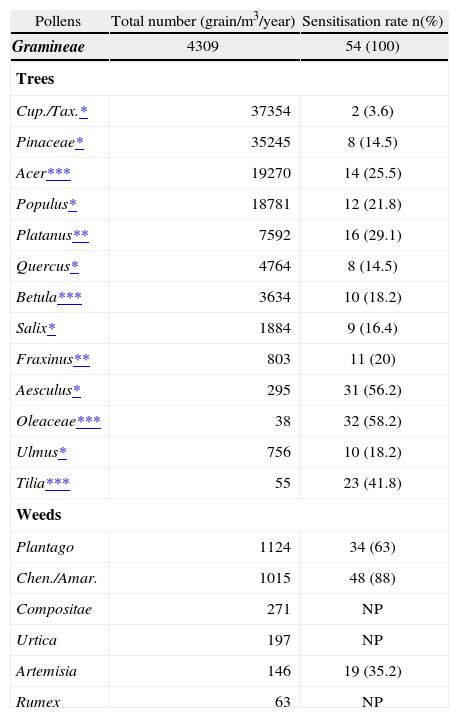
Sensitisation to Gramineae, to at least one weed; and to tree pollens were 100 %, 85.2 % and 94.4 %, respectively. The majority of the subjects (44; 81.5 %) had allergy to Gramineae, weed and tree pollens concomitantly, eight (14.8 %) had allergy to both Gramineae and weed pollens and only two (3.7 %) subjects had allergy to Gramineae pollens alone.
The most common positive SPTs among tree pollens were as follows: Oleaceae (olive) (32; 59.2 %), Aesculus (horse chestnut) (31; 57.4 %); Tilia (linden) (23; 42.5 %) and Platanus (plane) (16; 29.6 %). Among weed pollens, the patients were mainly sensitised to plantain (34; 63 %) and Chenopodium (48; 88 %) pollens.
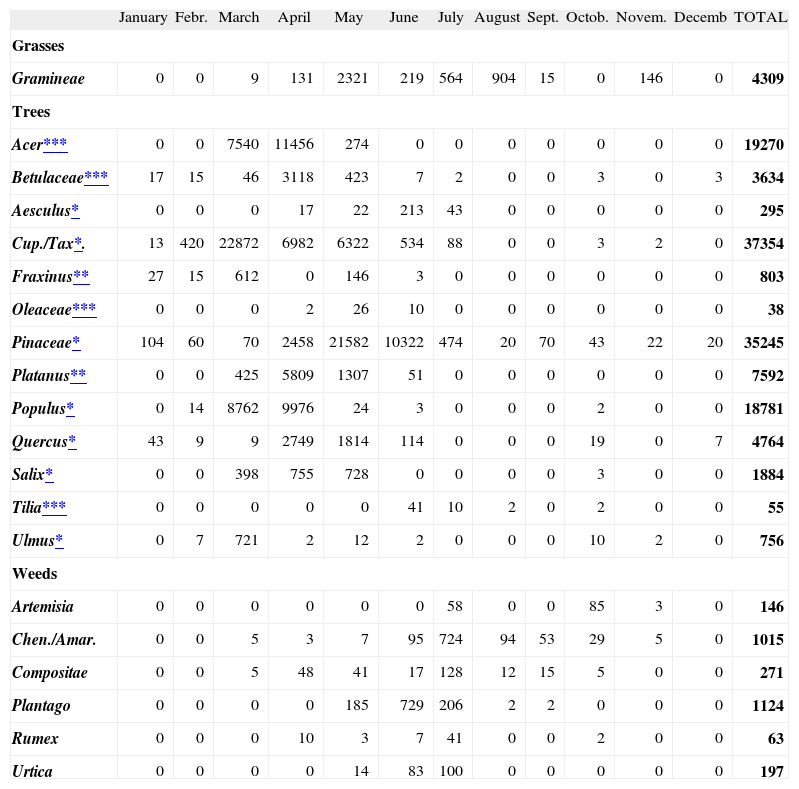
Pollen countsA total of 145345 pollen grains/m3 were counted in Ankara atmosphere in 2004. Trees were the most common pollen source consisting of 95% (138 200 grains/ m3/year) of the total amount and were followed by grasses (3 %; 4309 grains/ m3/year) and weeds (2 %; 2816 grains/ m3/year). The most prominent individual pollens from January to April were tree pollens (Cupresseceae; Pineceae; Quercus; Populus; Betula; Fraxinus; Salix; Acer, Platanus); from May to July were Gramineae, Pineceae and Cupresseceae/Taxaceae pollens; and in July and August were Gramineae, and weed pollens (Plantago, Chenopodiaceae/Amaranthaceae, Compositae) (Table III).
Distribution of pollen counts (pollen/m3) according to months in Ankara atmosphere in 2004
| January | Febr. | March | April | May | June | July | August | Sept. | Octob. | Novem. | Decemb | TOTAL | |
| Grasses | |||||||||||||
| Gramineae | 0 | 0 | 9 | 131 | 2321 | 219 | 564 | 904 | 15 | 0 | 146 | 0 | 4309 |
| Trees | |||||||||||||
| Acer*** | 0 | 0 | 7540 | 11456 | 274 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19270 |
| Betulaceae*** | 17 | 15 | 46 | 3118 | 423 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3634 |
| Aesculus* | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 22 | 213 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 295 |
| Cup./Tax*. | 13 | 420 | 22872 | 6982 | 6322 | 534 | 88 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 37354 |
| Fraxinus** | 27 | 15 | 612 | 0 | 146 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 803 |
| Oleaceae*** | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 26 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 |
| Pinaceae* | 104 | 60 | 70 | 2458 | 21582 | 10322 | 474 | 20 | 70 | 43 | 22 | 20 | 35245 |
| Platanus** | 0 | 0 | 425 | 5809 | 1307 | 51 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7592 |
| Populus* | 0 | 14 | 8762 | 9976 | 24 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 18781 |
| Quercus* | 43 | 9 | 9 | 2749 | 1814 | 114 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 7 | 4764 |
| Salix* | 0 | 0 | 398 | 755 | 728 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1884 |
| Tilia*** | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 55 |
| Ulmus* | 0 | 7 | 721 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 756 |
| Weeds | |||||||||||||
| Artemisia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 58 | 0 | 0 | 85 | 3 | 0 | 146 |
| Chen./Amar. | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 95 | 724 | 94 | 53 | 29 | 5 | 0 | 1015 |
| Compositae | 0 | 0 | 5 | 48 | 41 | 17 | 128 | 12 | 15 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 271 |
| Plantago | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 185 | 729 | 206 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1124 |
| Rumex | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 63 |
| Urtica | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 83 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 197 |
Details of comparison of pollen counts and sensitisation rates of various pollens are shown in Table IV. Among tree pollens, the most common sensitizers were Oleaceae, Aesculus, Tilia, Platanus and Acer. Among them, Acer and Platanus were the second and fifth, respectively, in contributing to tree pollen load in Ankara atmosphere. On the other hand, Oleaceae, Tilia and Aesculus were among the ones with lowest atmospheric pollen counts in Ankara in 2004 (Table III).Among tree pollens, the most common sensitizers were Oleaceae, Aesculus, Tilia, Platanus and Acer. Among them, Acer and Platanus were the second and fifth, respectively, in contributing to tree pollen load in Ankara atmosphere. On the other hand, Oleaceae, Tilia and Aesculus were among the ones with lowest atmospheric pollen counts in Ankara in 2004 (Table III).
Sensitisation rates and pollen counts of trees and weed pollens
| Pollens | Total number (grain/m3/year) | Sensitisation rate n(%) |
| Gramineae | 4309 | 54 (100) |
| Trees | ||
| Cup./Tax.* | 37354 | 2 (3.6) |
| Pinaceae* | 35245 | 8 (14.5) |
| Acer*** | 19270 | 14 (25.5) |
| Populus* | 18781 | 12 (21.8) |
| Platanus** | 7592 | 16 (29.1) |
| Quercus* | 4764 | 8 (14.5) |
| Betula*** | 3634 | 10 (18.2) |
| Salix* | 1884 | 9 (16.4) |
| Fraxinus** | 803 | 11 (20) |
| Aesculus* | 295 | 31 (56.2) |
| Oleaceae*** | 38 | 32 (58.2) |
| Ulmus* | 756 | 10 (18.2) |
| Tilia*** | 55 | 23 (41.8) |
| Weeds | ||
| Plantago | 1124 | 34 (63) |
| Chen./Amar. | 1015 | 48 (88) |
| Compositae | 271 | NP |
| Urtica | 197 | NP |
| Artemisia | 146 | 19 (35.2) |
| Rumex | 63 | NP |
NP: not performed.
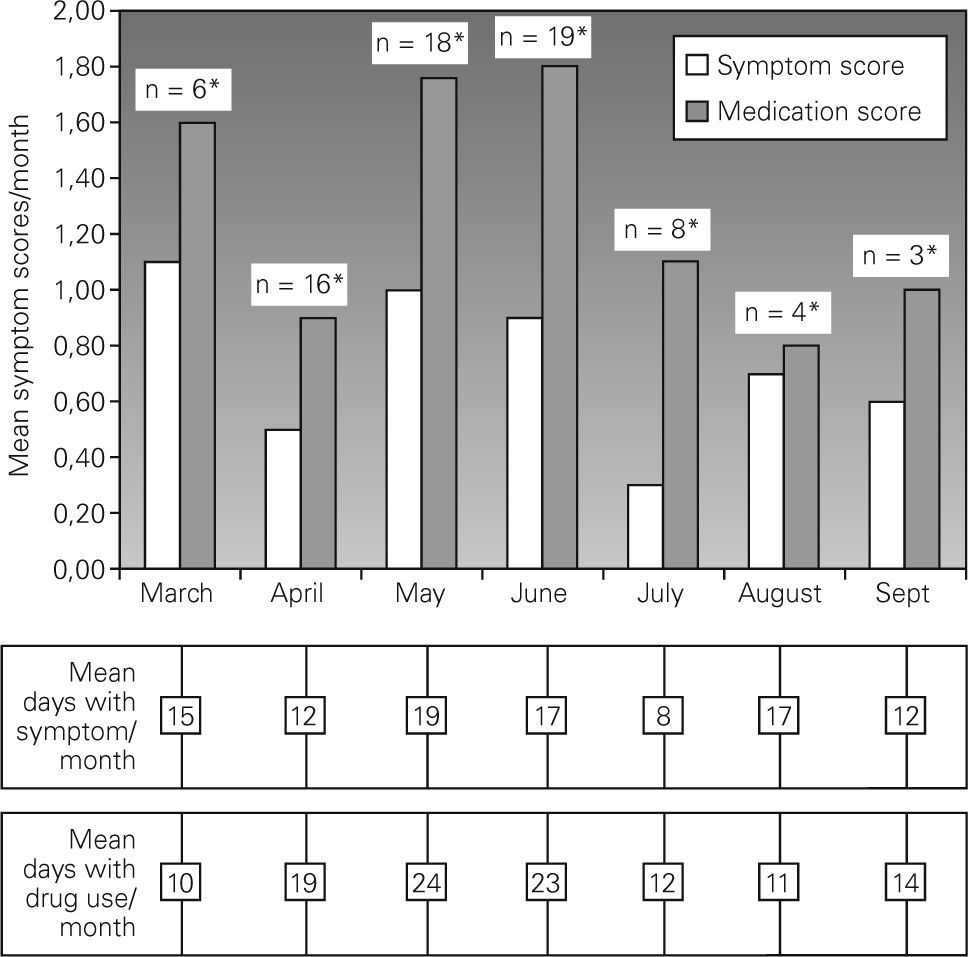
Twenty patients returned symptom-medication scores. The minority of the subjects showed symptoms in January and February followed by an increase starting from March. In March only six patients revealed symptoms and medication use with mean scores of 1.1 and 1.6/month, respectively. The majority of the subjects (n = 18 and 19 for May and June, respectively) showed symptoms with mean symptom scores of 1 and 0.9 in May and June 2004, respectively (Fig. 2). There was also an increase in medication use in these months. In July, where there was a peak of weed pollens and 75 % reduction in Gramineae pollens, eight patients had symptoms requiring medication. In August and September, symptoms and medication use persisted in a small number of subjects despite a decrease in symptoms and medication use.
DISCUSSIONIn this study, we have shown that sensitisation to Gramineae pollens was the leading cause for SAR in the region. Our data also revealed that regional tree pollen load as well as certain plantation with low pollen counts had a particular contribution to both sensitisation and clinical presentations of seasonal allergy in subjects living in Ankara. Our results also highlighted the clinical significance of weed allergy in our region.
Regarding geographic and climate properties, plantation in Turkey is similar to the south-eastern part of Europe. This similarity also reflects to clinical expression. As a result of this, Gramineae pollen allergy has been reported to be the main reason for seasonal allergy in our country2–6 in accordance with a recent study conducted in many countries of Europe within the frame work of GA2LEN14. Our current clinical data also showed that Gramineae pollen was the leading allergen influencing the patient with SAR in the central part of our country, Ankara region.
Despite being located in the central part of the country, plantation in Ankara also resembles the Mediterranean region with some differences particularly in weeds and some trees such as olive. Subjects living in regions with overabundance of tree pollens were reported to have a high incidence of positive reactions to tree pollens as an important cause of SAR15–17. In this sense, despite the fact that Gramineae pollens are the main cause of SAR all around the country as well as in our city, the role of tree pollens on seasonal allergy needs to be clarified in our region as Ankara city is rich in several trees such as poplar, pine, plane, horse chestnut, maple, cypress and others. Emphasizing this, our recent trial supported a high sensitisation rate to a mixture of tree pollens in subjects with SAR living in the region3.
This study showed that pollen composition generally reflected the vegetation of gardens, parks, and roadsides in the city. Thus, pollens of cypress, pines, and maple and poplar trees had the highest contribution to the regional pollen load. Regarding the sensitisation rates, our results indicated that 94.4 % of the study subjects had positive SPT to at least one of the tree pollens. However, sensitisation rates did not seem to correlate with pollen counts as the higher sensitisation rates for trees were caused by tress such as Oleaceae, Aesculus, and Tilia with the lowest pollen counts in the city. Pollens of olive tree are known to be highly allergenic18, yet, as there is no olive tree in the city and the olive tree is found very commonly on the southern and western coasts of Turkey, finding a high Oleaceae sensitivity rate in skin testing was one of the most surprising data in our study. Supporting our data, another study from Eskis¸ehir, whose climate and vegetation is very close to Ankara, also showed that Oleaceae family had the highest sensitivity (22 %) in patients with seasonal allergy19. One explanation could be cross-reactivity between Oleaceae and Fraxinus, which is frequent in Ankara as they are in the same family. Another is that long distance transport might be responsible for sensitisation in areas far from the source of pollen1. A further speculation could be sensitisation to olive pollen during vacation(s) to these regions, which was not investigated in this study. On the other hand, despite low atmospheric pollen counts of Aesculus and Tilia, we also observed high sensitivity rates (over 40 % of each) to these pollens. Tilia is primarily insect pollinated and of little allergenic importance in North America18. However, our results indicated that these plants cause significant sensitisation in the residents of our city where both trees are frequently encountered which emphasized the re-direction of policy for new plantation in the region.
On the other hand, regarding the correlation between skin test reactivity and regional pollen counts, we obtained low to moderate sensitisation rates to pollens of cypress and pine trees. Cupresseceae/Taxaceae allergy has been reported to be common in the south of France and Italy and regarded to cause a significant sensitisation20. However, our result showed a very low sensitisation rate to Cupresseceae/Taxaceae. A possible explanation for this discrepancy could be using of different pollen extracts.
Regarding clinical presentations of the subjects, despite the fact that few subjects revealed symptoms in early spring, especially in March, both medication and symptom scores were, however, close to those in May and June. Regarding the very low counts for Gramineae pollens in March, this result suggested that in a susceptible person, exposure to tree pollens in high amounts might be responsible for clinical presentation. Trees with high pollen counts in March were Cupresseceae/Taxaceae; Populus; Acer; Ulmus; Fraxinus; and Platanus. Regarding the low clinical impact of exposure to Poplar tree pollens in sensitised subjects21 and allergenic properties of other tree pollens8,22, we may assume that Acer, Platanus and Fraxinus pollens could be the main reason for clinical presentations in this month19.
Generally, it is believed that weeds are an important pollen source with highly allergenic properties in the American continent. In our country, weeds are found to be clinically important in Mediterranean and Aegean Sea coasts of the country23. However, our data also strengthen the clinical importance of some weed pollens such as Plantago and Chenopodiaceae Amaranthaceae in our particular region On the other hand, finding a higher rate for weed sensitivity when skin test applied by individual weed allergens in comparison to another study performed in our region also emphasizes the importance of doing skin testing on individual allergen bases24.
Thus, the results of the current study carry important information related to associations with regional pollen counts/plantation and sensitisation/symptom development in subjects with SAR and living in Ankara/central Anatolia. Besides Gramineae pollens, some tree and weed pollens also have a particularly important effect on the clinical profile of the sensitised patient for our region. This study has also shown us that not only the trees with high pollen counts but also some insect pollinated trees such as Aesculus, and Tilia might have a significant contribution to sensitisation. This data points out the necessity of preventive measures to be taken by means of selection of the plantation in the region in the future. For the definite determination of sensitivity rates of the individual pollens in subjects living in Ankara, in addition to Gramineae pollens, SPT panels should also include particular tree pollens such as Cupresseceae/Taxaceae, Acer, Populus, Aesculus, Tilia and Platanus and particular weed pollens such as Plantago and Chenopodiaceae/Amaranthaceae.
The authors thank Allergopharma/Germany for providing skin prick testing materials and Suzan Kisa and Gülay Ülger for performing skin prick tests.