A 59-year-old man with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia on alemtuzumab presented with neutropenic fever, intermittent nausea, and multiple ill-defined low attenuation foci in the liver on abdominal computed tomography scan which were suspicious for metastatic disease. Histological examination revealed the diagnosis of adenovirus hepatitis. Patient responded well to cidofovir. Adenovirus hepatitis is a rare but important entity to be considered by the clinicians, radiologists, and pathologists. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to improve the prognosis of adenovirus hepatitis in immunocompromised patients.
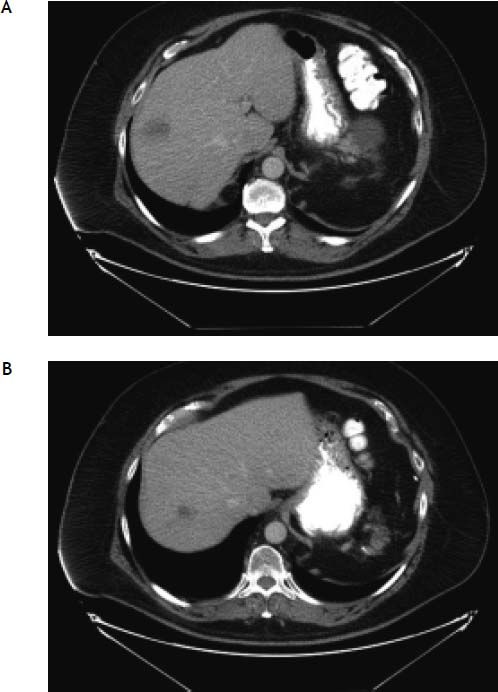
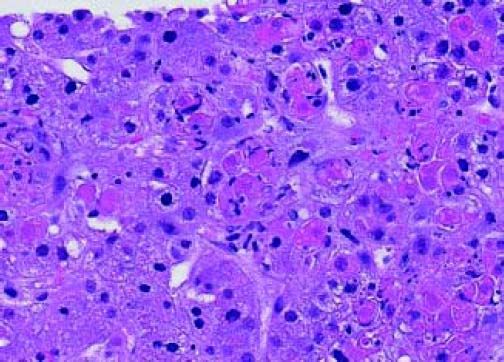
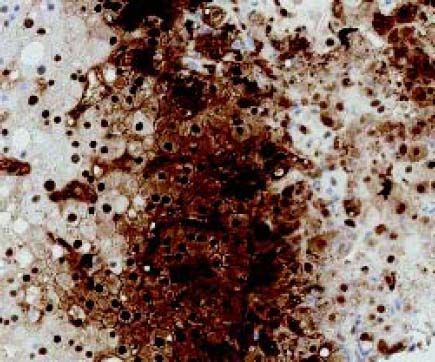
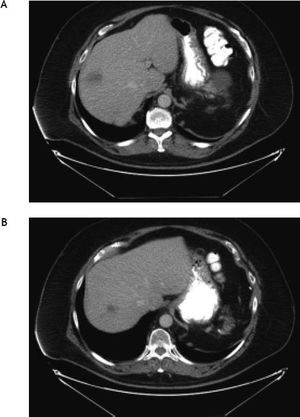
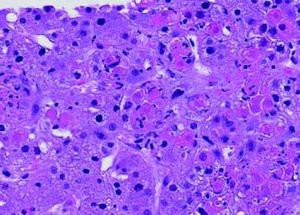
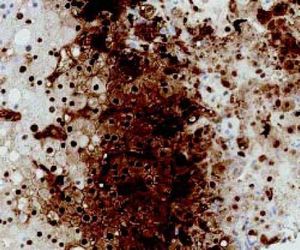
A 59-year old man with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia on alemtuzumab presented with neutropenic fever. His past medical history was significant for hepatitis C and splenectomy several years ago due to splenic involvement of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. His febrile and intermittent nausea persisted despite several days of cephalosporin therapy. No localized signs or symptoms of infection were identified on the physical examination. The laboratory analysis was significant for leukopenia (0.3 x 103/mcL) and transaminitis (ALT 87 U/L, AST 284 U/L). Meanwhile, other liver function tests were within normal limits (total bilirubin 0.3 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 75 U/L, albumin 3.2 g/dL, and total protein 7.8 g/dL). Computed tomography scan of the abdomen with contrast revealed multiple hypodense lesions in the liver (Figure 1). The largest lesion was seen in the posterior right lobe, measuring approximately 4.4 cm. Differential diagnosis included metastatic lesions, and less likely infectious etiology. Computed tomography-guided needle core biopsy of the lesions revealed numerous hepatocytes with smudgy nuclear appearance (Figure 2), which were characteristic of adenovirus infections. Diagnosis of adenovirus hepatitis was also confirmed by diffuse immunostaining (Figure 3). In addition, quantitative polymerase chain reaction revealed high-copy number of adenovirus DNA (2,000,000 copies/mL) and culture of the liver biopsy was positive for adenovirus. Treatment with cidofovir improved his condition dramatically. Adenovirus DNA detection by quantitative polymerase chain reaction was within normal range (< 500 copies/mL) 3 months after the treatment was initiated.
Adenovirus, a double-stranded DNA virus, is a common cause of self-limiting upper respiratory infection in immunocompetent patients.1 Adenovirus infections occur more frequently in immunocompromised patients and may result in more severe manifestations, such as pneumonia, nephritis, hepatitis, encephalitis, pancreatitis, or disseminated disease.1–3 The reported incidence of adenovirus infections in immunosuppressed patients ranges from 3 to 21%.3 Different methods can be utilized to diagnose adenovirus hepatitis. The imaging features of acute hepatitis are often nonspecific. The most essential role of radiology in patients with suspected hepatitis is to help rule out other etiologies. The nonspecific findings on computed-tomography and magnetic resonance imaging include hepatomegaly and periportal edema. On computed-tomography, heterogeneous enhancement and well-defined regions of low attenuation may be present. Meanwhile, periportal edema appears as high-signal-intensity areas on T2-weighted images on magnetic resonance imaging.4 Familiarity with the most relevant radiologic key features, combined with critical clinical information may provide enough information to characterize the lesion and differentiate it from other types of focal lesion (neoplastic and developmental). Adenoviral infections can also be diagnosed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or immunofluorescence assay, complement fixation test or viral culture.1 However, these patients often require tissue biopsy to render a definitive diagnosis. The histologic hallmark of adenovirus infection in the liver is the presence of patchy necrosis with “blueberry” basophilic intranuclear inclusions in the hepatocytes, which often referred as smudge cells.5 Furthermore, immunohis-tochemistry is useful to confirm the microscopic findings. We demonstrated that adenovirus hepatitis may present as tumoral lesions on computed tomography scan. Furthermore, timely diagnosis is essential to obtain favorable outcomes.
Conflict of InterestBoth authors have nothing to disclose.