Background and aim: Some patients with SARSCov-2 infection develop severe disease (SARS); however, the factors associated with severity are not yet fully understood. Some reports indicate that liver injury may be a poor prognostic factor. AIM: To identify the biochemical factors related to the development of SARS with mechanical ventilation (MV) requirement in patients with SARSCov-2 and COVID-19.
Methods. Type of study: Observational. Cohort study. Procedure: Data from COVID-19 patients were collected at admission time to a tertiary care center. Differential factors were identified between seriously ill SARS+MV patients versus stable patients without MV. Transformation to the natural logarithm of significant variables was performed and multiple linear regression was applied, then a predictive model of severity called AAD (Age-AST-D dimer) was constructed.
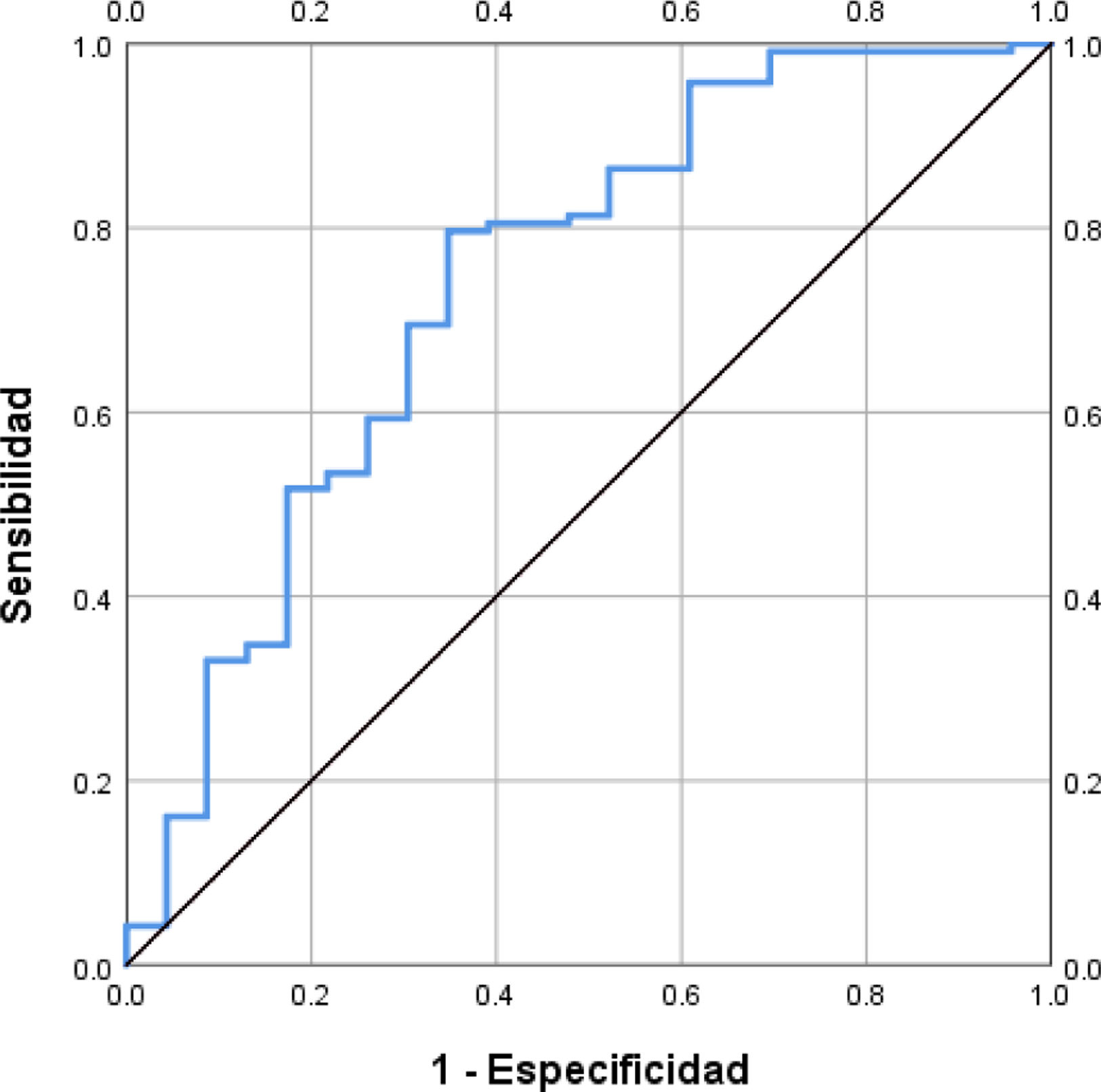
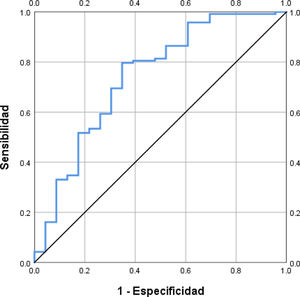
Results: 166 patients were included, 114(68.7%) men, mean age 50.6±13.3 years-old, 27(16.3%) developed SARS+MV. In the comparative analysis between those with SARS+MV versus stable patients without MV we found significant raises of ALT (225.4±341.2 vs. 41.3±41.1; P=0.003), AST 325.3±382.4 vs. 52.8±47.1; P=0.001), LDH (764.6±401.9 vs. 461.0±185.6; P=0.001), D dimer (7765±9109 vs. 1871±4146; P=0.003), age (58.6±12.7 vs. 49.1±12.8; P=0-001). The results of the regression are shown in the Table, where model 3 was the one that best explained the development of SARS+MV; with these variables was constructed the model called AAD, where: [AAD=3.896+ln(age)x-0.218+ln(AST)x-0.185+ln(DD)x0.070], where a value ≤ 2.75 had sensitivity=0.797 and 1-specificity=0.391, AUROC=0.74 (95%CI: 0.62-0.86; P<0.0001), to predict the risk of developing SARS+MV (OR=5.8, 95%CI: 2.2-15.4; P=0.001).
Conclusions: Elevation of AST (probable marker of liver damage) is an important predictor of progression to SARS, together with elevation of D-dimer and age early (at admission) and efficiently predict which patients will potentially require MV.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
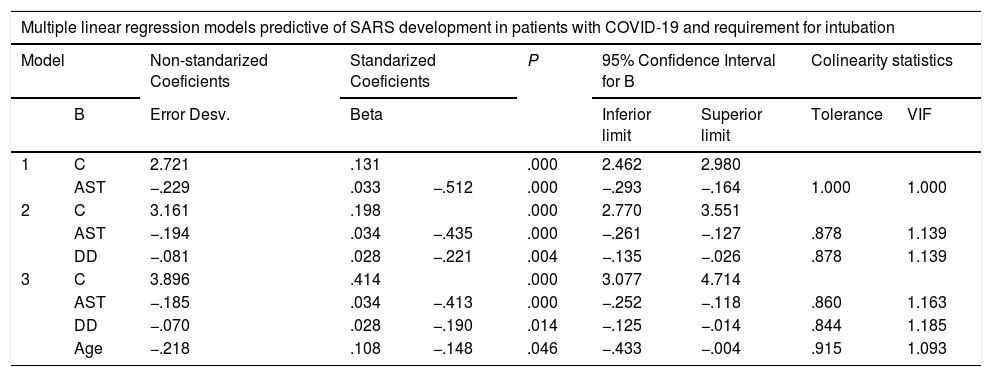
| Multiple linear regression models predictive of SARS development in patients with COVID-19 and requirement for intubation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-standarized Coeficients | Standarized Coeficients | P | 95% Confidence Interval for B | Colinearity statistics | ||||
| B | Error Desv. | Beta | Inferior limit | Superior limit | Tolerance | VIF | |||
| 1 | C | 2.721 | .131 | .000 | 2.462 | 2.980 | |||
| AST | −.229 | .033 | −.512 | .000 | −.293 | −.164 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 2 | C | 3.161 | .198 | .000 | 2.770 | 3.551 | |||
| AST | −.194 | .034 | −.435 | .000 | −.261 | −.127 | .878 | 1.139 | |
| DD | −.081 | .028 | −.221 | .004 | −.135 | −.026 | .878 | 1.139 | |
| 3 | C | 3.896 | .414 | .000 | 3.077 | 4.714 | |||
| AST | −.185 | .034 | −.413 | .000 | −.252 | −.118 | .860 | 1.163 | |
| DD | −.070 | .028 | −.190 | .014 | −.125 | −.014 | .844 | 1.185 | |
| Age | −.218 | .108 | −.148 | .046 | −.433 | −.004 | .915 | 1.093 | |
AST, aspartate aminotransferase; C, constant; DD, D dimer; VIF, variance inflation factors.
Resume of the model:
R=0.512, r2=0.262, r2 adjusted=0.256, standard error=0.331.
R=0.552, r2=0.305, r2 adjusted=0.294, standard error=0.322.
R=0.570, r2=0.325, r2 adjusted=0.310, standard error=0.318. Durbin-Watson=1.53.
AAD MODEL TO PREDICT SEVERE FORM (SARS)+INTUBATION