Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
More infoSpontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is a frequent complication in cirrhotic patients; the start of treatment is empirical and is adjusted with cultures. The antibiotic of choice is cephalosporins, which have reported high resistance. Improving SBP conditions has an impact on the evolution of patients. This study aimed to assess the early treatment response of SBP treated with empiric antibiotics.
Patients and MethodsPatients with a diagnosis of cirrhosis and SBP were included who underwent diagnostic paracentesis and paracentesis thee days after starting treatment; a decrease in ascites cellularity was evaluated as a criterion of response to treatment and the culture report. Descriptive and inferential statistics were performed. The trial was approved by the research ethics committee, and informed consent was obtained.
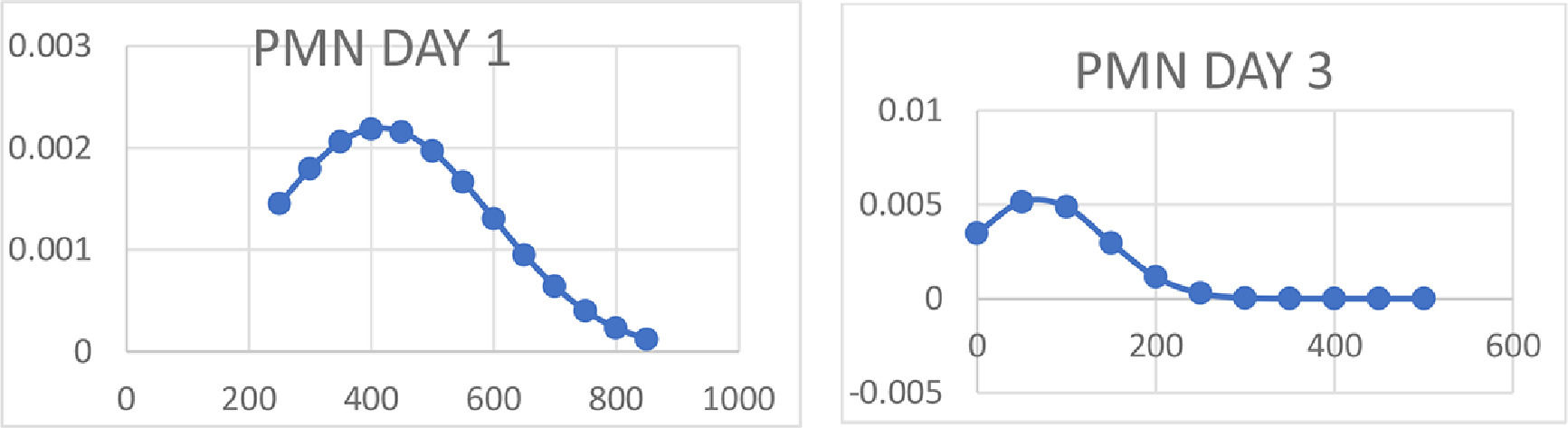
ResultsSix hundred twenty-one patients diagnosed with liver cirrhosis were included. Forty-seven met the criteria for SBP. Thirty men (63%) and 17 women (36%); the causes of cirrhosis were: Alcohol 25 (53%), MAFLD 9 (19%), autoimmune 2 (4%) and unknown 10 (21%) By Child-Pugh B 12 (25%) and 35 (74%) C. 89% (42) received cephalosporins, of which 78% (33) responded to treatment (figure 1), of which 66% (23) did not isolated agent in culture, only 31% (10) developed bacterial agent, mainly E. coli (60%).
ConclusionsSBP is the most common cause of infections in cirrhotic patients, with a high impact on morbidity and mortality. Despite reports of resistance to cephalosporins in our population, the response to empirical treatment with cephalosporins is still optimal.
FundingThe resources used in this study were from the hospital without any additional financing
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.