Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
More infoTo compare various prognostic scales to verify which one has the best performance in predicting 28-day mortality in patients with severe toxic-alcoholic hepatitis (AH).
Materials and MethodsObservational, cohort study. Data were collected from patients with severe AH who were hospitalized between January 2010 and May 2022. MELD, MELDNa, MELD3.0, ABIC, Maddrey, and Glasgow scale for AH were calculated at admission and their outcome at 28 days was verified. ROC curves were constructed to compare the different prognostic scales.
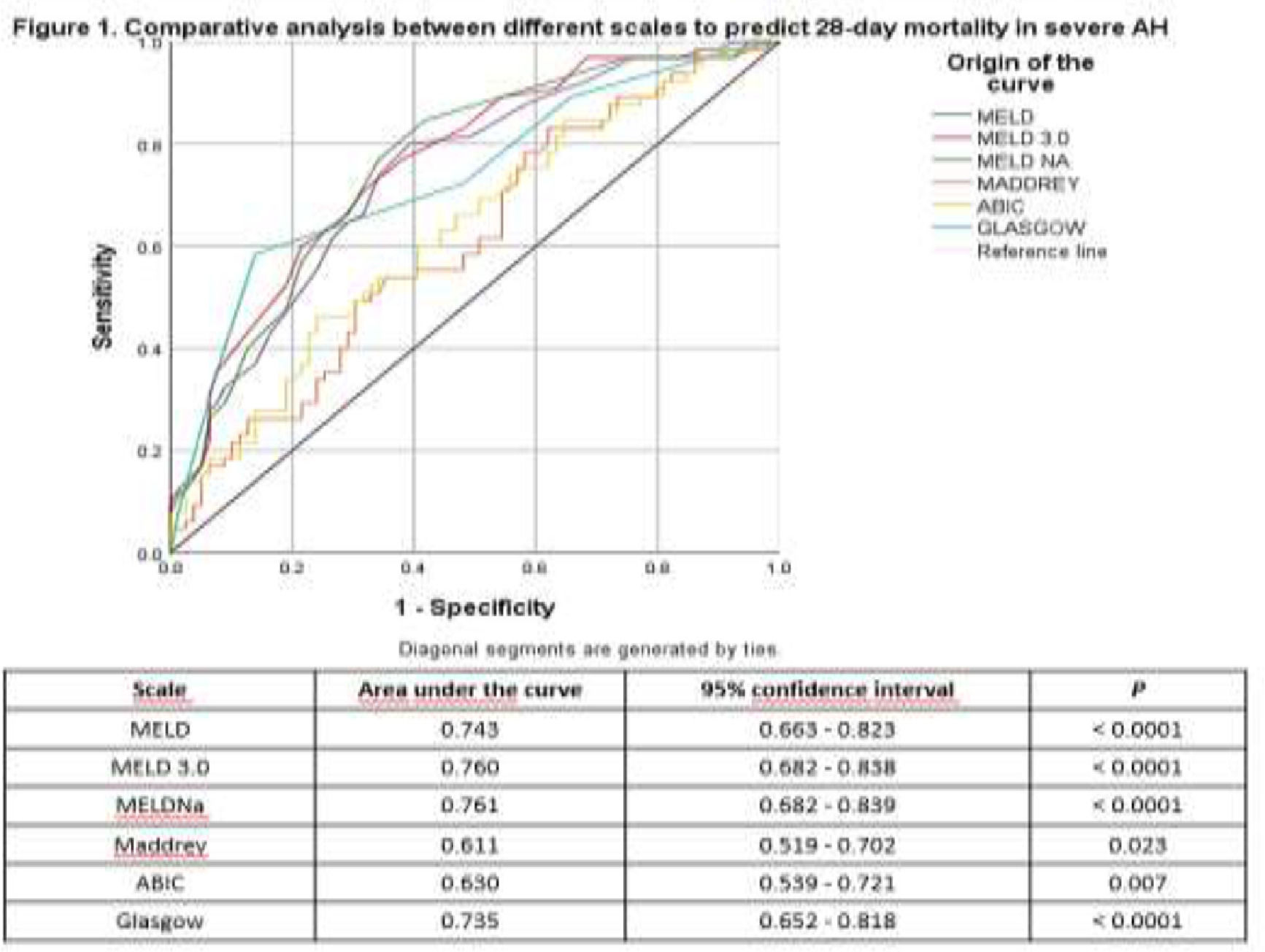
ResultsA total of 144 patients were included, 129 (89.6%) men, with a mean age of 43.3±9.3 years, and median grams of alcohol consumed/day was 320 (range: 60-1526). 65 (45.1%) died. The mean of MELD, MELDNa and MELD3.0 was higher among the deceased vs. survivors (33.5±7.5 vs. 27.1±6.2; 34.6±5.7 vs. 29.1±5.7; and 35.8±6.0 vs. 30.1±5.5 respectively; p<0.0001). The ROC curve analysis comparing the prognostic scales is shown in Figure 1.
ConclusionsAH mortality is high. MELDNa and MELD3.0 have the best performance in predicting on admission which patients with AH are at risk of dying in the following 28 days and can be useful tools for prioritizing patients who are candidates for liver transplantation.
FundingThe resources used in this study were from the hospital without any additional financing
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.