Liver involvement in tuberculosis in absence of miliary tuberculosis is rare. This study was performed to analyse the spectrum and response to treatment of hepatic tuberculosis in the absence of miliary abdominal tuberculosis. Retrospective analysis of seven cases of hepatic tuberculosis without miliary abdominal tuberculosis who presented at the single tertiary referral center were analyzed. All patients presented with fever and hepatomegaly. Five of them had pain in upper abdomen and vomiting. HIV serology was positive in one patient. All patients had normocytic normochromic anaemia, raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate (Mean 65). Mild elevation of liver enzymes and low albumin (Mean 2.4 gm%) with reversal of albumin globulin ratio (Mean 0.6) were seen in all. Two had jaundice. Prothrombin time was normal in all and lactate dehydrogenase values were elevated in all (Mean 794 IU/L). On ultrasonography, 2 had multiple hypodense lesion, 1 had coarse echotexture of liver, 1had hyperechoic pattern and 3 had just hepatomegaly. Complete resolution of liver lesions on treatment with 4-drug anti-tuberculosis drug chemotherapy was seen. In conclusion, liver tuberculosis has protean manifestations with nonspecific alteration of liver function tests and is best diagnosed on liver biopsy. Overall response to therapy is satisfactory.
The incidence of peritoneal tuberculosis is rising the world over.1,2 Abdominal tuberculosis is a common clinical entity in Indian subcontinent, however, hepatic tuberculosis in the absence of miliary abdominal tuberculosis is restricted to case reports3,4 and small case series in English literature.5 Hepatic tuberculosis mimics common liver diseases such as liver abscess and tumor6,7 or at times presents with varied forms of systemic diseases like fever of unknown origin.8,9 We analyzed seven cases of isolated hepatic tuberculosis with respect to their presentation, diagnosis and management.
Patients and methodsPatients presenting to the single tertiary referral center between 2001 to 2004 and diagnosed as isolated hepatic tuberculosis were retrospectively analyzed by reviewing the case notes of all patients presenting with abdominal tuberculosis as well as reviewing the records of the pathology department for biopsies reported as tuberculosis. The presentation and biochemical parameters were studied. Findings on ultrasonography, CT Scan and histopathology were noted. The association with existence of tuberculosis other organ system & immunodeficiency were studied. Treatment given and final outcome were noted.
ResultsOf the 76 cases of abdominal tuberculosis diagnosed in the Department of Gastroenterology, seven cases of isolated hepatic tuberculosis were identified over a two years period. There age range was 2 to 65 years, 6 were male. All presented with fever anorexia and weight loss. Five patients had pain in upper abdomen and vomiting. Two of these patients were icteric. On examination, all of them had hepatomegaly.
All patients had anemia (Table I) which was normocytic normochromic. Only two patients had lymphocytosis (defined as a differential count > 45%) and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. At least one liver enzyme was elevated in all. All patients had low albumin with reversal of albumin globulin ratio. Prothrombin time was normal in all patients.
| No. abnormal | Mean | Range* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 7 | 9.0 g/dL | 6.9-11.8 g/dL |
| Erythrocyte | |||
| sedimentation rate | 7 | 65 mm at 1 hour | 35-105 mm |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 5 | 67 U/L | 45-91 U/L |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 4 | 97 U/L | 55-159 U/L |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 2 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | 6 | 445 IU/L | 109-626 IU/L |
| Albumin | 7 | 2.4 g/dL | 1.3-3.1 g/dL |
| Albumin: Globulin | 7 | 0.6 | 0.4-0.9 |
| Prothrombin time | nil | ||
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 7 | 794 IU/L | 402-1597 IU/L |
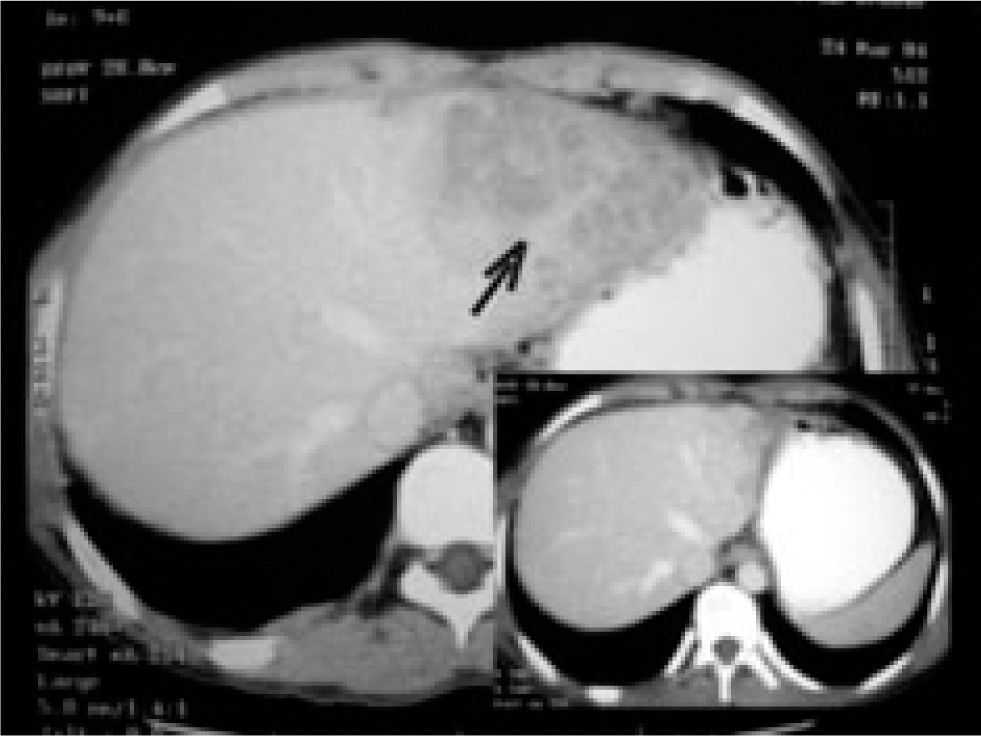
Ultrasonography was performed in all patients. All had hepatomegaly. Two patients had multiple hypodense lesion, 1 had coarse echotexture, 1 had hyperechoic parenchyma and 3 had just hepatomegaly without any specific pattern. None of the patients had evidence of any lymphadenopathy on other organ involvement on abdominal ultrasound examination. CT Scan was performed in the patients with liver lesions, showing no vascular enhancement of these lesions (Figure 1). Chest X-ray showed no evidence of active pulmonary tuberculosis in any patient. HIV serology was positive in one patient.
Liver biopsy was performed in all cases with a Tru-cut needle. The biopsy showed granulomas (Figure 2) within the liver, non-caseating in 6 cases while one showed caseation. Three of these had visible acid-fast bacilli (AFB) on Ziehl-Neelson staining of tissue. A further two patients grew M. tuberculosis on culture. Serum angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) levels were normal in the other patients.
All patients were treated with 4-drug anti-tuberculous chemotherapy-rifampicin, isoniazid, ethambutol and pyrazinamide for 2 months and rifampicin and isoniazid for further 4 months. All surviving patients had complete resolution of symptoms, liver function abnormality and imaging (Figure 1). One of these patients who was under treatment for lymphoproliferative disease with chemotherapy, died in the same admission.
DiscussionInvolvement of the liver alone by tuberculosis is uncommon. Its true incidence is difficult to assess but appears to be rare. Literature suggests that the presentation is as a protracted illness frequently associated with fever, malaise, weight loss, jaundice and hepatomegaly,5,10,11 however, some reports indicate that this may mimic common liver diseases such as abscess, tumour6,7 and at times may present with isolated elevated alkaline phosphatase.12 Most of our patients presented with fever, anorexia, weight loss and upper abdominal pain.
Physical findings in such cases are variable. Hersch13 described hepatomegaly in 95% of cases having liver involvement and splenomegaly was described in 18-55% of cases.11,13 All of our patients had hepatomegaly. All of our patients had mild elevation liver enzymes, which was also described by Gupta et al.14 Only two patients had raised bilirubin levels, which may be due to direct destruction of parenchyma.11
Radiological investigations in cases of hepatic tuberculosis usually mimic that of other common disease.7 Histopathological examination alone of tissue obtained cannot be considered the gold standard for diagnosis. Only one of our patients showed characteristic caseating granuloma in the biopsy specimen. Hepatic epitheloid cell granuloma alone can occur in primary biliary cirrhosis, sarcoidosis, Crohn’s disease, chronic active hepatitis, drug hypersensitivity and extra-hepatic biliary obstruction.15 Therefore, it is important to demonstrate the presence of acid fast bacilli. Alvarez11 had described the importance of presence of acid-fast bacilli in specimen in the absence of caseation, but presence of this is rarely reported in literature.12 We had 5 out of 7 patients showing AFB positivity by smear or culture in the biopsy specimen. Where doubt exists between tuberculosis and sarcoidosis, other means of achieving the diagnosis like ACE levels or transbronchial biopsy need to be resorted to. The final proof is only a response seen to anti tuberculous therapy, which was seen in all survivors in this series. AFB culture positivity would be a good clue, however, the diagnosis is rarely suspected even in endemic areas so tissue is rarely sent for this. Treatment is similar to that used for pulmonary tuberculosis. Quadruple therapy (using four anti-tuberculosis drugs) is recommended. Most of our patient had good outcome (6 of 7). One of our patients who had lymphoproliferative disease died due to acute respiratory distress syndrome.
In summary, liver tuberculosis has protean manifestations and must be suspected in patients coming from endemic areas with nonspecific alteration of liver function tests. This is best diagnosed on liver biopsy. Overall response to therapy is satisfying with reversal of structural and biochemical abnormalities.