Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
More infoHigh-grade monomorphic B-cell jejunal lymphoma in a post-liver transplant patient: the post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) hepatic has an incidence of 3%, 85% for B cells and 15% for T cells. The incidence increases in rich organs with B cells, like the small intestine. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is crucial in the pathogenesis. Up next is the case of a patient post-liver transplant (PLT) with proximal jejunal stenosis for lymphoma. This study aimed to report a case of jejunal lymphoma in a patient with PLTD.
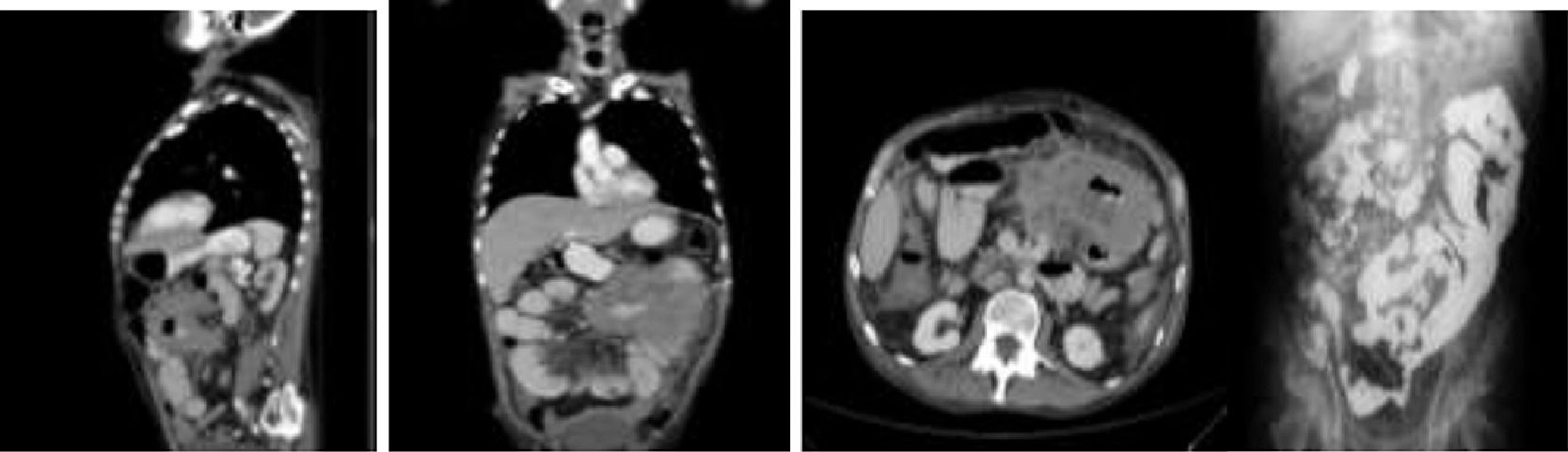
Material and MethodsMale of 71 years, in 2007 PLT for cirrhosis related to alcohol consumption, in treatment with cyclosporine and mycophenolic acid. It started in 2002 with 10 kg weight loss, nausea and vomit for three months of evolution; the abdominal tomography was performed and founded jejunal stenosis, enteroscopy found ulcerated tumor in the proximal jejunum of 60%, and the biopsy reported lymphoma diffuse of large cells CD 20+bcl-6/Ki-67 90%, PCR for EBV (-). Started treatment with R-CHOP-21.
DiscussionPTLD in adults frequently occurs late in presentation, up to 20% intestinal. What is relevant in our case is the 15 years between transplant and presentation, EBV (-) and intestinal presentation.
ConclusionsThe PTLD occurs in a period between the transplant and the diagnosis of 5.5 years, our patient, it occurs after 15 years. The negative serology is related to late PTLD, it does not respond to immunosuppression and it is treated with chemotherapy like in our patient.
FundingThe resources used in this study were from the hospital without any additional financing
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.