Abstracts of the 2021 Annual meeting of the ALEH (Asociación Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Hígado)
More infoDrug-induced liver injury (DILI) manifests as a spectrum of clinical presentations that carries morbidity and mortality. Patients with chronic liver disease (CLD), particularly hospitalized, are at high risk for developing DILI. We aimed to investigate the use of potentially hepatotoxic drugs (PHD) in patients with CLD in a tertiary university hospital.
Materials and MethodAdult (≥ 18 years-old) with CLD admitted to the hospital from January 2016 to December 2018 were evaluated regarding PHD, assessing the risk of DILI and liver enzymes behavior after exposure.
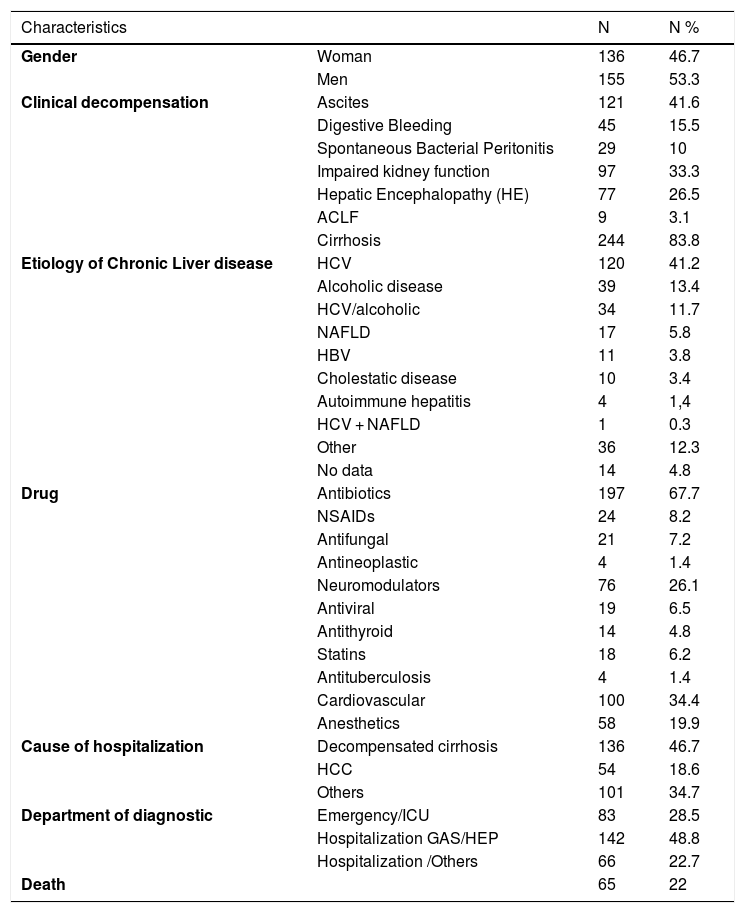
ResultsFrom 931 hospitalized patients with CLD, 291 (31.3%) were exposed to hepatotoxic drugs during their hospitalization. Of those, 244 (83.8%) were cirrhotic. The most frequent causes of liver disease were hepatitis C (41.2%), followed by alcohol (13.2%), hepatitis C/alcohol (11.7%) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (5.8%). Decompensated cirrhosis (46.7%) was the main reason for hospital admission. The most often prescribed PHD were antibiotics (67.7%), cardiovascular drugs (34.4%), neuromodulators (26.1%) and anesthetics (19.9%). After exposure, 113 patients (38.8%) presented significant elevated liver enzymes. Surprisingly, PHD were more often prescribed in GI/Liver unit (48.8%) followed by emergency/intensive care unit (28.5%). A total of 65 patients (22%) died, however in neither case was it possible to safely infer causal relationship among PHD, liver enzymes and death.
ConclusionPHD prescription is frequent in patients with CLD even in a tertiary university hospital and in the gastroenterology and hepatology department, exposing these patients to an additional risk.
Conflict of interest statementThe authors have nothing to disclose.