Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoLiver biopsy is an invasive technique through which we obtain a small sample of tissue for histopathological analysis under a microscope. This technique is considered a gold standard for the study of low clinical-analytical expression. Currently, its usefulness is directed toward the diagnosis, prognosis and evaluation of liver disease. This study aimed to define the clinical-pathological correlation in liver samples biopsied in our hospital.
Materials and MethodsThis study was retrospective, observational and descriptive. Data from 78 patients (47 women and 31 men) were included. Liver mass biopsies were generated at our institution from November 2016 to March 2021. The data were organized and analyzed in a spreadsheet matrix.
ResultsPresumptive diagnoses, prior to biopsy, were classified as liver metastases, malignant lesions, benign lesions, and inconclusive mass. The most frequent histopathological diagnoses identified in our sample were:
- Metastasis 38 (49%): originated in colon 11 (29%), uncertain 6 (16%), lung 5 (13%), breast 3 (8%), pancreas 3 (8%), uterus 2 (5%), gallbladder 2 (5%), cholangiocarcinoma 1(3%), right maxilla 1 (3%), skin 1(3%), prostate 1 (3%), rectum 1(3%), and testicular 1 (3%).
- Malignant lesions 30 (38%): hepatocellular carcinoma 19 (24%), cholangiocarcinoma 5 (7%), adenocarcinoma 4 (5%). non-hodgkin B lymphoma 1 (1%), and GIST 1 (1%)
- Benign lesions 8 (10%): benign liver nodule 2 (4%), liver adenoma 1 (1%), liver cirrhosis 1 (1%), hemangioma 1 (1%), focal nodular hyperplasia 1(1%), chronic inflammation 1 (1%), and polycystic liver disease 1(1%)
- Inconclusive hepatic mass 2 (3%)
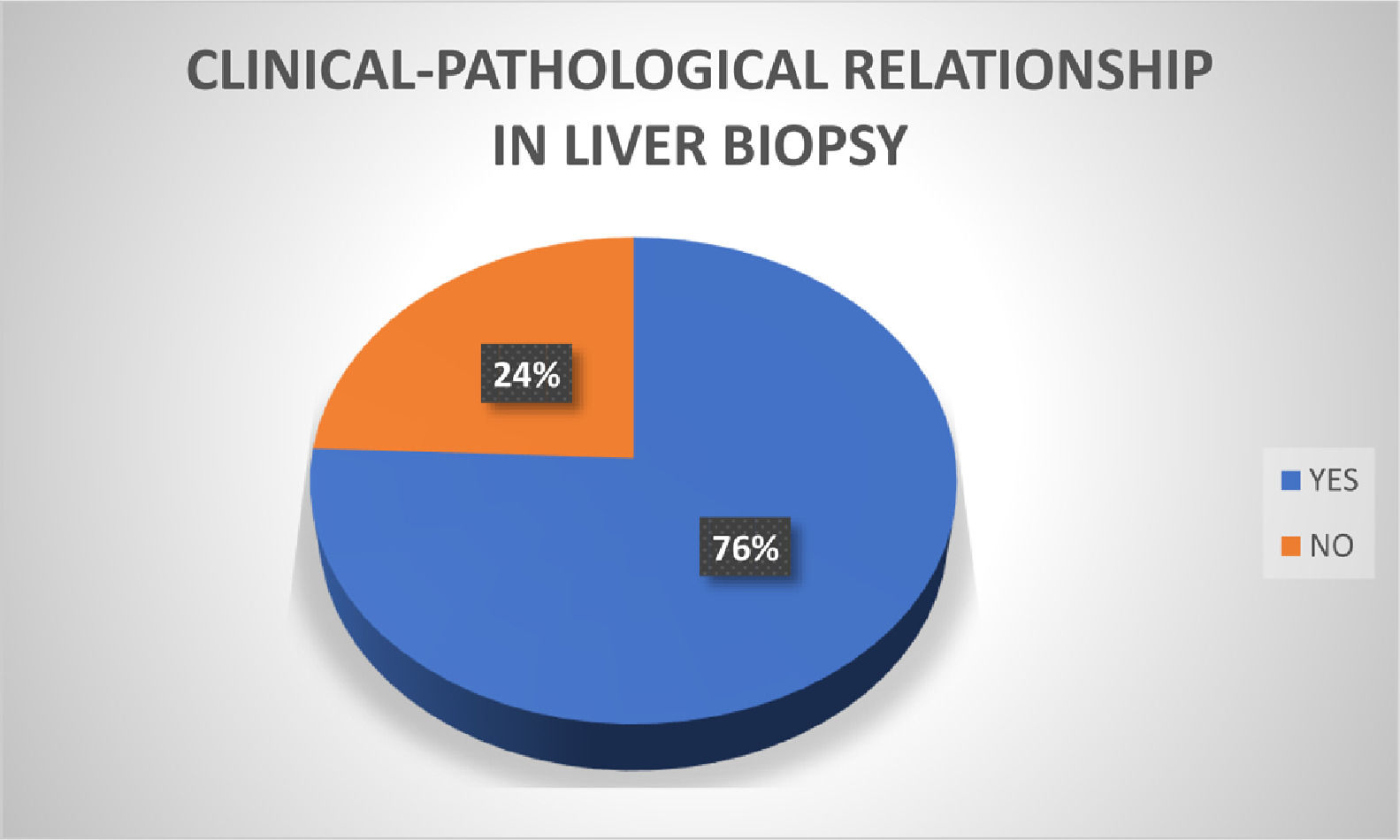
ConclusionsOur comparison between presumptive and histopathological diagnoses suggested that there was an adequate relationship in 59 cases (76%). In those cases that did not, there was probably a presumptive misdiagnosis. Our data showed that most cases presented clinical and histological correlation, supporting the usefulness of performing a biopsy in liver lesions.