Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoThe identification, characterization and management of focal lesions detected at hepatic and biliary level are a common problem in daily clinical practice. Occasionally, these constitute an incidental finding in health check-ups and in other situations due to their symptoms, becoming a challenge for the Ecuadorian health system. Since 2019, the HEE has created a multidisciplinary group for the analysis and management of these injuries. This study aimed to determine the diagnosis of focal hepatobiliary lesions by comparing cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients.
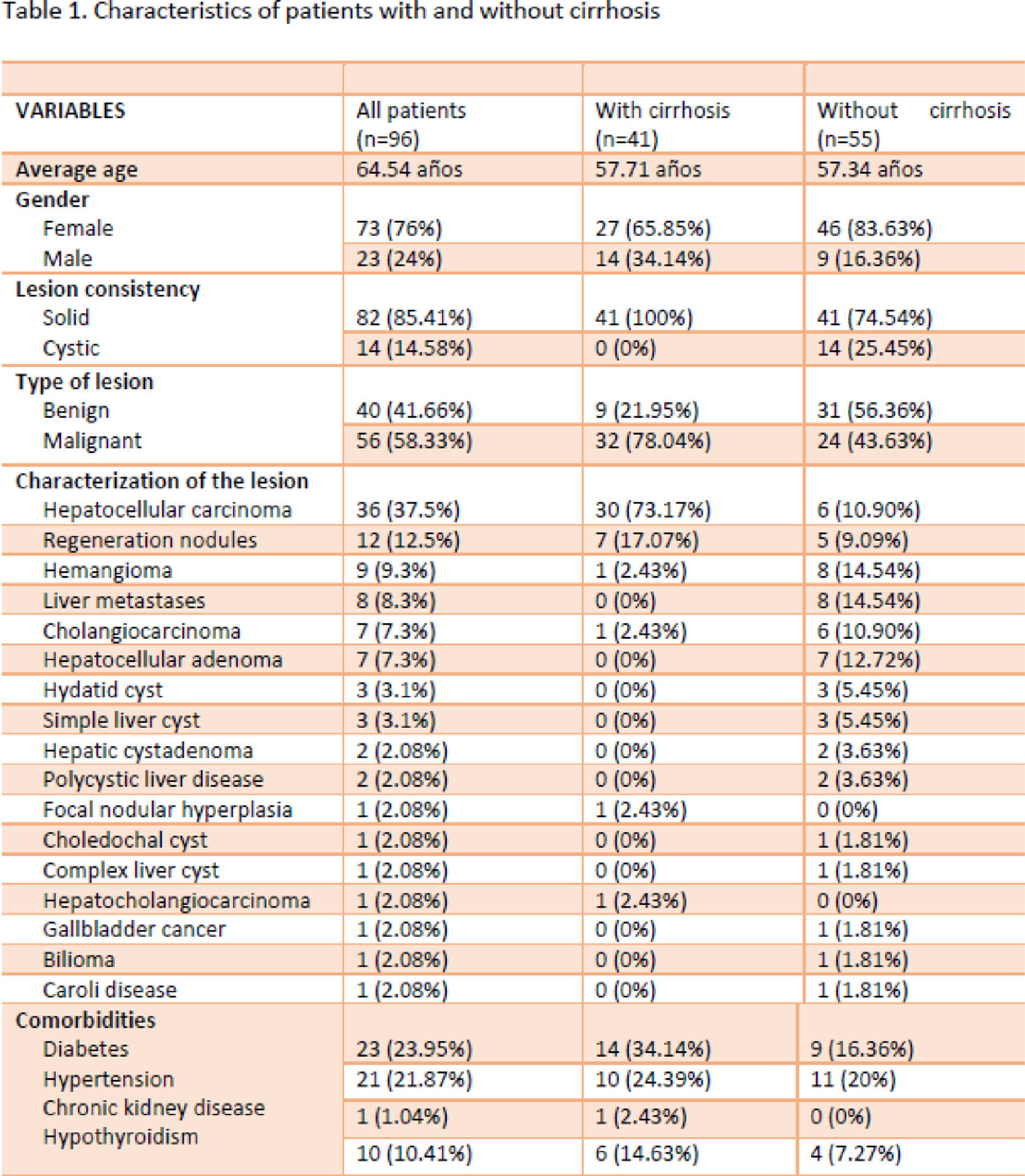
Materials and MethodsThis study was descriptive, observational and retrospective. Data from 96 patients (73 women and 23 men) were analyzed by a multidisciplinary committee from 2019 to June 2022. The average age was 64.5 years. Patients were diagnosed with hepatobiliary lesions through imaging methods or liver biopsy. The analysis was performed using the R software version 4.1.2
ResultsAmong the 96 cases analyzed, a total of 41 (42.7%) presented cirrhosis. The most common hepatobiliary injuries included: hepatocellular carcinoma 36 (37.5%), regeneration nodules 12 (12.5%), hemangioma 9 (9.3%), liver metastases 8 (8.3%), cholangiocarcinoma 7 (7.3%).), adenoma 7 (7.3%), hydatid cyst 3 (3.1%), simple cyst 3 (3.1%), hepatic cystadenoma 2(3.6%), polycystic liver disease 2 (3.6%), focal nodular hyperplasia 1 (1.8%), choledochal cyst 1 (1.8%), complex cyst 1 (1.8%), hepatocholangiocarcinoma 1 (1.8%), gallbladder cancer 1 (1.8%), bilioma 1(1.8%), and Caroli disease 1 (1.8 %)
ConclusionsOur data revealed that cirrhotic patients presented solid lesions, and the vast majority were malignant with hepatocellular carcinoma followed by metastasis. In the group of patients without cirrhosis, the majority presented benign lesions. A relationship of 3:1 between the solid type was found. Mostly included: hemangiomas, adenomas, and cystic type complex (including hydatid disease). In both groups, the main risk factor was the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.