Abstracts of the 2024 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoNo
Introduction and ObjectivesStopping rules following transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), either tumor progression or “unTACEable” progression are needed. Avoiding liver decompensation after TACE may lead better access to systemic treatment and survival. These scenarios are unknown in our region. We aimed to evaluate accessibility to systemic therapy following TACE and its impact on survival.
Patients / Materials and MethodsA multicenter prospective cohort study conducted in Latin America, included HCC patients receiving TACE from May 15, 2018 to March 15, 2024. We excluded patients on the liver transplant waiting list, or Child Pugh C. Survival since first TACE was compared between groups accessing (A) and not accessing (no-A) to systemic therapy after TACE through Cox proportional hazard survival analysis, and adjusted treatment effect was further evaluated using a propensity score (PS) and inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW).
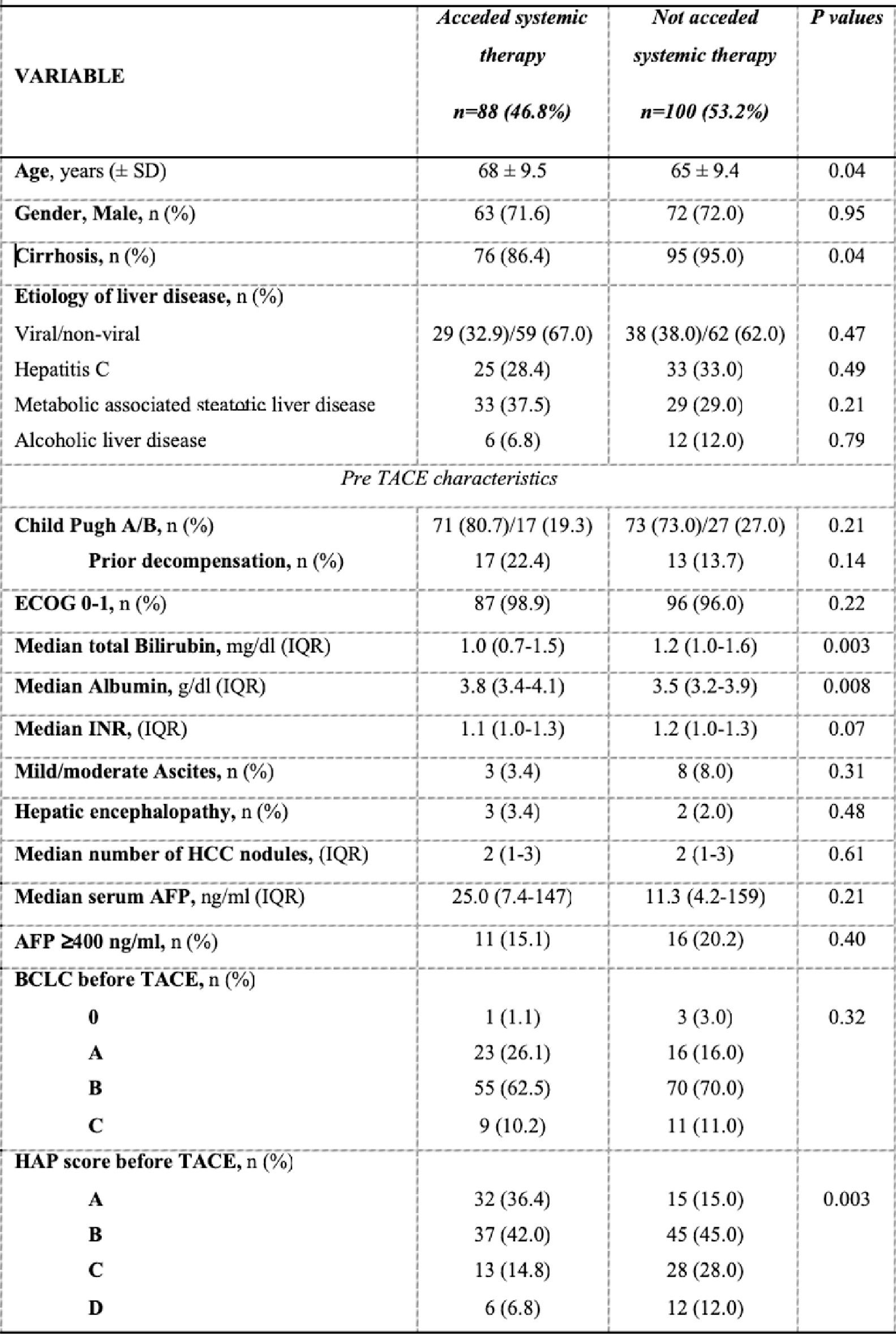
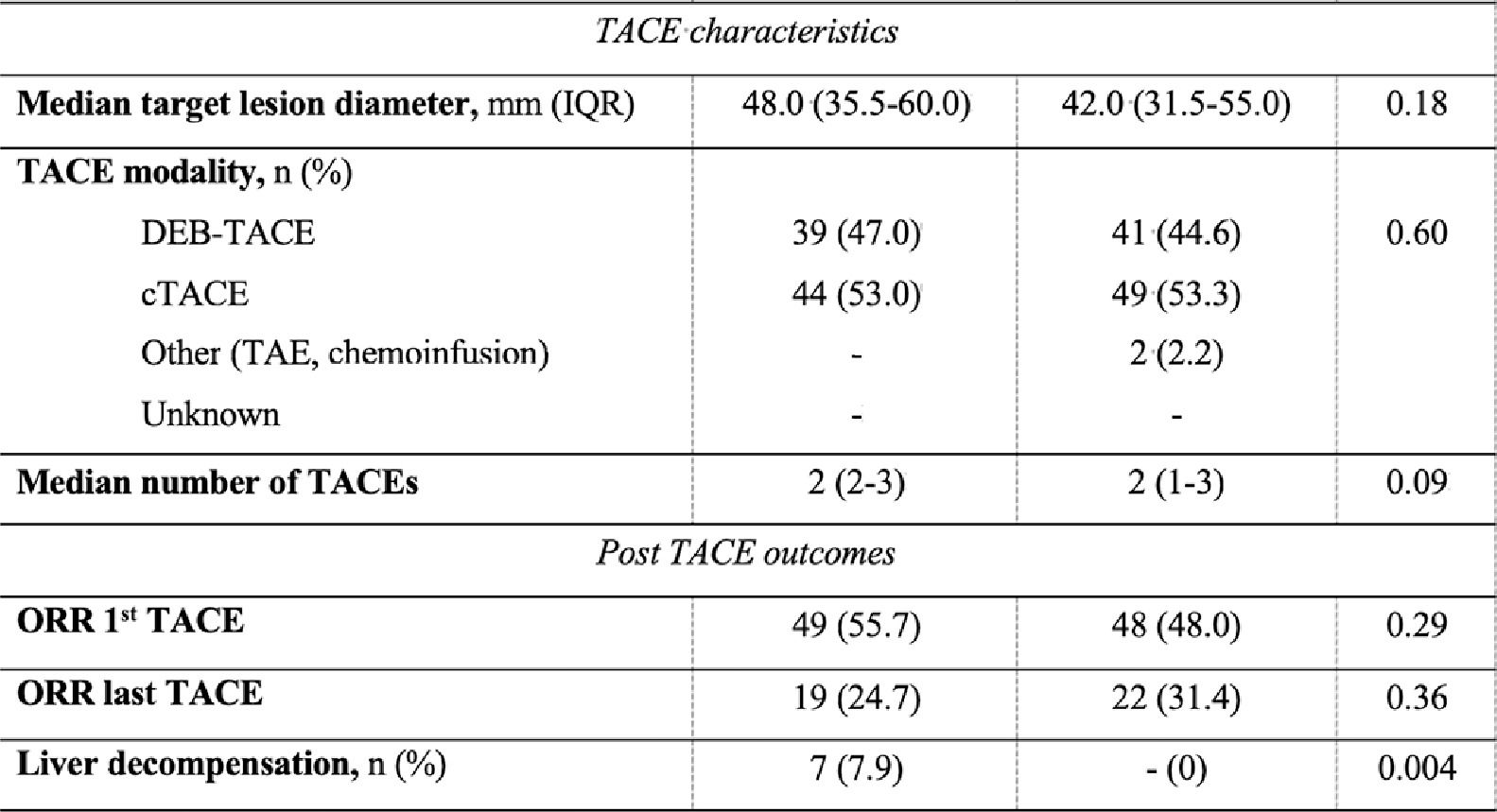
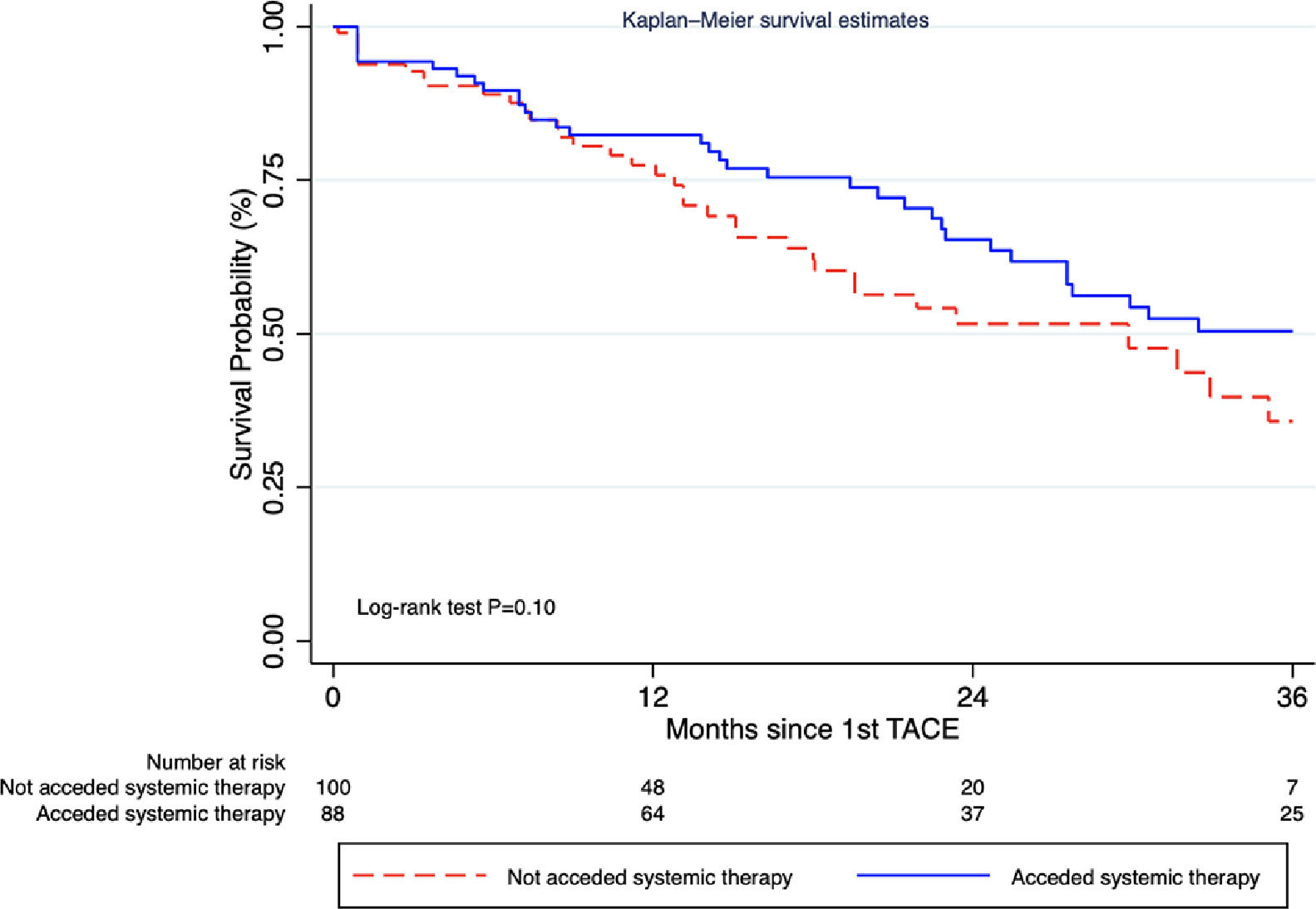
Results and Discussionrom 258 receiving TACE, 188 were included after excluding 33 patients on the waiting list and 37 Child C (Table). Access to any systemic therapy was 46.8% (95% CI 39.5-54.2%), within a median time from TACE to first line of 9 months (range 3.7-17.0). In group A (n=88) systemic treatments following TACE were sorafenib 62.5%, atezolizumab + bevacizumab 31.8%, and lenvatinib 4.5%. Paradoxically, while presenting better liver function reserve, liver decompensation after TACE was more frequent in group A (7% vs 0%; P=0.004), without significant differences regarding median number of TACEs, modality, or tumor burden. Median survival since first TACE between groups was A 37.4 months vs no-A 29.8 months [HR 0.69 (95% CI 0.44-1.10), adjusted for the HAP score (Figure), which was unchanged after PS and IPTW.
ConclusionsIn our region, less than half of HCC systemic treatment candidates acceded to sequential TACE-systemic therapy. Although not statistically significant, due to underpowered estimations, numerically higher survival was achieved with TACE-systemic therapies.