Abstracts of the 2022 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoHepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Still, there are epidemiological and clinical data in Latin America. In Chile, this is the first study regarding HCC with a significant number of patients. This study aimed to obtain and analyze clinical and epidemiological data of Chilean patients with HCC.
Materials and MethodsMulticenter study from 12 Chilean hospitals that have members of the Chilean Association of Hepatology as members of their staff. Clinical records from 2015-2021 were included. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and Cox regression analysis were obtained.
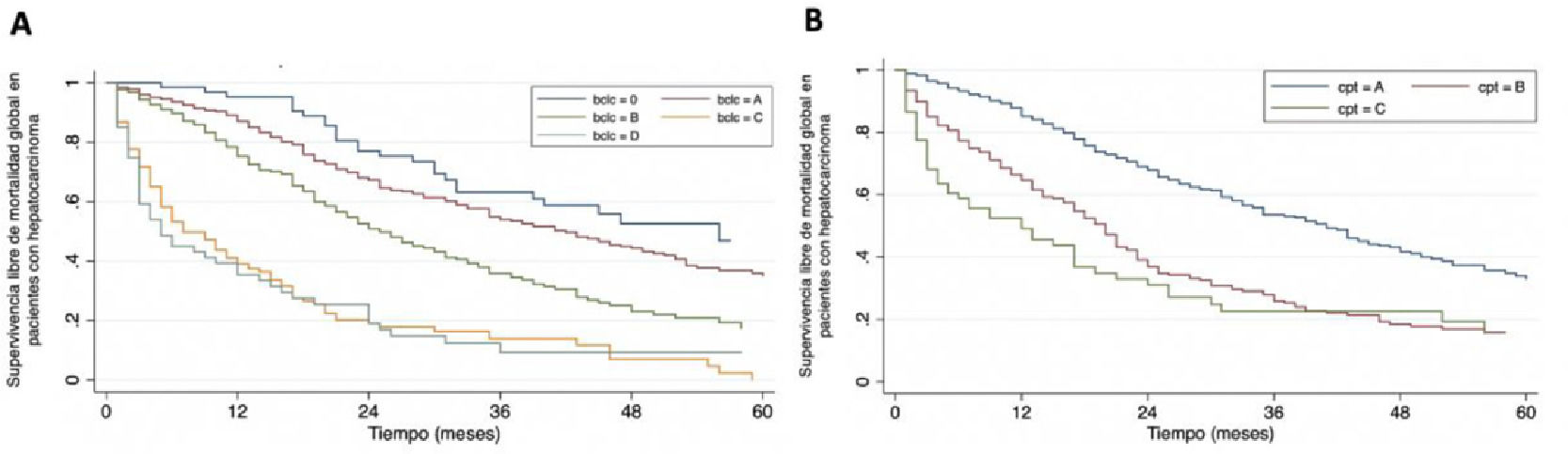
ResultsWe obtained data from 856 patients with HCC from 12 different centers. Median age 67 years old; 58.7% male. Cirrhosis is present in 91.2% (779) of cases. Main risk factors reported: fatty liver 47.9%(410), alcohol 19.6% (68), viral 12.2%(104) and autoimmune 3.5% (30). The median MELD score was 11.7 (CI95% 11,4-12). 38% (322) were diagnosed during surveillance; this was associated with earlier BCLC stage (OR 2,6; CI95%1,9-3,4). BCLC stages at diagnosis were 0; 8,2%(69), A: 38,5%(326), B:29,9%(253), C: 15,4%(130) and D: 8,2%(69). The main initial treatments were TACE, ablation, resection, liver transplant and sorafenib in 27,4%(226), 19,3%(159), 11,4%(94), 8%(66) and 5,5%(45), respectively. 53,4%(452) pts were in Milan Criteria at diagnosis. 9,1%(78) patients got a liver transplant. Five-year survival was 24% (CI95%20-28). The main factors associated with survival are depicted in Figure 1.
ConclusionsFatty liver was remarkably the main risk factor reported for HCC in our Chilean cohort. This is a worrisome number since NAFLD is on the rise worldwide, and especially in Latin America. Surveillance is key for early detection. The liver function defined by Child-Pugh and HCC stage using BCLC staging is strongly associated with survival. Liver transplant is still a scarce treatment resource.