The DRESS (drug rash, eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome, also known as DIHS (drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome), is a severe idiosyncratic reaction to several drugs, mainly antiepileptics and antibiotics, which can occasionally produce acute liver failure. In this article we present two cases of the DRESS syndrome presenting with severe acute hepatitis, including the first case of DRESS associated with levetiracetam. Although both cases finally resolved with good outcomes, DRESS can lead to acute liver failure and has a bad prognosis when liver damage is present. Rapid diagnosis is crucial since withdrawal of the offending drug is the key of treatment, while the potential role of corticosteroids is discussed.
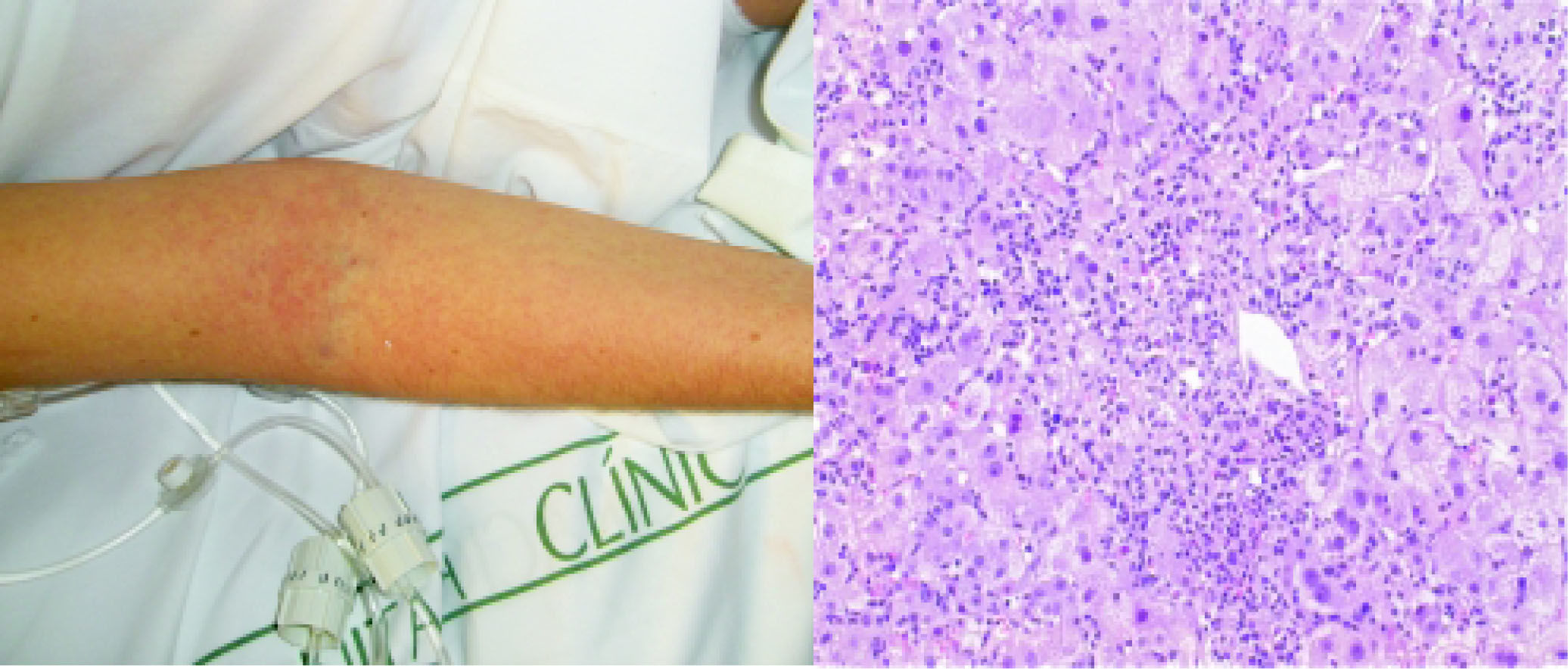
A 29-year-old caucassian woman was admitted to our Liver Unit with ten days history of high fever, generalized maculopapular rash (Figure 1A) and jaundice. On physical examination she presented es-plenomegalia, peripheral lymph node enlargement, bilateral pleural effusion and ascites. She had a history of seronegative polyarthritis treated with oral methotrexate, which had been replaced by salazo-pyrine 8 weeks before her hospital admission. She denied illicit drug use or alcohol abuse, recent travels or blood transfusion. Blood tests showed a marked impairment in liver function (AST 1319 IU/L, ALT 1117 IU/L, AP 1171 UI/L, total bilirubin 13.5 mg/dL (direct 10 mg/dL), INR 3.18 and eosinophilia (2388 cells/mm3, normal < 500). Serological tests for HAV, HBV, HCV, EBV, CMV, HSV, VZV, HIV and syphillis were negative. In contrast, IgG and PCR for HHV-6 was positive. Blood, urine and ascitic fluid cultures for bacteria were negative. Autoimmu-nity studies (ANA, AMA, Anti LKM) and plasma ceruloplasmin level were normal. Abdominal ultrasound did not detect biliary dilatation or liver masses. A transjugular liver biopsy was performed to clarify the diagnosis and exclude malignancy. The histology revealed important centrolobular necrosis and dense portal and lobular inflammatory infiltrates containing lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1B), in keeping with the diagnosis of drug-induced hepatitis. Salazopyrine was stopped at admission and oral corticoid therapy was started on the third day at a dose of 60 mg/day (1 mg/kg of weight) due to the suspicion of DRESS. There was no response in the following two days with worsening of the general condition and signs of liver failure in biological tests, with transaminases over 2,500 IU/L, total bilirubin 18 mg/dL and INR 3.18. Clinical signs of hepatic encephalopathy were absent. Intravenous methylprednisolone was increased up to 1 g/24 h during three more days and then slowly tapered. The skin lesions progressively improved within the next week, as did the eosinophilia and liver function reaching normal values after 21 days and during the 12-month-follow up.
Generalised maculopapular rash affecting the arm. B. HE staining. Acute hepatitis. Marked lobular disarray and multiple necroinflammatory foci are seen through the hepatic parenchyma. The inflammatory infiltrate is lymphoplasmacytic, including clusters of eosinophils as easily seen around the small portal tract seen at the center of the picture.
An 18-year-old Hispanic woman was admitted to the hospital due to a week duration of high fever with a morbilliform macular rash affecting the palms, facial edema and pharyngeal purulent plaques. There were no lymphadenopathies or splenomegaly on physical examination. She had a history of epilepsy treated with valproic acid and levetiracetam had been added 3 weeks before hospital admission because of a relapse of her epilepsy. She denied illicit drug use or alcohol abuse, recent travels or blood transfusions. Blood tests showed 810 eosino-phils/mm3 which increased up to 4700/mm3 on day 7 and liver dysfunction: AST/ALT 60/178 IU/L, AP 1209 UI/L, total bilirubin 1.8 mg/dL (direct 0.9 mg/ dL) and INR 1.25. After 24 hours, she complained of respiratory distress. A chest X-ray showed a bilateral interstitial infiltrate, and arterial blood gas analysis displayed hypoxemia and normocapnia. Se-rological tests for HAV, HBV, HCV, CMV, HSV, EBV, HIV and HH6-V were negative, while PCR for HHV-6 was positive. Urine and blood cultures were negative for bacteria. Autoimmunity studies (ANA, AMA, Anti LKM) and plasma ceruloplasmin level were normal. Abdominal ultrasound was normal. Skin biopsies showed an inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of lymphocytes and endo-thelial tumefaction. Levetiracetam was discontinued at admission and valproic acid was continued as an-ticonvulsant. Intravenous methylprednisolone was started at 90 mg/day (patient’s weight 50 Kg) and rapidly tapered over four days. She presented a relapse of respiratory symptoms, grade II hepatic ence-phalopathy and progressive worsening of liver tests (AST/ALT 1145/1357 IU/L, total bilirubin 5.4 mg/dL and INR 3.03). At this point a transjugular liver biopsy was performed due to the high suspicion of
DRESS demonstrating the presence of confluent necrosis, Councilman bodies and an inflammatory infiltrate with a marked increase of eosinophils. Intravenous corticosteroid therapy was resumed with clinical and analytical improvement within the following days. During a 3-month follow-up, the dosage of corticosteroids was gradually tapered and stopped, and the patient remains well with normal liver tests 9 months after the episode.
DiscussionDrug induced liver injury (DILI) is a common cause of hepatitis and acute liver failure. Diagnosis of hepatotoxicity remains difficult because of the lack of specific clinical and biochemical markers and sometimes relies on exclusion of other causes of liver in-jury.1 In this setting, several clinical indexes have been developed in order to evaluate causality in drug adverse events. Regarding our cases, we assessed the probability of a hepatotoxic adverse drug reaction with the CIOMS/RUCAM scale, achieving a definite causality in both of our cases (score > 8 points).2
When hepatotoxicity is mediated by an allergic mechanism it can be accompanied by systemic manifestations. Bocquet, et al. established the term DRESS in 19963 to describe a hypersensitivity syndrome presenting with fever, skin rash and multi-organic involvement in the first 8 weeks after the initiation of a new drug. Diagnostic criteria include the simultaneous presence of three conditions:
- 1.
Drug-induced skin eruption.
- 2.
Eosinophil > 1,500/L.
- 3.
At least one of the following systemic abnormalities: enlarged lymph nodes, hepatitis (transaminases > 2N), interstitial nephropathy, interstitial lung disease or myocardial involvement. Mortality in this syndrome, due to liver, kidney and heart failure, may be as high as 107.4,5
A large number of drugs have been described as inducers of the condition, the most common being sulfasalazine, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, allopu-rinol, and some antibiotics such as vancomicyn and minocycline.6,7
The pathophysiology of the syndrome is unclear. It has been suggested that certain drugs may cause hypersensitivity as a result of abnormalities in the production and detoxification of its active metabolites in patients with pharmacogenetic or acquired variations in drug metabolism.7 The hypersensitivity reaction is associated with high levels of IL-5 and eosinophil accumulation7 and may justify the use of steroids in this syndrome. In addition, as shown in the two cases presented and reported in others.4,8,9 the strong association between DRESS and HHV-6 reactivation points to a complex interaction among virus, antiviral immunity and drug-specific immune responses.4,8 This association seems to be disease-specific, as other drug reactions are not related to HHV-6 reactivation, and has led some investigators to propose the term drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS), highlighting the importance of HHV-6 reactivation in their diagnostic criteria.10,11 Nevertheless, a recent report12 suggests that certain drugs may stimulate a massive expansion of drug specific cytotoxic T cells that destroy hepatocytes via a cell-contact-dependent mechanism.
Liver involvement in DRESS/DIHS is common and may range from a transitory increase in liver enzymes to liver necrosis with fulminant hepatic failure. Histological features are those of a drug-induced acute hepatitis: centrolobular necrosis and dense inflammatory infiltrates containing lymphocytes and eosinophils. Most reports in the literature describe cases of mild hepatitis,6,13,14 but acute liver failure resulting in death or liver transplantation can also occur. Even though the cases of DRESS presenting with severe acute hepatitis (defined as ALT levels 10xULN and/or acute liver failure, ie. coagulopathy and/or encephalopathy) reported in the literature12,15-18 are scarce, they seem to be more frequent in women between the second and fourth decade of life and they have been mostly related to the use of sulfasalazine. Approximately fifty per cent of the reported cases resulted in death or liver transplantation, and apparently the outcome was independent of the use or dose of immunosuppressive therapy. The use of corticosteroids is usually recommended in cases of drug induced hepatitis with allergic features such as DRESS, specially with life-threatening visceral manifestations not responding to withdrawal of the responsible drug, although scientific basis of this recommendation is lacking and the ideal dosage and length of therapy, if required, are unknown. 1,5 Interestingly, our two cases presented a relapse of symptoms after initial tapering of medication which required resuming high dose corticosteroids to control the disease. Thus, our limited experience would suggest that high doses of systemic steroids may be helpful and that tapering should be performed slowly during follow-up.
OLT has also been used in cases of acute liver failure in this setting. Although long-term outcomes are unknown due to the absence of follow-up of the reported cases, a recent article12 warns about the possibility that the condition can recur after liver transplantation despite withdrawing the precipitating drug and potent immunosuppression.
In summary, physicians providing care to liver patients should be aware of this entity, as it can mimic other pathologies and is potentially life-threatening. Prompt withdrawal of the incriminating drug is crucial as well as avoiding re-exposure to drugs known to cause the syndrome. All cases of the DRESS syndrome should be reported to local phar-macosurveillance centers.
Abbreviations- •
DRESS: Drug rash, eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.
- •
DIHS: Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome.
- •
AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
- •
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
- •
INR: Index Normalized Ratio.
- •
HAV: Hepatitis A virus.
- •
HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- •
HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- •
EBV: Ebstein-Barr virus.
- •
VZV: Varicella zoster virus.
- •
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
- •
PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
- •
HHV-6: Human herpes virus 6.
- •
CMV: Cytomegalovirus.
- •
ANA: Antinuclear antibodies.
- •
AMA: Antimitocondrial antibodies.
- •
Anti LKM: Anti liver-kidney microsomal antibodies.
- •
AP: Alkaline phosphatase.
- •
HSV: Herpes simple visrus.
Gonzalo Crespo was granted by Hospital Clinic (Ajut a la Recerca Josep Font) and Fundación BBVA.