To determine the expression profile of immune response and inflammation (IRI) mediator molecules in tears from patients with dry eye (DE), and those suspected of having or have primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) under treatment and compare them with healthy controls.
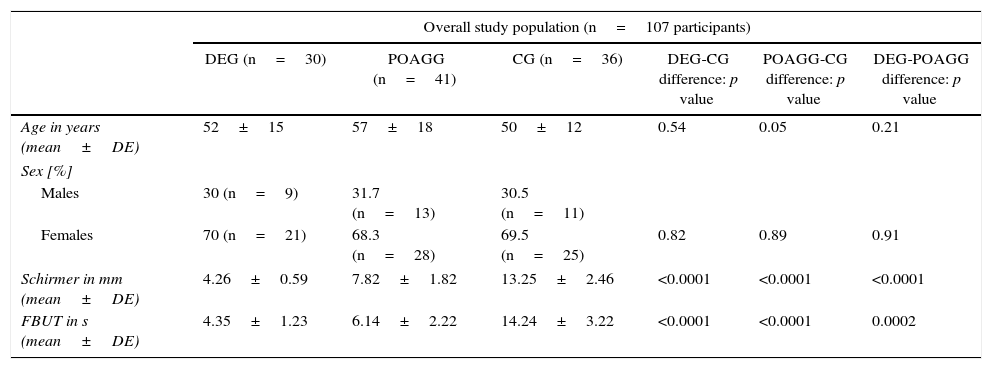
MethodsA prospective observational cohort study including 107 participants sub-divided into: healthy controls (CG; n=30), patients with DE (DEG; n=41) and patients suspected of having or have POAG and on hypotensive treatment (POAG-G; n=36). Tear samples were collected by capillary to be processed using a multi-immunoassay system based on flow cytometry (Luminex R-200®), in order to determine the interleukins (IL): 1β, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 10, and the growth factors: tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-α), vascular endothelial (VEGF), and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating (GM-CSF). Data were processed using the SPSS 20.0 program.
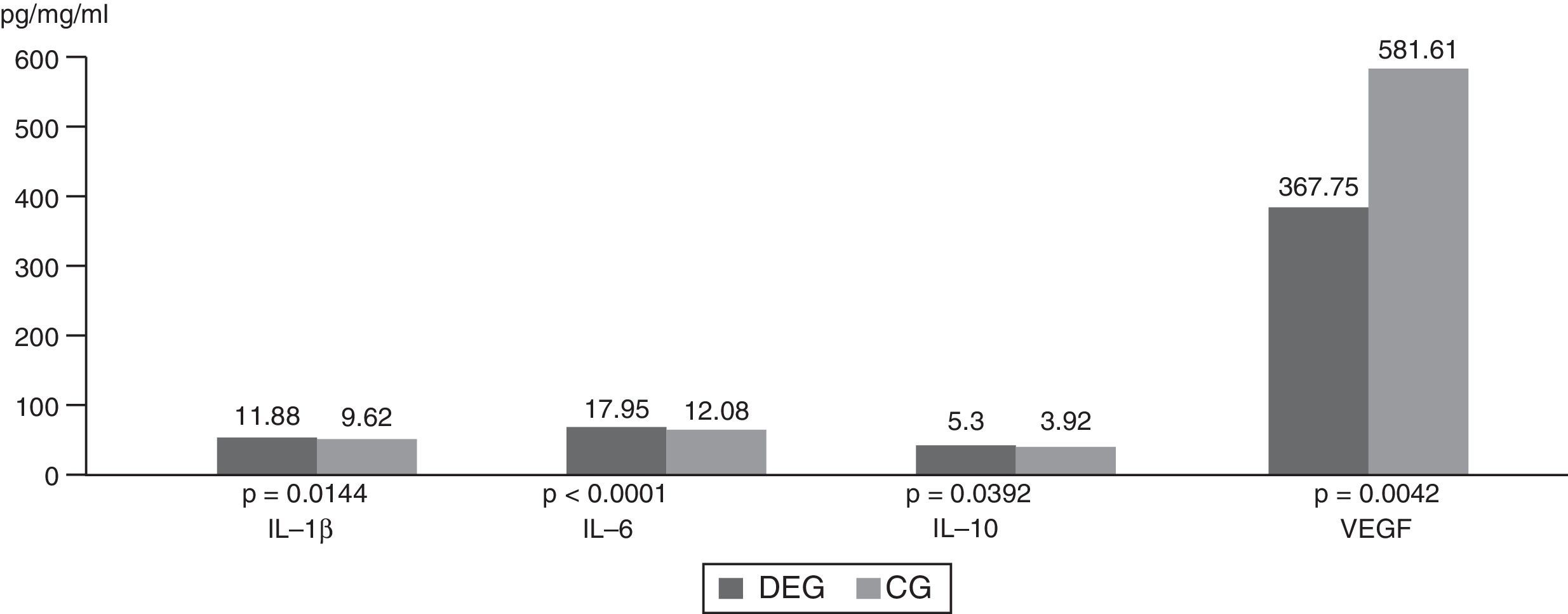
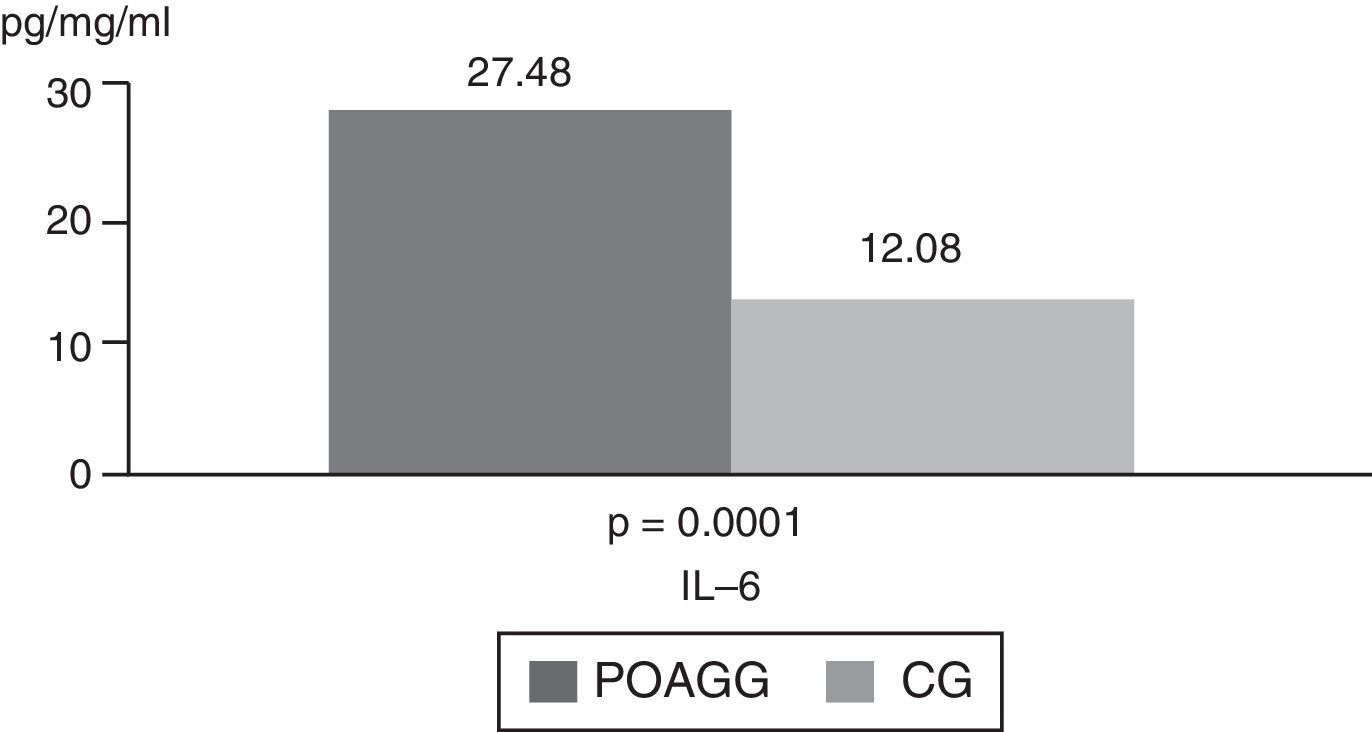
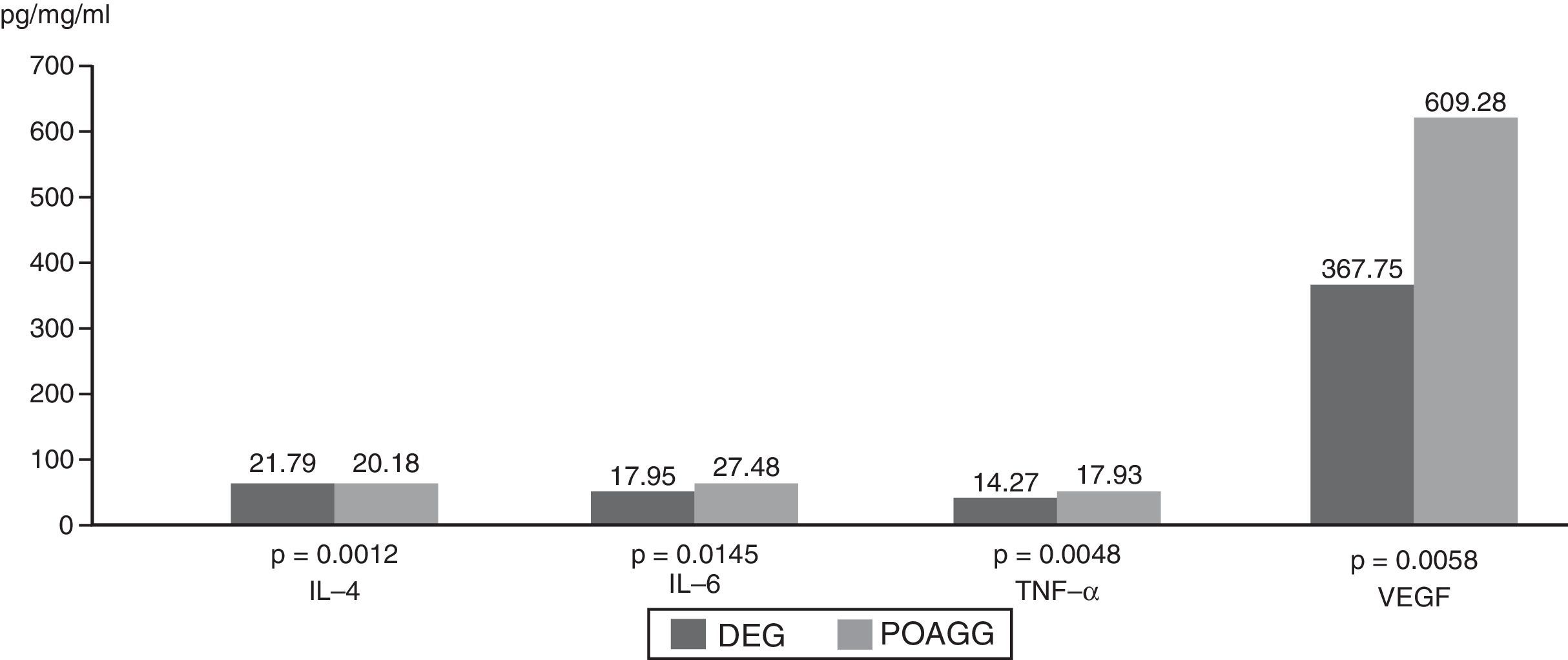
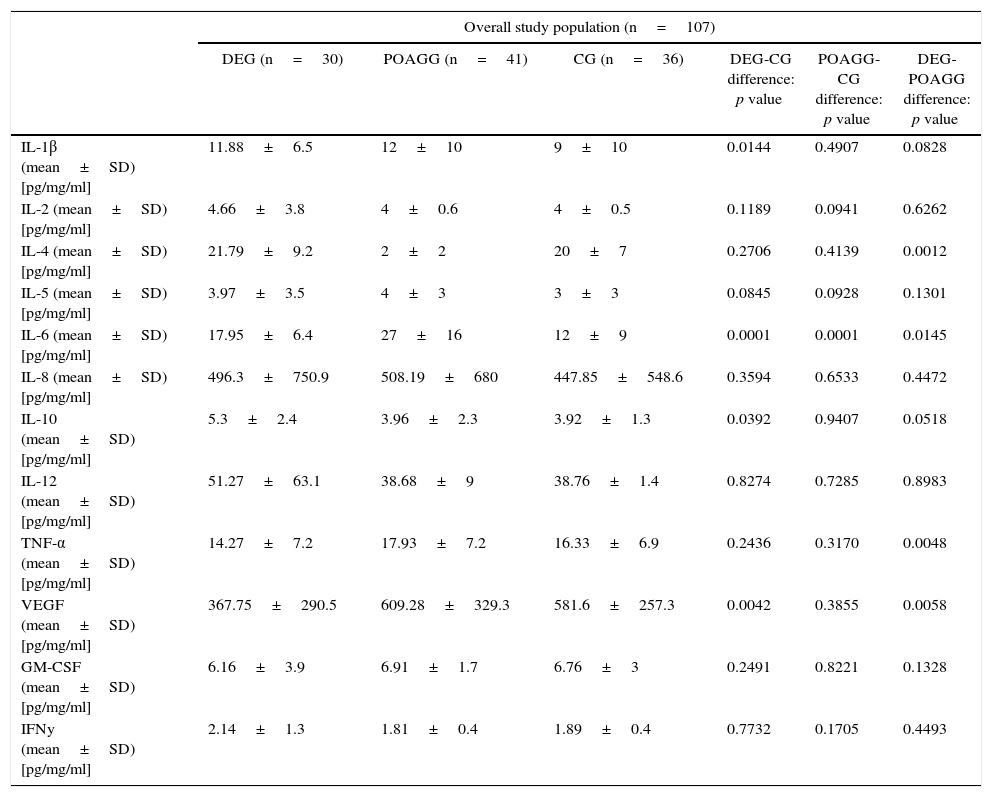
ResultsMolecules that significantly increased in tears from DEG vs. POAG-G patients were: IL-1 (p=0.01), IL-6 (p=0.004), IL-10 (p=0.04), whereas VEGF significantly decreased in the DEG. The POAG-G showed significantly higher IL-6 values (p<0.0001) as compared to the CG. When comparing both the DEG and POAG-G, significant differences were observed in tear expression of IL-4 (p=0.004), IL-6 (p=0.002), TNF-α (p=0.03), GM-CSF (p=0.03), and VEGF (p=0.002).
ConclusionsThe increased expression of IRI mediators in tears from patients with DE or POAG strongly demonstrated the importance of immune response in both pathologies. However, the different molecules involved also suggest distinct signaling pathways for these processes that still require further research.
Determinar el perfil de expresión de las moléculas mediadoras de inflamación y respuesta inmune (IRI) en lágrimas de pacientes con ojo seco (OS) y pacientes en tratamiento médico por sospecha o diagnóstico de glaucoma primario de ángulo abierto (GPAA) para compararlos con sujetos sanos.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo observacional de cohortes de 107 participantes subdivididos en: pacientes con OS (GOS; n=30), pacientes con sospecha o diagnóstico de GPAA con tratamiento hipotensor ocular (GGPAA; n=41) y controles sanos (GC; n=36). Se obtuvieron muestras de lágrimas mediante capilaridad para analizarlas mediante sistema de multiinmunoanálisis basado en citometría de flujo (Luminex R-200®), determinando diversas interleucinas (IL): 1β, 2, 4, 5, 6 y 10, y también los factores de necrosis tumoral alfa (TNF-α), de crecimiento endotelial vascular (VEGF) y de crecimiento de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos (GM-CSF). Los datos se procesaron mediante el programa SPSS 20.0.
ResultadosLas moléculas que aumentaron significativamente en lágrimas de pacientes en el GOS versus GGPAA fueron: IL-1β (p=0.01), IL-6 (p=0,004), IL-10 (p=0,04), mientras que el VEGF disminuyó significativamente en el GOS. El GGPAA mostró aumento significativo de IL-6 (p<0,0001) frente al GC. Comparando GOS y GGPAA, observamos diferencias significativas para IL-4 (p=0,004), IL-6 (p=0,002), TNF-α (p=0,03), GM-CSF (p=0,03) y VEGF (p=0,002).
ConclusionesEl aumento de expresión de los mediadores de IRI en lágrimas de pacientes con OS o GPAA demuestra la importancia de estos procesos en ambas enfermedades, aunque las distintas moléculas implicadas indican diferentes vías de señalización para ambas, que requieren más investigaciones.