To analyze the changes in the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces measured with a Scheimpflug imaging device in keratoconus patients implanted with intracorneal ring segments (ICRS) and to correlate those changes with the visual outcomes.
MethodsThis prospective interventional case series study included 92 eyes of 60 patients with keratoconus who underwent Kerarings (Mediphacos, Belo Horizonte, Brazil) ICRS implantation. Keratometric (K) readings, corneal asphericity (Q value) and elevations of both anterior and posterior corneal surfaces were evaluated using a Scheimpflug imaging device preoperatively and at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months after surgery.
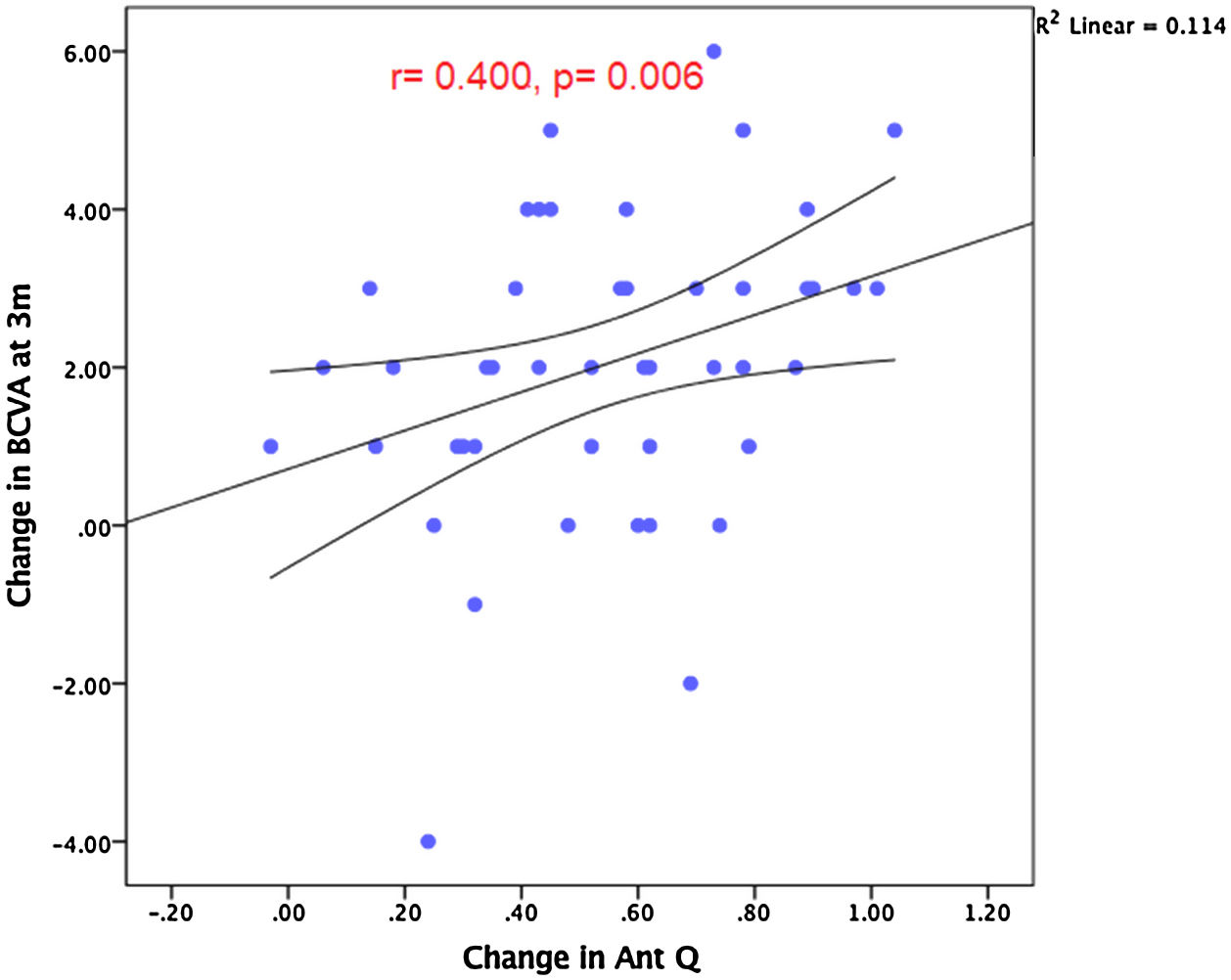
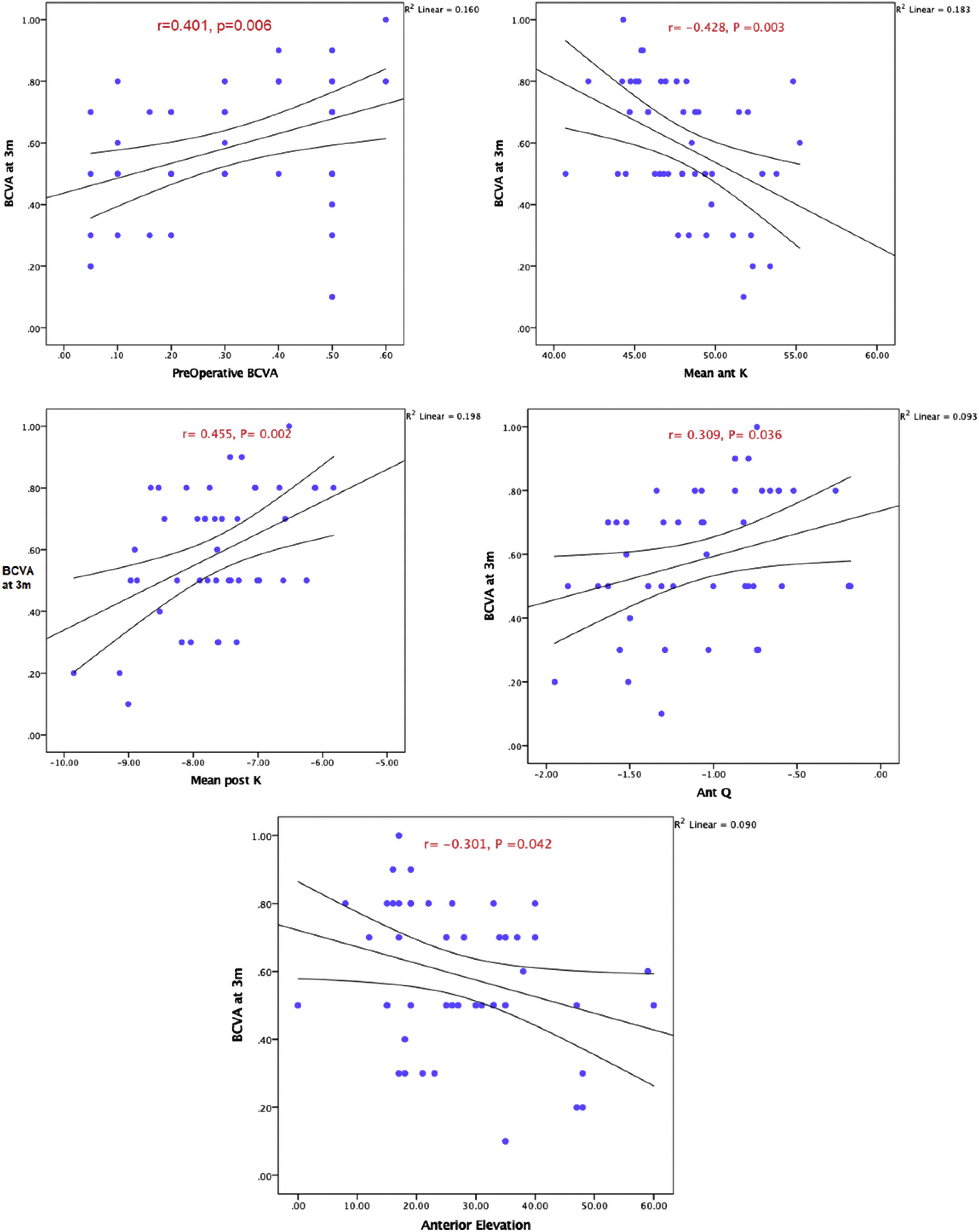
ResultsThe mean best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improved from 0.61 to 0.19 logMAR at 12 months after surgery. Both anterior and posterior corneal surfaces showed significant flattening with statistically significant reduction of the mean anterior K reading by 3.39 D and the mean posterior K reading by 0.39 D (p<0.001) at 12 months. Statistically significant change of the anterior Q to a less negative value (from -1.05 to -0.36) was observed (p<0.001) with no significant change of the posterior Q value. Improvement of the anterior Q was significantly correlated to better postoperative BCVA (p=0.03). Better postoperative BCVA significantly correlated to better preoperative BCVA, flatter preoperative anterior and posterior K, less prolate anterior Q value and lower anterior elevations.
ConclusionsICRS implantation has a significant flattening effect on both anterior and posterior corneal surfaces. Improvement of corneal asphericity is correlated to better visual outcome. Certain preoperative parameters were predictive factors of the postoperative visual improvement.
Analizar los cambios en las superficies corneales anterior y posterior medidos con un dispositivo de imágenes Scheimpflug en pacientes con queratocono implantados con segmentos anulares intracorneales y correlacionar esos cambios con los resultados visuales.
MétodosEste estudio prospectivo de serie de casos de intervención incluyó 92 ojos de 60 pacientes con queratocono a los que se implantó el SAIC de Kerarings (Mediphacos, Belo Horizonte, Brasil). Se evaluaron las lecturas queratométricas (K), la asfericidad corneal (valor Q) y las elevaciones de las superficies corneales anterior y posterior mediante un dispositivo de imágenes Scheimpflug antes de la operación y a los uno, 3, 6 y 12 meses después de la misma.
ResultadosLa mejor agudeza visual corregida (MAVC) mejoró de 0,61 a 0,19 logMAR a los 12 meses de la cirugía. Tanto la superficie corneal anterior como la posterior mostraron un aplanamiento significativo con una reducción estadísticamente significativa de la lectura K anterior media en 3,39 D y de la lectura K posterior media en 0,39 D (p<0,001) a los 12 meses. Se observó un cambio estadísticamente significativo del Q anterior a un valor menos negativo (de −1,05 a −0,36) (p<0,001) sin que se produjera ningún cambio significativo en el valor del Q posterior. La mejora del Q anterior se correlacionó significativamente con una mejor MAVC postoperatoria (p=0,03). Una mejor MAVC postoperatoria se correlacionó significativamente con una mejor MAVC preoperatoria, una K anterior y posterior más plana, un valor Q anterior menos prolato y menores elevaciones anteriores.
ConclusionesLa implantación de SAIC tiene un efecto de aplanamiento significativo en las superficies corneales anteriores y posteriores. La mejora de la asfericidad corneal se correlaciona con un mejor resultado visual. Algunos parámetros preoperatorios fueron factores predictivos de la mejora visual postoperatoria.