To describe the changes in vessel density (VD) using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) of the different sectors in the macular area between retinitis pigmentosa (RP) patients and controls.
MethodsObservational case-control study. We initially included 22 patients with RP and 21 controls. We obtained 6 × 6 OCTA images of the macular area using Angio-OCT SS-DRI-Triton 1.22 (Topcon, Japan), together with visual acuity, biomicroscopy, visual field and optical coherence tomography examination. We compared the VD values in both groups for both superficial (SVP) and deep vascular plexus (DVP). Correlation between VD and macular thickness was also calculated.
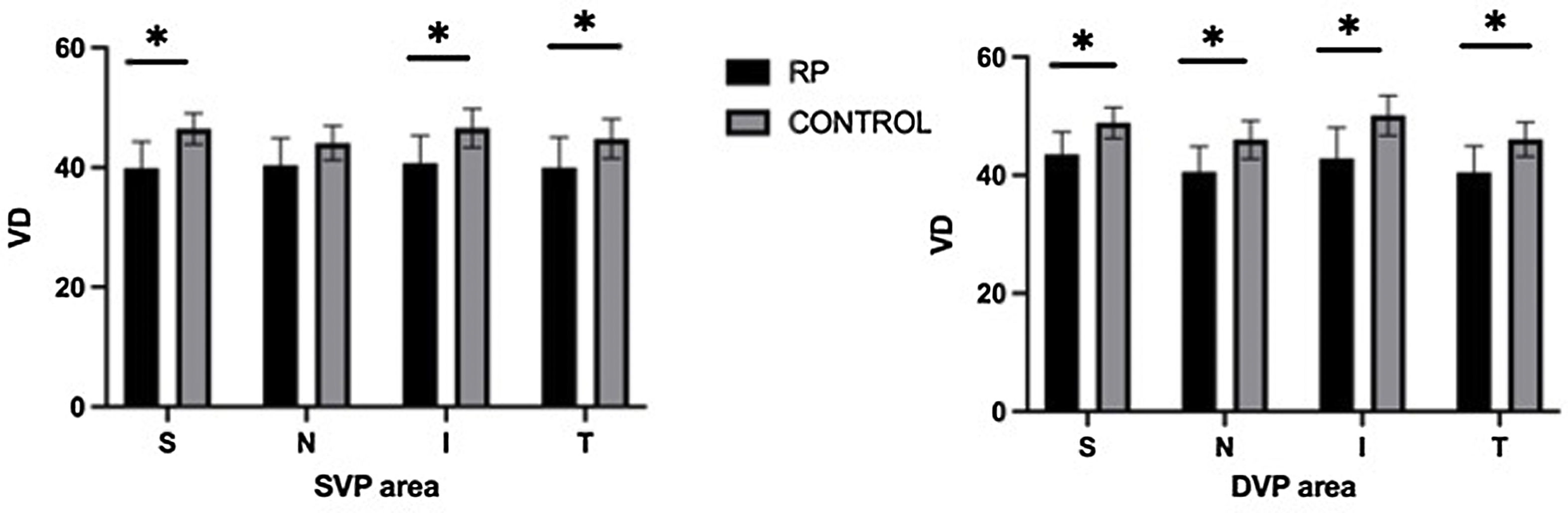
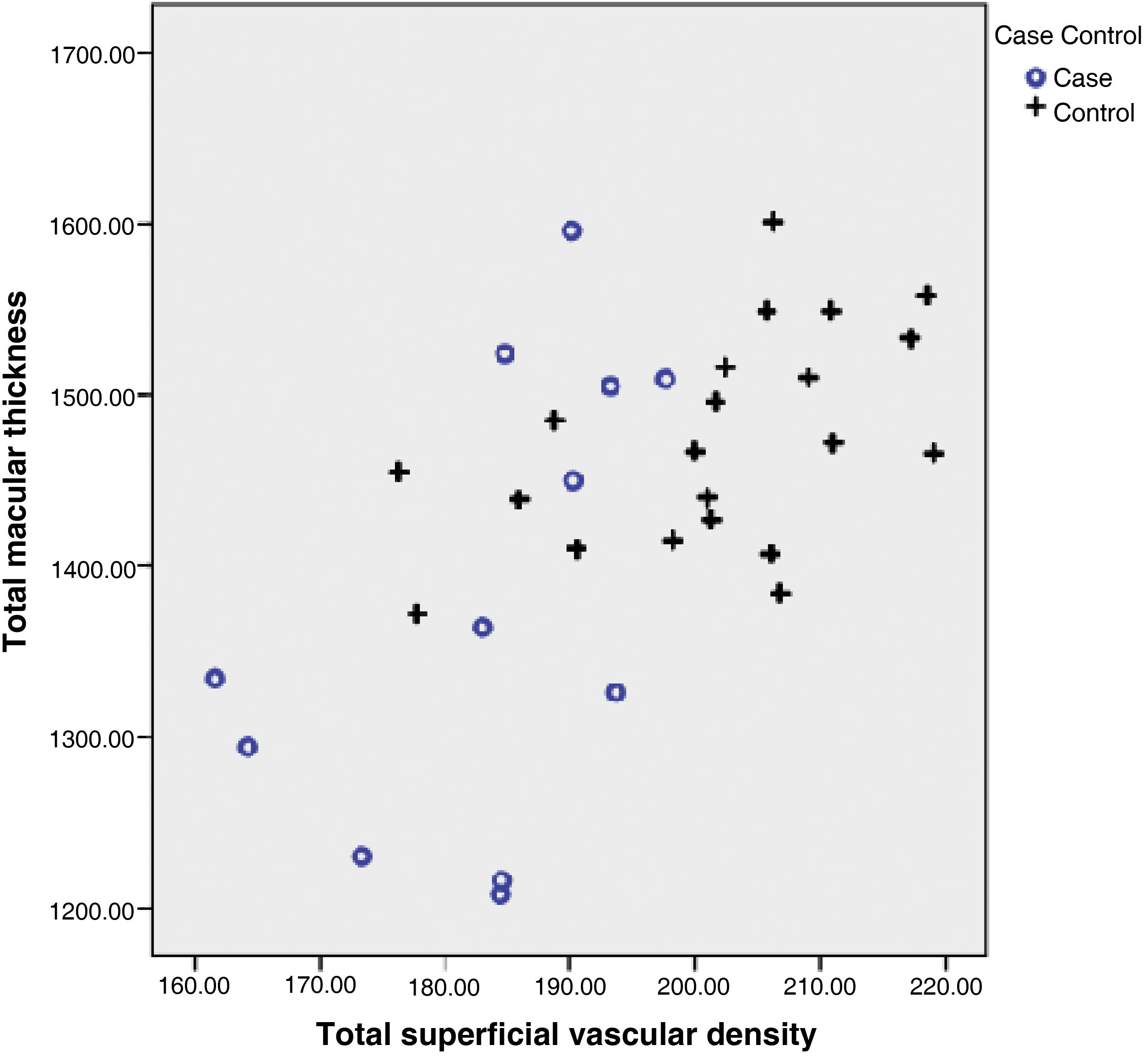
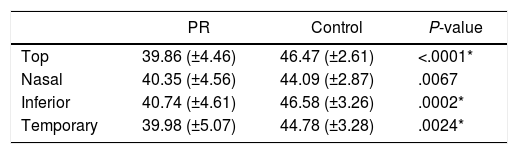
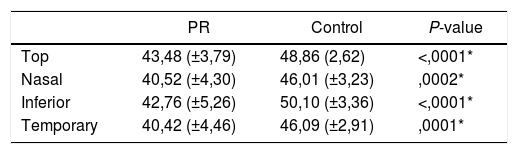
ResultsThe mean visual field index (VFI) in the RP group was 26.11% (±17.29). VD was significantly lower in the RP group compared with healthy controls in all sectors of the DVP (Superior 43.48 ± 3.79 vs 48.86 ± 2.62, P < .0001; Nasal 40,52 ± 4.30 vs 46,01 ± 3.23, P = .0002; Inferior 42.76 ± 5.26 vs 50.10 ± 3.36, P < .0001; Temporal 40.42 ± 4.46 vs 46.09 ± 2.91, P = .0001) and in all but nasal sector in the SVP (Superior 39.86 ± 4.46 vs 46.47 ± 2.61, P < .0001; Nasal 40.35 ± 4.56 vs 44.09 ± 2.87, P = .0067; Inferior 40.74 ± 4.61 vs 46.58 ± 3.26, P = .0002; Temporal 39.98 ± 5.07 vs 44.78 ± 3.28, P = .0024). Correlation between VD and macular thickness was positive and significant (RP: r = 0.59, P = .043; controls r = 0.51, P = .018).
ConclusionsPatients with advanced forms of RP have less vessel density in the macular area than healthy subjects. These differences are present in all four quadrants in the DVP and three in the SVP.
Evaluar cambios en la densidad vascular (VD) mediante de angiografía por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCTA) en los diferentes sectores maculares de pacientes con retinitis pigmentosa (RP) y controles.
MétodosEstudio observacional de 22 casos y 21 controles. Se reclutan 22 pacientes con RP y 21 controles. Se obtienen imágenes de tamaño 6 × 6 del área macular mediante Angio-OCT SS-DRI-Triton 1.22 (Topcon, Japan), desechando imágenes con mala calidad. Se recoge agudeza visual, biomicroscopía, campo visual y tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) estructural. El área macular se divide en 4 sectores (nasal, superior, inferior y temporal), y se comparan los valores de VD entre ambos grupos en los plexos superficial (SVP) y profundo (DVP). Se estudia también la correlación entre VD y grosor macular.
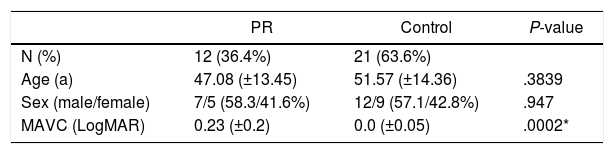
Resultados10 pacientes con RP se desecharon por mala calidad de imagen. Se analizan 12 pacientes con RP y 21 controles sanos. El índice de campo visual (VFI) medio en el grupo RP fue de 26.11% (±17.29). VD fue significativamente inferior en el grupo RP comparado con los controles en todos los sectores maculares del DVP (Superior 43.48 ± 3.79 vs 48.86 ± 2.62, P < .0001; Nasal 40,52 ± 4.30 vs 46,01 ± 3.23, P = .0002; Inferior 42.76 ± 5.26 vs 50.10 ± 3.36, P < .0001; Temporal 40.42 ± 4.46 vs 46.09 ± 2.91, P = .0001) y en todos menos en el sector nasal en el SVP (Superior 39.86 ± 4.46 vs 46.47 ± 2.61, P < .0001; Nasal 40.35 ± 4.56 vs 44.09 ± 2.87, P = .0067; Inferior 40.74 ± 4.61 vs 46.58 ± 3.26, P = .0002; Temporal 39.98 ± 5.07 vs 44.78 ± 3.28, P = .0024). La correlación entre VD y grosor macular se mostró positiva y significativa (RP: r = 0.59, P = .043; controles r = 0.51, P = .018).
ConclusionesLos pacientes con formas avanzadas de RP muestran menor VD en el área macular que los controles sanos. Estas diferencias están presentes en todos los cuadrantes del DVP y en tres de ellos en el SVP.